1、关于配置文件一些使用
组件与组件之间的耦合,采用依赖注入管理;基本类型的成员变量值,应该直接在代码中设置。
2、获取其他bean的属性值
PorpertyPathFactoryBean用来获取目标bean的属性值(实际上就是它的getter方法的返回值),获得的值可以注入给其他bean,也可以直接定义成新的bean。使用PorpertyPathFactoryBean来调用其他bean的getter方法需要指定如下信息:
调用哪个对象:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)的方法指定。
调用哪个getter方法:由PorpertyPathFactoryBean的setPropertyPath(String propertyPath)方法指定。
举个例子:

Person.java
package com.lfy.bean; public class Person { private int age; private Son son; public Son getSon() { return son; } public void setSon(Son son) { this.son = son; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
Son.java
package com.lfy.bean; public class Son { private int age; public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Son[age="+age+"]"; } }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="GBK"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.0.xsd"> <!--下面配置定义一个将要被引用的目标bean--> <bean id="person" class="com.lfy.bean.Person"> <property name="age" value="30"/> <property name="son"> <!-- 使用嵌套Bean定义setSon()方法的参数值 --> <bean class="com.lfy.bean.Son"> <property name="age" value="11" /> </bean> </property> </bean> <!-- 将指定Bean实例的getter方法返回值定义成son1 Bean --> <bean id="son1" class= "org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"> <!-- 确定目标Bean,指定son1 Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法 --> <property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/> <!-- 指定son1 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,son代表getSon() --> <property name="propertyPath" value="son"/> </bean> <!-- 下面定义son2 Bean --> <bean id="son2" class="com.lfy.bean.Son"> <property name="age"> <!-- 使用嵌套Bean为调用setAge()方法指定参数值 --> <!-- 以下是访问指定Bean的getter方法的简单方式, person.son.age代表获取person.getSon().getAge()--> <bean id="person.son.age" class= "org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"/> </property> </bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 --> <bean id="theAge" class= "org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"> <!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge Bean来自哪个Bean的getter方法的返回值 --> <property name="targetBeanName" value="person"/> <!-- 使用复合属性来指定getter方法。son.age代表getSon().getAge() --> <property name="propertyPath" value="son.age"/> </bean> <!-- 将基本数据类型的属性值定义成Bean实例 --> <bean id="theAge2" class= "org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPathFactoryBean"> <!-- 确定目标Bean,表明theAge2 Bean来自哪个Bean的属性。 此处采用嵌套Bean定义目标Bean --> <property name="targetObject"> <!-- 目标Bean不是容器中已经存在的Bean, 而是如下的嵌套Bean--> <bean class="com.lfy.bean.Person"> <property name="age" value="30"/> </bean> </property> <!-- 指定theAge2 Bean来自目标bean的哪个getter方法,age代表getAge() --> <property name="propertyPath" value="age"/> </bean> <!-- son1的简化配置 --> <util:property-path id="son3" path="person.son"/> <!-- son2的简化配置 --> <bean id="son4" class="com.lfy.bean.Son"> <property name="age"> <util:property-path path="person.son.age"/> </property> </bean> <!-- theAge的简化配置 --> <util:property-path id="theAge3" path="person.son.age"/> </beans>
SpringTest.java
package com.lfy.main; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.lfy.bean.Person; /** * * @author lfy * */ public class SpringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建spring容器 ApplicationContext ctx=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); System.out.println("系统获取son1:"+ctx.getBean("son1")); System.out.println("系统获取son2:"+ctx.getBean("son2")); System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge")); System.out.println("系统获取theAge:"+ctx.getBean("theAge2")); //简化配置 System.out.println("系统获取son3:"+ctx.getBean("son3")); System.out.println("系统获取son4:"+ctx.getBean("son4")); System.out.println("系统获取theAge3:"+ctx.getBean("theAge3")); } }
运行结果:
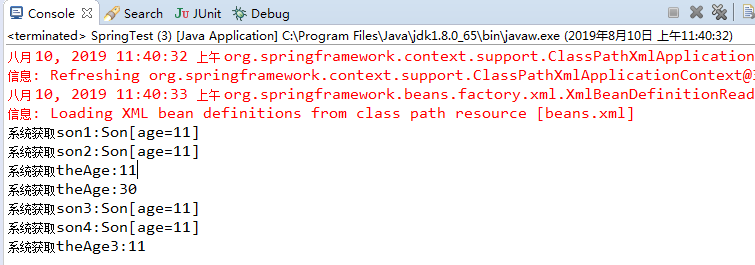
总结:<util:property-path.../>元素可以作为PropertyPathFactoryBean的简化配置,需要使用该元素,必须在配置文件中声明util:命名空间。其配置时指定的两个属性
id:该属性指定将getter方法的返回值定义成名为id的bean实例,如本例的son3。
path:该属性指定将哪个bean实例、哪个属性(可以是复合属性)暴露出来。
3、获取Field字段值
FieldRetrievingFactoryBean,可以访问类的静态Field或对象的实例Field值。使用FieldRetrievingFactoryBean访问Field分两种情形:
1》要访问的Field是静态Field,需要指定
调用哪个类:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
2》要访问的Filed是实例Field(要求实例的Field使用public控制访问权限,没太大用处),需要指定
调用哪个对象:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(String targetObject)方法指定。
访问哪个Field:由FieldRetrievingFactoryBean的setTargetField(String targetField)方法指定。
4、获取方法返回值
MethodInvokingFactoryBean工厂bean,使用MethodInvokingFactoryBean两种情形:
1》要访问的是静态方法,需要指定
调用哪个类:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetClass(String targetClass)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。
2》要访问的是实例方法,需要指定
调用哪个对象:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetObject(Object targetObject)方法指定。
调用哪个方法:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetMethod(String targetMethod)方法指定。
调用方法的参数:由MethodInvokingFactoryBean的setTargetArguments(Object[] arguments)方法指定。方法无参数该配置可以省略。