1、创建数据库
create database db_name;
show create database db_nameG; //查看数据创建语句
show databases; //查看当前创建的数据库
2、删除数据库
drop database db_name; //删除的数据库要存在
3、数据库存储引擎
MySQL可以针对每一张表使用不同的存储引擎。
mysql> show engines G *************************** 1. row *************************** Engine: InnoDB Support: DEFAULT Comment: Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys Transactions: YES XA: YES Savepoints: YES *************************** 2. row *************************** Engine: MRG_MYISAM Support: YES Comment: Collection of identical MyISAM tables Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 3. row *************************** Engine: MEMORY Support: YES Comment: Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 4. row *************************** Engine: BLACKHOLE Support: YES Comment: /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 5. row *************************** Engine: MyISAM Support: YES Comment: MyISAM storage engine Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 6. row *************************** Engine: CSV Support: YES Comment: CSV storage engine Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 7. row *************************** Engine: ARCHIVE Support: YES Comment: Archive storage engine Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 8. row *************************** Engine: PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA Support: YES Comment: Performance Schema Transactions: NO XA: NO Savepoints: NO *************************** 9. row *************************** Engine: FEDERATED Support: NO Comment: Federated MySQL storage engine Transactions: NULL XA: NULL Savepoints: NULL 9 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
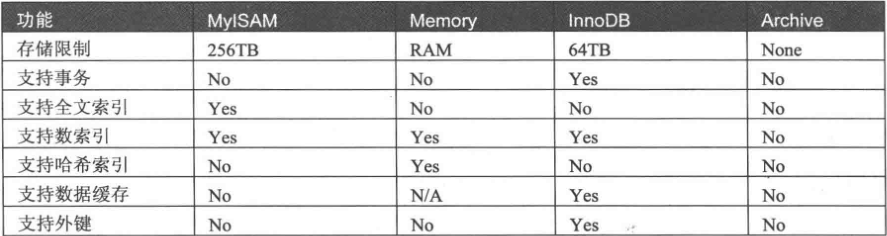
InnoDB存储引擎:支持事务安全表(ACID,提交、回滚、崩溃恢复的事务安全)、行级锁、外键。
MyISAM存储引擎:较高的插入、查询速度,但不支持事务。
Memory存储引擎:将表中的数据存储到内存中。
存储引擎的比较:
4、数据库表操作
1》创建表:
create table <表名> ( column1 datatype [列级约束] [默认值], column1 datatype [列级约束] [默认值] ... [表级约束] );
2》主键约束:primary key 或者 [constraint <约束名>] primary key [字段名]
单字段主键:primary ley(column1)
多字段主键:primary key(column1,column2,...)
3》外键约束:
外键可以为空值,如果不为空值,则该值必须等于被参照表某记录某字段(或者某些字段的组合)的值。
[constraint <外键名>] foreign key column1[,column2,column3,...] references <主表名> 主键列1[,主键列2,...]
4》非空约束:not null
5》唯一约束:unique。可以有空值。unique(column1)或者[constraint <约束名>] unique(column1,column2,...)
6》默认值:default。
7》设置表的属性值自动增加:auto_increment。一个表只能有一个字段使用该约束,且该字段必须为主键的一部分。约束的字段可以是任何整数类型(tinyint,smallin,int,bigint)。
5、查看表结构:describe / desc、show create table
1》describe / desc:
mysql> desc test; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(25) | NO | | NULL | | | deptId | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | salary | float | YES | | NULL | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.01 sec) mysql> describe test; +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(25) | NO | | NULL | | | deptId | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | | salary | float | YES | | NULL | | +--------+-------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql>
2》show create table:查看表详细结构语句,包括存储引擎、字符编码等信息。
show create table <表名 G>;
“G”是为了显示更美观。
6、删数据表
1》删除没有关联的表:可以一次删除一个或者多个没有被其他表关联的表
drop table [if exists]表1,表2,...表n;
2》删除被其他表关联的主表:一般直接删除主表会失败。如果只需要删除主表,而从表需要保留,可以先删除从表的外键约束,然后再删除主表;级联删除。
7、改数据表
常用的操作:修改表名、修改字段数据类型或字段名、增加和删除字段、修改字段的排列位置、更改表的存储引擎、删除表的外键约束等。
1》修改表名:
alter table <旧表名> rename [to] <新表名>;
2》修改字段名、字段数据类型:
alter table <表名> change <旧字段名> <新字段名> <字段数据类型>;
alter table <表名> modify <字段名> <新数据类型>; //或者alter table <表名> change <旧字段名> <旧字段名> <新字段数据类型>;
3》添加字段
alter table <表名> add <新字段名> <数据类型> [约束条件] [first|after [已存在的字段名]];
4》删除字段
alter table <表名> drop <字段名>;
5》修改字段的排列位置:first指定字段作为表的第一个字段,after指定字段在“字段2”后面。
alter table <表名> modify <字段1> <数据类型> first|after <字段2>;
6》更改表的存储引擎(MySQL特有的):
alter table <表名> engine=<更改后的存储引擎名>;
7》删除表的外键约束:
alter table <表名> drop foreign key <外键约束名>
8、总结
1》外键约束不能夸引擎使用,即主表与从表应该使用相同的存储引擎。