1.封装:
广义上:把方法和属性根据类别装进类中。
狭义上:私有化的方法和属性。
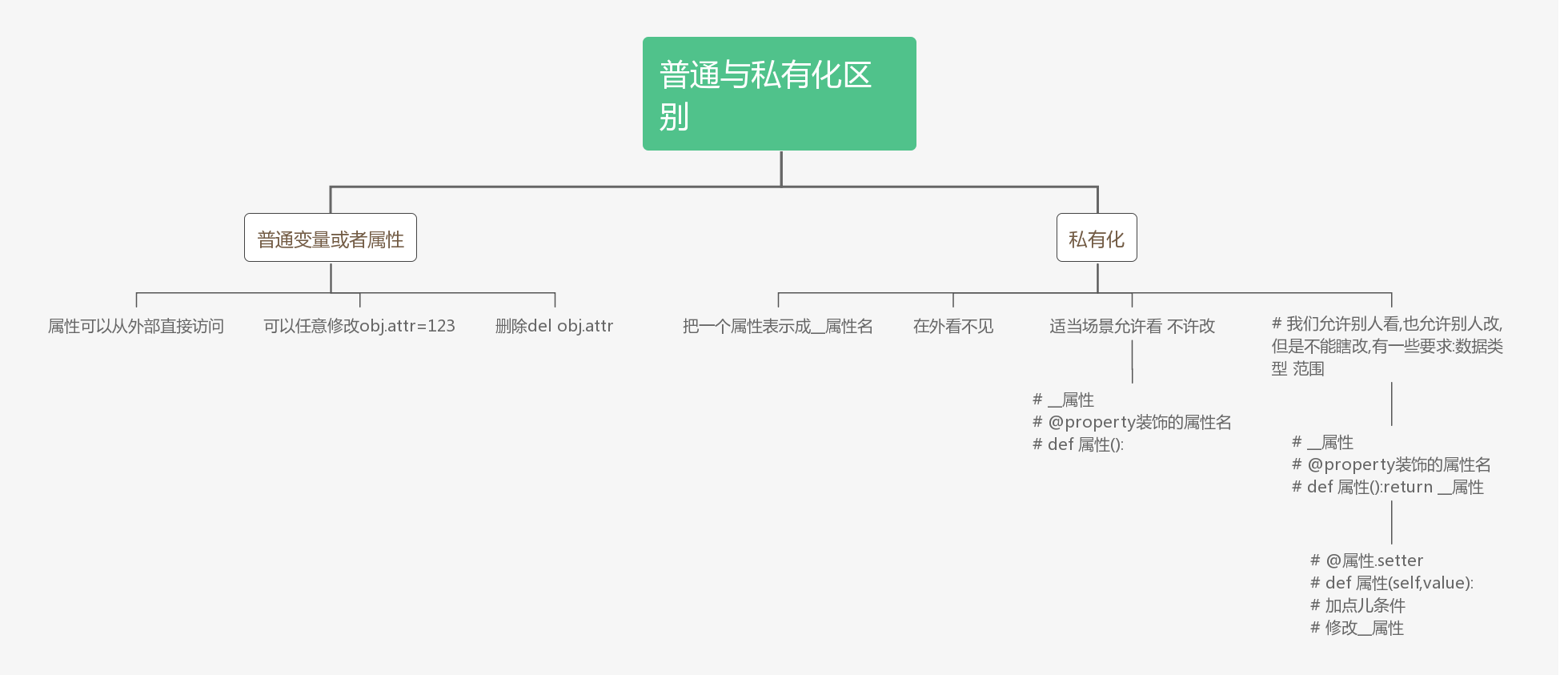
私有化:只能在类的内部可见,类的外部不可访问、查看
私有化的内容:方法、静态变量、实例变量(对象属性)
A.私有化属性:
class Goods:
def __init__(self,name,price):
self.name=name
self.__price=price #私有属性
def get_price(self):
print(self.__price)
apple=Goods('苹果',20)
print(apple.name)
apple.get_price() #只能在类的内部可见
apple.__price #类的外部不可见
结果:
苹果
20
File "F:/pycharmproject/新建文件夹/day0329/demo.py", line 30, in <module>
apple.__price
AttributeError: 'Goods' object has no attribute '__price'
B.私有化静态变量:
#私有化静态变量:
class Role(object):
__country='China' #私有化静态变量
def fun(self):
print(self.__country)
print(Role.__country)
结果:
AttributeError: type object 'Role' has no attribute '__country'
class Role(object):
__country='China' #私有化静态变量
def fun(self):
print(self.__country)
Role().fun()
结果:
China
C.私有化方法:
import hashlib
class Auth(object):
def __init__(self,user,pwd):
self.user=user
self.pwd=pwd
def __md5_code(self):
md5=hashlib.md5(self.user.encode('utf-8'))
md5.update(self.pwd.encode('utf-8'))
return md5.hexdigest()
def login(self):
if 'alex'==self.user and 'ee838c58e5bb3c9e687065edd0ec454f' == self.__md5_code():
return True
user=input('>>>')
pwd=input('>>>')
obj=Auth(user,pwd)
# obj._Auth__md5_code() #这是调用了类内私有化方法 不建议使用
ret = obj.login()
if ret:
print('登陆成功!')
结果:
>>>alex
>>>alex3714
登陆成功!
2.私有化怎么完成的?
所有的私有的变化都是在类的[内部]定义的时候完成的
3.私有属性可以被继承吗?
示例一:
class Foo:
def __init__(self): #传参
self.__func()
def __func(self):
print('in foo')
class Son(Foo):
def __func(self):
print('in son')
Son()
结果:
in foo
示例二:
class User:
def func(self):
self.__wahaha() #在所有的空间里找不到 _User__wahaha
class VipUser(User):
def __wahaha(self):
print('in vip user')
VipUser().func() #报错
示例三:
class User:
def __wahaha(self):
print('in user')
class VipUser(User):
def func(self):
self.__wahaha()
VipUser().func() ## 报错,因为在命名空间中根本不存在一个_VipUser__wahaha
结果:
AttributeError: 'VipUser' object has no attribute '_VipUser__wahaha'
# 私有的这个概念 但凡在类的外面 都不能用
# 私有的所有内容 :实例变量(对象属性),静态变量(类变量),方法都不能被子类继承
# 公有的 在类的内部外部随便用 public
# 私有的 private 只能在类的内部使用 既不能被继承 也不能在类的外部使用
4.私有 和 @property 的一起用:
class Circle:
def __init__(self,r):
self.r=r
@property
def area(self):
return 3.14*self.r**2
@property
def perimeter(self):
return 3.14*self.r*2
c=Circle(4.5)
print(c.area) #这里其实是调用的是函数 但是没有加上括号,类似属性一样的使
用,这里就是property的功能
print(c.perimeter)
结果:
63.585
28.26
import time
class Person:
def __init__(self,name,birth):
self.name=name
self.birth=birth
@property
def age(self):
print(time.localtime(time.time()).tm_year-int(self.birth.split('-')[0]))
alex=Person('alex','1978-12-12')
alex.age
结果:
41
# 只能看 不能改
alex.age=54 去改变age 是会报错的 can't set attribute
那么想改变值怎么办???
5.@setter
class Goods:
discount=0.85
print('discount:',discount)
def __init__(self,name,price):
self.name=name
self.__price=price
@property #只支持obj.price 查看结果,只能查看,不能修改,不能删除
def price(self):
return self.__price*self.discount #这里调用静态变量要用self.变量或者Goods.变量
@price.setter
def price(self,value):
self.__price=value
apple=Goods('苹果',10)
print(apple.price)
apple.price=50 #对私有属性进行改变,调用被setter装饰的函数price
print(apple.price) #调用被property装饰的函数price
结果:
discount: 0.85
8.5
42.5
格式:
@property
def 函数名():
@函数名(保证相同).setter
def 函数名(保证相同)():
.
.
.