1、Vector和ArrayList以及LinkedList区别和联系、应用场景
线程安全:
Vector:如果创建Vector时没有指定容量,则默认容量为10,底层基于数组实现,线程是安全的,底层采用synchronized同步方法进行加锁
Vector与ArrayList一样,也是通过数组实现的,不同的是它支持线程的同步,即某一时刻只有一个线程能够写Vector,避免多线程同时写而引起的不一致性,但实现同步需要很高的花费,因此,访问它比访问ArrayList慢
ArrayList:底层基于数组,线程不安全,查询和修改效率高,但是增加和删除效率低
ArrayList是最常用的List实现类,内部是通过数组实现的,它允许对元素进行快速随机访问。数组的缺点是每个元素之间不能有间隔,当数组大小不满足时需要增加存储能力,就要讲已经有数组的数据复制到新的存储空间中。当从ArrayList的中间位置插入或者删除元素时,需要对数组进行复制、移动、代价比较高。因此,它适合随机查找和遍历,不适合插入和删除。
LinkedList:底层双向链表结构,线程不安全,查询和修改效率低,但是增加和删除效率高,另外,它还提供了List接口中没有定义的方法,专门用于操作表头和表尾元素,可以当作堆栈,队列和双向队列使用;
使用场景:
- Vector很少用
- 如果需要大量的添加和删除则可以选择LinkedList
- 如果需要大量的查询和修改则可以选择ArrayList
Vector源码:
/** * Adds the specified component to the end of this vector, * increasing its size by one. The capacity of this vector is * increased if its size becomes greater than its capacity. * * <p>This method is identical in functionality to the * {@link #add(Object) add(E)} * method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). * * @param obj the component to be added */ public synchronized void addElement(E obj) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = obj; }
Arraylist源码:
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
LinkedList源码:
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
2、如果要保证ArraList线程安全,有几种方式?
2.1 自己表写一个ArrayList集合类,根据业务一般来说,add/set/remove加锁
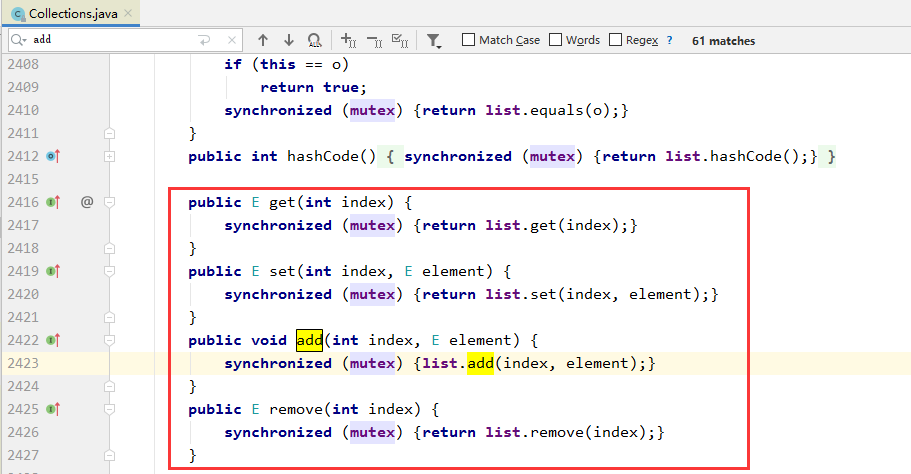
2.2 利用List<Object> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>()); //采用synchronized加锁
public E get(int index) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.get(index);} } public E set(int index, E element) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.set(index, element);} } public void add(int index, E element) { synchronized (mutex) {list.add(index, element);} } public E remove(int index) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.remove(index);} }
2.3 new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>().add(""); //采用 ReentrantLock加锁
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { //加锁 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; lock.lock(); try { //获取原始集合 Object[] elements = getArray(); int len = elements.length; //复制一个新集合 Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); newElements[len] = e; //替换原始集合为新集合 setArray(newElements); return true; } finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } }
3、了解CopyOnWriteArrayList底层、CopyOnWriteArrayList与Collections.synchronizedList有什么区别
3.1 CopyOnWriteArrayList底层实现:
CopyOnWriteArrayList在执行修改操作的时候,会复制一份新的数组数据,代价昂贵,修改过后将原来的集合指向到新的集合完成操作使用ReentrantLock保证多线程环境下的集合安全
add添加:
在添加的时候是需要加锁的,否则多线程写的时候会Copy出N个副本出来;使用ReentrantLock保证多线程环境下的集合安全;
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { //获取了一把锁 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //加锁 lock.lock(); try { //获取当前数组数据,给elements Object[] elements = getArray(); //记录当前数组的长度 int len = elements.length; //复制一个新的数组 Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); /将数据填入到新数组当中 newElements[len] = e; //将当前array指针指向到新的数据 setArray(newElements); return true; } finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } }
get读取:
读的时候没有加锁,如果读的时候有多个线程正在向CopyOnWriteArrayList添加数据,读还是会读到旧的数据,因为写的时候不会锁住旧的CopyOnWriteArrayList;
/** * {@inheritDoc} * * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { return get(getArray(), index); }
CopyOnWriteArrayList应用场景:
适用于读取操作远大于写操作场景(底层get读取时没有加锁,直接获取)
3.2 Collections.synchronizedList几乎底层方法都加上了synchronized的锁
public E get(int index) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.get(index);} } public E set(int index, E element) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.set(index, element);} } public void add(int index, E element) { synchronized (mutex) {list.add(index, element);} } public E remove(int index) { synchronized (mutex) {return list.remove(index);} }
应用场景:
写操作的性能比CopyOnWriteArrayList要好,但是读取的性能不如CopyOnWriteArrayList
4、CopyOnWriteArrayList设计思想是怎么样的,有什么缺点?
设计思想:
读写分离,最终一致
缺点:
内存占用,由于写时复制,内存中就会出现两个对象占用空间,如果对象大则容易发生YongGC和FullGC
5、 ArrayList扩容机制是怎么样的
JDK1.7 以及之前版本JDK,首先从默认大小来讲,默认为10
JDK1.8 ArrayList集合大小如果创建时没有指定,则默认为0,若已经指定集合大小,则初始值为指
当第一次添加数据的时候,集合大小扩容为10,第二次及其后续每次按照int oldCapacity = elementData.length; newCapacity = oldCapacity+(oldCapacity>>1)
5.1 属性
默认初始值的大小:
/** * Default initial capacity. */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
默认的空对象数组:
/** * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when * first element is added. */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
实际存储数据的数组:
/** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
5.2 无参构造器
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */ public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
5.3 扩容机制(源码)
/** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; }
//ensureCapacityInternal方法接受了size+1作为minCapacity,并且判断如果数组是空数组,那么10和minCapacity的较大值就作为新的minCapacity。 private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity); }
//判断传入的minCapacity和elementData.length的大小,如果elementData.length大于minCapacity,说明数组容量够用,就不需要进行扩容, //反之,则传入minCapacity到grow()方法中,进行扩容 private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // overflow-conscious code //如果其元素个数大于其容量,则进行扩容; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); }
/** * Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the * number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument. * * @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity */ private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code //原来的容量 int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //新的容量,原来容量的1.5倍 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; //如果大于ArrayList可以允许的最大容量,则设置为最大容量 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: //最终进行扩容,生成一个1.5倍元素 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
进入grow()方法,会将newCapacity设置为旧容量的1.5倍,这也是ArrayList每次扩容都为原来的1.5倍的由来。然后进行判断,如果newCapacity小于minCapacity,那么就将minCapacity的值赋予newCapacity。
然后在检查新容量是否超出了定义的容量,如果超出则调用hugeCapacity方法,比较minCapacity和MAX_ARRAY_SIZE的值;如果minCapacity大,那么新容量为Integer。MAX_VALUE,否则新容量为MAX_ARRAYSIZE。最后调用Arrays.cpoyOf传递elementData和新容量,返回新的elementData;
6、ArrayList集合框架(牢记)
//默认初始容量 /** * Default initial capacity. */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
//代表默认情况下,创建集合时,是一个空数组 /** * Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We * distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when * first element is added. */ private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
//代表集合真正存储的数据 /** * The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored. * The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any * empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA * will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added. */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
//当前集合大小 /** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */ private int size;
/** * Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten. */ public ArrayList() { //创建一个空数组 this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; }
/** * Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. * * @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity * is negative */ public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { //判断指定集合大小 if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { //参数异常 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } }
/** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. * * @param index index of the element to return * @return the element at the specified position in this list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } /** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with * the specified element. * * @param index index of the element to replace * @param element element to be stored at the specified position * @return the element previously at the specified position * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } /** * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. * * @param e element to be appended to this list * @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) */ public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } /** * Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this * list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and * any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices). * * @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted * @param element element to be inserted * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public void add(int index, E element) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, size - index); elementData[index] = element; size++; } /** * Removes the element at the specified position in this list. * Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their * indices). * * @param index the index of the element to be removed * @return the element that was removed from the list * @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc} */ public E remove(int index) { rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; } /** * Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list, * if it is present. If the list does not contain the element, it is * unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index * <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt> * (if such an element exists). Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list * contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list * changed as a result of the call). * * @param o element to be removed from this list, if present * @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element */ public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } return false; }