1.表格样式创建
表格视觉样式:Dataframe.style → 返回pandas.Styler对象的属性,具有格式化和显示Dataframe的有用方法
样式创建:
① Styler.applymap:elementwise → 按元素方式处理Dataframe
② Styler.apply:column- / row- / table-wise → 按行/列处理Dataframe
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt % matplotlib inline
#样式 df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 4), columns=['a','b','c','d']) sty = df.style print(sty, type(sty)) # 查看样式类型 sty # 显示样式
---->
<pandas.formats.style.Styler object at 0x00000000097731D0> <class 'pandas.formats.style.Styler'>
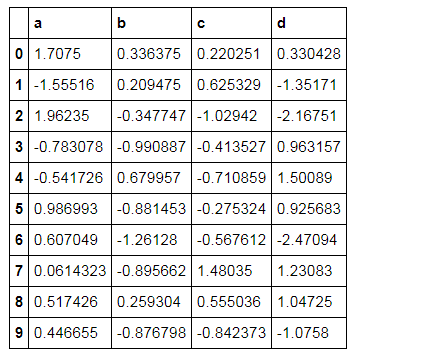
按元素处理样式 df.style.applymap( 函数 )
# 按元素处理样式:style.applymap()
def color_neg_red(val):
if val < 0:
color = 'red'
else:
color = 'black'
return ('color:%s'% color)
df.style.applymap(color_neg_red)
# 创建样式方法,使得小于0的数变成红色
# style.applymap() → 自动调用其中的函数
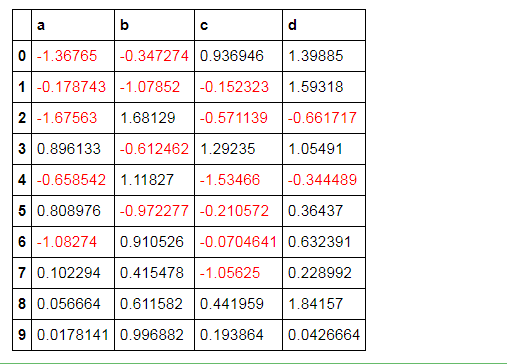
按行/列处理样式 df.style.apply( 函数, axis=0按列, subset=['b','c']处理b、c列 )
# 按行/列处理样式:style.apply()
def highlight_max(s):
is_max = s == s.max()
print(is_max)
lst = []
for v in is_max:
if v:
lst.append(' padding: 0px; color: rgb(128, 0, 0); line-height: 1.5 !important;">')
else:
lst.append('')
return (lst)
df.style.apply(highlight_max, axis=0, subset=['b', 'c']) # axis:0为列,1为行,默认为0; # subset:索引
# 创建样式方法,每列最大值填充黄色
0 False 1 False 2 True 3 False 4 False 5 False 6 False 7 False 8 False 9 False Name: b, dtype: bool 0 False 1 False 2 True 3 False 4 False 5 False 6 False 7 False 8 False 9 False Name: b, dtype: bool 0 False 1 False 2 False 3 True 4 False 5 False 6 False 7 False 8 False 9 False Name: c, dtype: bool
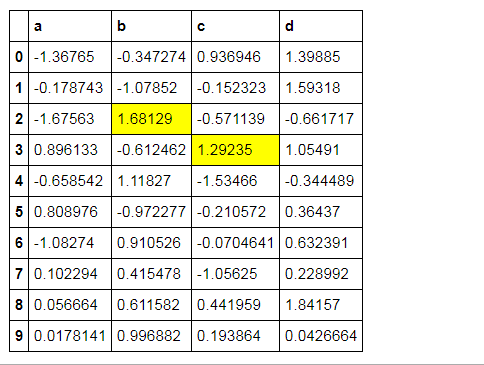
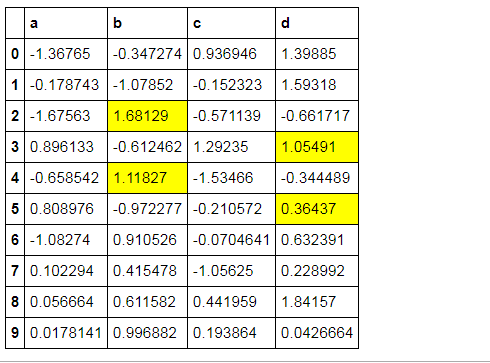
样式索引、切片
df.style.apply(highlight_max, axis = 1,
subset = pd.IndexSlice[2:5,['b', 'd']]) 按照index索引,再切片b、d列所对应的值
# 样式索引、切片
df.style.apply(highlight_max, axis = 1,
subset = pd.IndexSlice[2:5,['b', 'd']]) # 通过pd.IndexSlice[]调用切片
# 也可:df[2:5].style.apply(highlight_max, subset = ['b', 'd']) → 先索引行再做样式
b True d False Name: 2, dtype: bool b True d False Name: 2, dtype: bool b False d True Name: 3, dtype: bool b True d False Name: 4, dtype: bool b False d True Name: 5, dtype: bool
2.表格显示控制
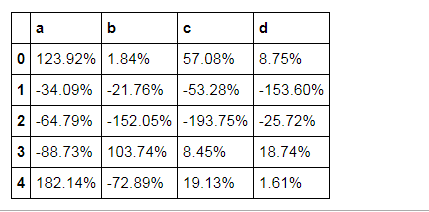
df.head().style.format("{:.2%}")
# 按照百分数显示
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10,4),columns=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df.head())
df.head().style.format("{:.2%}")
a b c d 0 1.239244 0.018364 0.570776 0.087462 1 -0.340928 -0.217569 -0.532815 -1.535981 2 -0.647936 -1.520526 -1.937499 -0.257186 3 -0.887309 1.037361 0.084524 0.187425 4 1.821439 -0.728899 0.191298 0.016149
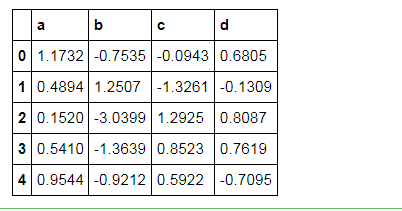
df.head().style.format("{:.4f}")
# 显示小数点数
df.head().style.format("{:.4f}")
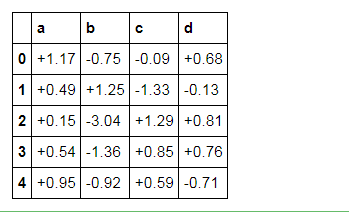
df.head().style.format("{:+.2f}")
# 显示正负数
df.head().style.format("{:+.2f}")
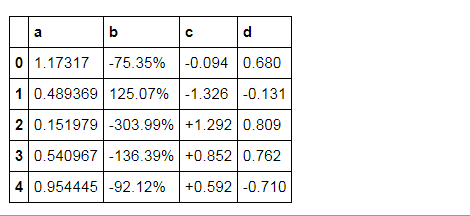
df.head().style.format({'b':"{:.2%}", 'c':"{:+.3f}", 'd':"{:.3f}"})
# 分列显示
df.head().style.format({'b':"{:.2%}", 'c':"{:+.3f}", 'd':"{:.3f}"})
3.表格样式调用
Styler内置样式调用
df.style.highlight_null(null_color='red') #定位空值
# 定位空值
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(5, 4), columns=list('ABCD')) df['A'][2] = np.nan df.style.highlight_null(null_color='red')

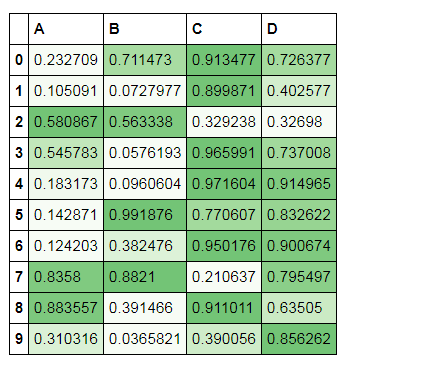
df.style.background_gradient(cmap='Greens',axis =1,low=0,high=1) 色彩映射
# 色彩映射
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,4),columns = list('ABCD'))
df.style.background_gradient(cmap='Greens',axis =1,low=0,high=1) # cmap:颜色; # axis:映射参考,0为行,1以列
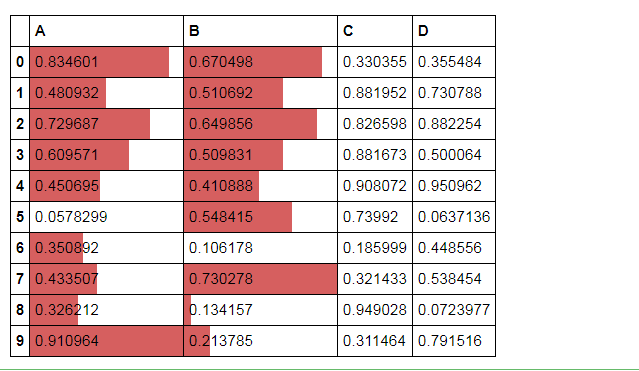
df.style.bar(subset=['A', 'B'], color='#d65f5f', width=100)
# 条形图
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,4),columns = list('ABCD'))
df.style.bar(subset=['A', 'B'], color='#d65f5f', width=100) # width:最长长度在格子的占比
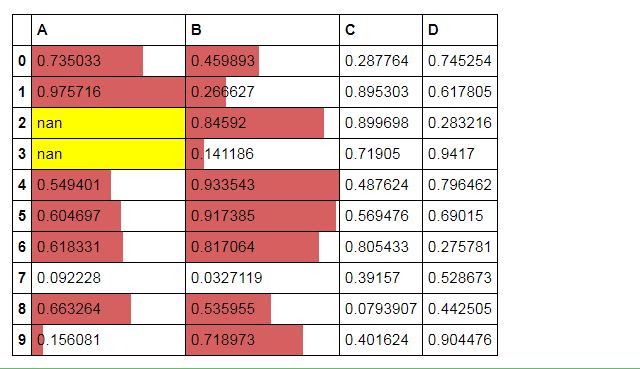
# 分段式构建样式
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(10,4),columns = list('ABCD'))
df['A'][[3,2]] = np.nan
df.style.
bar(subset=['A', 'B'], color='#d65f5f', width=100).
highlight_null(null_color='yellow')
原文地址:
