Python is a great language for doing data analysis, primarily because of the fantastic ecosystem of data-centric python packages. Pandas is one of those packages and makes importing and analyzing data much easier.
Pandas str.cat() is used to concatenate strings to the passed caller series of string. Distinct values from a different series can be passed but the length of both the series has to be same. .str has to be prefixed to differentiate it from the Python’s default method.
Syntax: Series.str.cat(others=None, sep=None, na_rep=None)
Parameters:
others: Series, index, data frame or list of strings to concatenate
sep: Separator to be put between the two strings
na_rep: None or string value to replace in place of null valuesReturn type: Series with concatenated string valus
To download the Csv file used, click here.
In the following examples, the data frame used contains data on some NBA players. The image of data frame before any operations is attached below.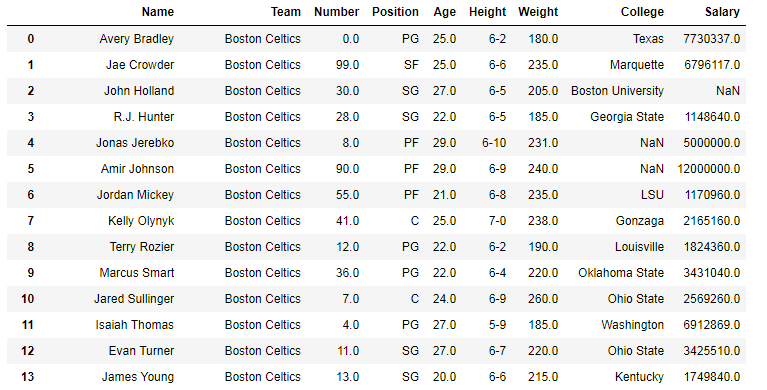
Example #1: Concatenating column with separator
In this example, the Team column is concatenated at the end of Name column with separator “, “. The Name column is overwritten with the new series and the data frame is then displayed.
# importing pandas module import pandas as pd # importing csv from link # making copy of team column new = data["Team"].copy() # concatenating team with name column # overwriting name column data["Name"]= data["Name"].str.cat(new, sep =", ") # display data |
Output:
As shown in the output image, every string in the Team column having same index as string in Name column have been concatenated with separator “, “.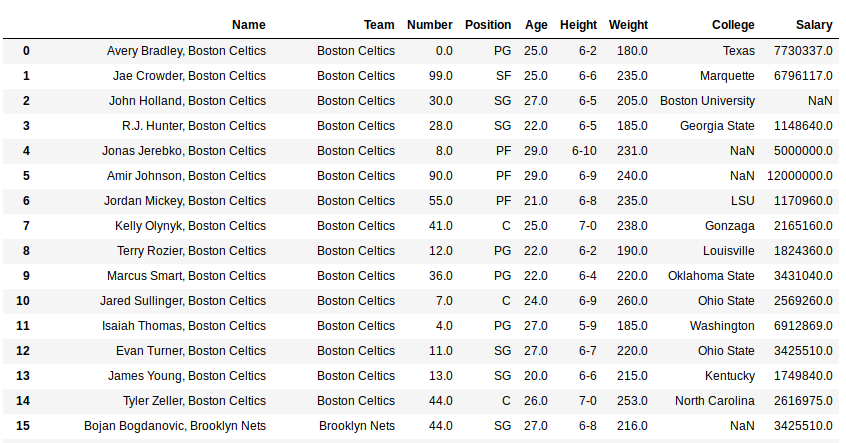
Example #2: Handling Null values
The most important part in analyzing data is handling null values. str.cat() provides a way to handle null values through na_rep parameter. Whatever is passed to this parameter will be replaced at every occurrence of null value.
In this example, college column is concatenated with team column. “No college” is passed to na_rep parameter to replace null with this string.
# importing pandas module import pandas as pd # importing csv from link # making copy of team column new = data["Team"].copy() # string to replace null values with na_string ="No College" # concatenating team with name column # overwriting name column data["College"]= data["College"].str.cat(new, sep =", ", na_rep = na_string) # display data |
Output:
As it can be seen in the data frame, at index position 4 and 5, there was NULL value which has been replaced with “No College” and the string from Team column have been concatenated successfully.