1 问题描述
给定n个重量为w1,w2,w3,…,wn,价值为v1,v2,…,vn的物品和一个承重为W的背包,求这些物品中最有价值的子集(PS:每一个物品要么选一次,要么不选),并且要能够装到背包。
附形象描述:就像一个小偷打算把最有价值的赃物装入他的背包一样,但如果大家不喜欢扮演小偷的角色,也可以想象为一架运输机打算把最有价值的物品运输到外地,同时这些物品的重量不能超出它的运输能力。
2 解决方案
2.1 蛮力法
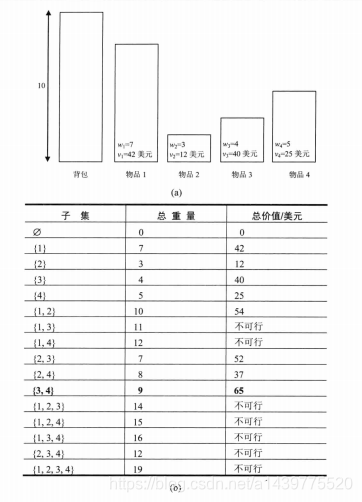
使用蛮力法解决包含n个物品的背包问题,首先得求出这n个物品的所有子集,对于每一个物品存在两种情况:选中(在程序中用1表示),未选中(在程序中用0表示)。该n个物品的所有子集数数量为2^n。下面请看一个简单示例:
package com.liuzhen.chapterThree;
public class Knapsack {
public int maxSumValue = 0; //定义满足背包问题子集的最大承重所得的总价值,初始化为0
/*
* 数组A的行数为2^n,代表n个物品共有2^n个子集,列数为n。即每一行的排列为一个背包实例
* 数组weight存放每个物品的具体重量
* 数组value存放每个物品的具体价值
* n代表共有n个物品
* maxWeight表示背包最大承重量
*/
public void bruteForce(int[][] A,int[] weight,int[] value,int n,int maxWeight){
for(int i = 0;i < Math.pow(2, n);i++){ //总共有2^n个子集,需要进行2^n次循环,及数组A有2^n行
int temp1 = i;
for(int j = 0;j < n;j++){ //数组A有n列,每一列代表一个物品
int temp2 = temp1%2;
A[i][j] = temp2;
temp1 = temp1/2;
}
}
printArray(A,weight,value,maxWeight);
}
//输出穷举方案的背包实例的选择物品(0代表不包含该物品,1表示包含该物品)的总重量及总价值,并输出最优实例的总价值
public void printArray(int[][] A,int[] weight,int[] value,int maxWeight){
int len1 = A.length; //二维数组的行数
int len2 = A[0].length; //二维数组的列数
for(int i = 0;i < len1;i++){
int tempWeight = 0; //暂时计算当前选中背包实例物品的总重量,初始化为0
int tempSumValue = 0; //暂时计算当前选中背包实例物品的总价值,初始化为0
for(int j = 0;j < len2;j++){
System.out.print(A[i][j]+" ");
// if(A[i][j] != 0)
// System.out.print(" 物品"+j);
tempWeight += A[i][j]*weight[j];
tempSumValue += A[i][j]*value[j];
}
System.out.print(" "+"总重量为:"+tempWeight);
if(tempWeight <= maxWeight)
System.out.print(" "+"总价值为:"+tempSumValue);
else
System.out.print(" "+"不可行(超出背包最大承重)");
if(tempWeight <= maxWeight && tempSumValue > maxSumValue)
maxSumValue = tempSumValue;
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("穷举查找得知,最优解的总价值为:"+maxSumValue);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Knapsack test = new Knapsack();
int[][] A = new int[16][4];
int[] weight = {7,3,4,5};
int[] value = {42,12,40,25};
test.bruteForce(A,weight,value,4,10); //背包的承重最大为10
}
}
运行结果:
0 0 0 总重量为:0 总价值为:0
0 0 0 总重量为:7 总价值为:42
1 0 0 总重量为:3 总价值为:12
1 0 0 总重量为:10 总价值为:54
0 1 0 总重量为:4 总价值为:40
0 1 0 总重量为:11 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
1 1 0 总重量为:7 总价值为:52
1 1 0 总重量为:14 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
0 0 1 总重量为:5 总价值为:25
0 0 1 总重量为:12 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
1 0 1 总重量为:8 总价值为:37
1 0 1 总重量为:15 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
0 1 1 总重量为:9 总价值为:65
0 1 1 总重量为:16 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
1 1 1 总重量为:12 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
1 1 1 总重量为:19 不可行(超出背包最大承重)
穷举查找得知,最优解的总价值为:65
2.2 减治法
2.2.1 递归求解
背包问题的实质是求取n个不同物品的所有子集,在此基础上寻找重量合适,总价值最大的子集。此处只给出如何求出n个不同物品的所有子集实现,至于如何寻找符合背包问题的子集,感兴趣的同学可以自己动手实现以下哟~
此处是运用减治法思想,根据二进制反射格雷码的算法思想,来实现此问题。具体解释,请看下面一段出自《算法设计与分析基础》第三版上讲解:

package com.liuzhen.chapter4;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class GrayCode {
//递归求取n个不同物品的所有子集
public String[] getGrayCode2(int n){
int len = (int) Math.pow(2, n);
String[] result = new String[len];
if(n == 1){
result[0] = "0";
result[1] = "1";
return result;
}
String[] temp = getGrayCode2(n-1); //递归求取n-1个不同物品的所有子集
for(int i = 0;i < temp.length;i++){ //根据格雷码去掉最高位,前一半和后一半二进制数完全一样的对称性
result[i] = "0" + temp[i]; //前一半格雷码,最高位为0
result[result.length-1-i] = "1" + temp[i]; //后一半格雷码,最高位为1
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
GrayCode test = new GrayCode();
String[] temp2 = test.getGrayCode2(3);
System.out.println("使用递归求解n个物品所有子集结果如下:");
for(int i = 0;i < temp2.length;i++)
System.out.println(temp2[i]);
}
}
运行结果:
使用递归求解n个物品所有子集结果如下:
001
010
111
100
2.2.2 非递归求解(运用异或运算)
此处也使用求取格雷码的思想,完成求取n个物品的所有子集,不过此处是使用非递归来实现,运用异或运算,其构造非常巧妙,个人感觉要理解这种编码方式和思想得多多运用,直至熟能生巧。
package com.liuzhen.chapter4;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class GrayCode {
//运用异或运算得到n个不同物品的所有子集
public List<Integer> getGaryCode1(int n){
List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<>();
if(n >= 0){
result.add(0);
int top = 1;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
System.out.print("result.size() = "+result.size()+" ");
for(int j = result.size()-1;j >= 0;j--){
System.out.print("result.get("+j+")^top = "+result.get(j)+"^"+top+" = "+(result.get(j)^top)+" ");
result.add(result.get(j)^top); //符号‘^’是异或运算(使用具体数字的二进制进行运算),即1^0=1,0^1=1,0^0=0,1^1=0
}
System.out.println();
top <<= 1; //top二进制左移1位,相当于top=top*2
System.out.println("top = "+top);
}
}
return result;
}
//把十进制数转换成长度为n的二进制数
public StringBuffer[] getBinary(List<Integer> A,int n){
StringBuffer[] result = new StringBuffer[A.size()];
for(int i = 0;i < A.size();i++){
int temp1 = A.get(i);
int judge = n;
char[] temp2 = new char[n]; //用于存放temp1的n位二进制数
while(judge > 0){
int temp3 = temp1%2;
temp2[judge-1] = (char) (temp3+48); //对照char的unicode编码,把int型数字转换为char型
temp1 = temp1/2;
judge--;
}
result[i] = new StringBuffer(String.valueOf(temp2));
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
GrayCode test = new GrayCode();
List<Integer> temp = test.getGaryCode1(3);
System.out.println(temp);
StringBuffer[] temp1 = test.getBinary(temp, 3);
for(int i = 0;i < temp1.length;i++)
System.out.println(temp1[i]);
}
}
运行结果:
result.size() = 1 result.get(0)^top = 0^1 = 1
top = 2
result.size() = 2 result.get(1)^top = 1^2 = 3 result.get(0)^top = 0^2 = 2
top = 4
result.size() = 4 result.get(3)^top = 2^4 = 6 result.get(2)^top = 3^4 = 7 result.get(1)^top = 1^4 = 5 result.get(0)^top = 0^4 = 4
top = 8
[0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 7, 5, 4]
001
010
111
100
2.3 动态规划法
此处编码思想主要参考自《算法设计与分析基础》第三版的一段讲解,具体如下:


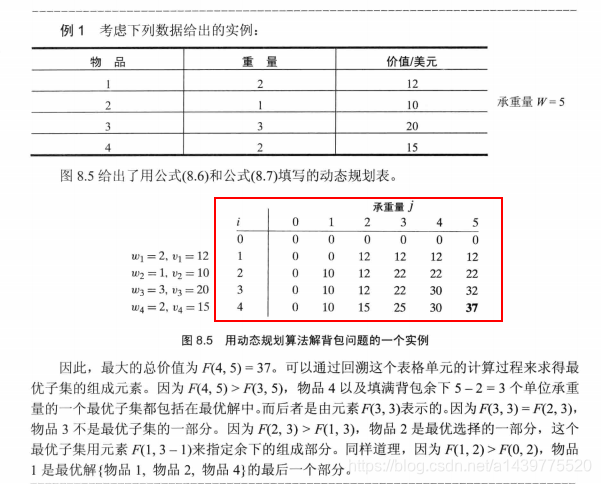
package com.liuzhen.chapter8;
public class MFKnapsack {
/*
* 参数weight:物品1到物品n的重量,其中weight[0] = 0
* 参数value:物品1到物品n的价值,其中value[0] = 0
* 函功能:返回背包重量从0到所有物品重量之和区间的每一个重量所能达到的最大价值
*/
public int[][] getMaxValue(int[] weight, int[] value) {
int lenRow = weight.length;
int lenColumn = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < weight.length;i++)
lenColumn += weight[i];
int[][] F = new int[lenRow][lenColumn+1]; //列值长度加1,是因为最后一列要保证重量值为lenColumn
for(int i = 1;i < weight.length;i++) {
for(int j = 1;j <= lenColumn;j++) {
if(j < weight[i])
F[i][j] = F[i-1][j];
else {
if(F[i-1][j] > F[i-1][j-weight[i]] + value[i])
F[i][j] = F[i-1][j];
else
F[i][j] = F[i-1][j-weight[i]] + value[i];
}
}
}
return F;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MFKnapsack test = new MFKnapsack();
int[] weight = {0,2,1,3,2};
int[] value = {0,12,10,20,15};
int[][] F = test.getMaxValue(weight, value);
System.out.println("背包承重从0到所有物品重量之和为8的承重能够达到的最大价值分别为:");
for(int i = 0;i < F.length;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < F[0].length;j++)
System.out.print(F[i][j]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果:
背包承重从0到所有物品重量之和为8的承重能够达到的最大价值分别为:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 12 12 12 12 12 12 12
10 12 22 22 22 22 22 22
10 12 22 30 32 42 42 42
10 15 25 30 37 45 47 57