学了这么多全是给他用的之Commons
用这个的前提需要导包,
①创建lib文件夹
②将下载的commos-io.jar拷贝到lib文件夹
③右键点击commons-io.jar,Build Path→Add to Build Path
然后介绍两个工具类
1.2 FilenameUtils
这个工具类是用来处理文件名,他可以轻松解决不同操作系统文件名称规范不同的问题
l 常用方法:
getExtension(String path):获取文件的扩展名;
getName(String filename):获取文件名;
isExtension(String fileName,String ext):判断fileName是否是ext后缀名;
//明确数据源 String str="D:\demo0611\e.txt"; //获取后缀名 String path=FilenameUtils.getExtension(str); System.out.println("文件拓展名"+path); String name=FilenameUtils.getName(str); System.out.println("名字叫"+name); boolean flag=FilenameUtils.isExtension("D:\demo0611\e.txt","txt"); System.out.println(flag);

1.1 FileUtils
提供文件操作(移动文件,读取文件,检查文件是否存在等等)的方法。
l 常用方法:
readFileToString(File file):读取文件内容,并返回一个String;
writeStringToFile(File file,String content):将内容content写入到file中;
copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir,File destDir);文件夹复制
copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile);文件复制
//文件的读取 File file=new File("D:\demo0611\e.txt"); //读取文件 String content=FileUtils.readFileToString(file); System.out.println(content); //复制文件夹 //明确数据源 File nowFile=new File("D:\demo0611\e.txt"); //明确目的地 File afterFile=new File("D:\demo0611\a\vvv.txt"); //开始复制 FileUtils.copyFile(nowFile, afterFile);

Properties String 键值对,属于Hashtable的子类,泛型就是String字符串
存储:setProperty()
获取:getProperty()

比较重要的是load,读取属性
它的主要操作是可以写一个文档来存储成对出现的值。
//用这个集合书写的键值对 driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java0611?characterEncoding=utf8 username=root password=123456
public static Connection getConn(){ Properties pro=new Properties(); try { //明确数据源 FileReader fr=new FileReader("src/com/oracle/tools/db.properties"); pro.load(fr); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } //直接获取文件即可,以后方便 //获得链接对象 String url=pro.getProperty("url"); String username=pro.getProperty("username"); String password=pro.getProperty("password"); //为了返回值,必须把它作为全局变量 Connection conn=null; try { //注册驱动 Class.forName(pro.getProperty("driver")); //获得连接对象 conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return conn; }
1.1 ObjectOutputStream 对象序列化流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//序列化流,把对象写到文件里
//明确目的地,必须是字节
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("D:\demo0611\person.txt");
//创建序列化流
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos);
//向文件中写入对象 有参构造方法,不需要new对象了
oos.writeObject(new Person("张三",18));
//释放资源
oos.close();
}
他存在的意义在于可以将按照自定义类书写的对象通过对象序列化流存储到文档中。
因为是字节存储所以乱码。
1.1 对象反序列化流ObjectInputStream
//反序列化流
//明确数据源
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("D:\demo0611\person.txt");
//创建反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//从文件中读取对象 因为读取的是万物父类object所以需要向下转型,读取子类独有元素。
Object obj=ois.readObject();
//向下转型
if(obj instanceof Person){
Person p=(Person)obj;
//向下转型之后就获取到了Person对象
System.out.println(p);
}
//释放资源
ois.close();
反序列化流是将自定义类的对象打印到程序里。向下转型是关键。调取子类独有对象
}
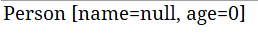
person类
public class Person implements Serializable{
private transient String name; //不想被序列化修饰可以用transient,这个是将内容进行序列化存储,而静态是直接在类加载时就完成存储。
public static int age;
public static final long serialVersionUID =1000L; 序列化流的关键在于,如果不表示一个序列号那么类一旦变化就会报错,这样就相当于生成了一个标识,获取的就是它。
//有参构造
public Person(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
打印流:
字节打印流 PrintStream
字符打印流 PrintWriter
方法:
void print(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,
void println(String str): 输出任意类型的数据,自动写入换行操作
打出来并自己更新。