一、继承Thread
public class ThreadDemo extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
}
}
Runable接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}

1.进入Thread
Thread实现Runable接口
private static native void registerNatives();
static {
registerNatives();
}
private volatile String name;
private int priority;
private Thread threadQ;
private long eetop;
2.优先级
/**
* The minimum priority that a thread can have.
*/
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
/**
* The default priority that is assigned to a thread.
*/
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
/**
* The maximum priority that a thread can have.
*/
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
/**
* Changes the priority of this thread.
* <p>
* First the <code>checkAccess</code> method of this thread is called
* with no arguments. This may result in throwing a
* <code>SecurityException</code>.
* <p>
* Otherwise, the priority of this thread is set to the smaller of
* the specified <code>newPriority</code> and the maximum permitted
* priority of the thread's thread group.
*
* @param newPriority priority to set this thread to
* @exception IllegalArgumentException If the priority is not in the
* range <code>MIN_PRIORITY</code> to
* <code>MAX_PRIORITY</code>.
* @exception SecurityException if the current thread cannot modify
* this thread.
* @see #getPriority
* @see #checkAccess()
* @see #getThreadGroup()
* @see #MAX_PRIORITY
* @see #MIN_PRIORITY
* @see ThreadGroup#getMaxPriority()
*/
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
ThreadGroup g;
checkAccess();
if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) {
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
setPriority0(priority = newPriority);
}
}
/**
* Returns this thread's priority.
*
* @return this thread's priority.
* @see #setPriority
*/
public final int getPriority() {
return priority;
}
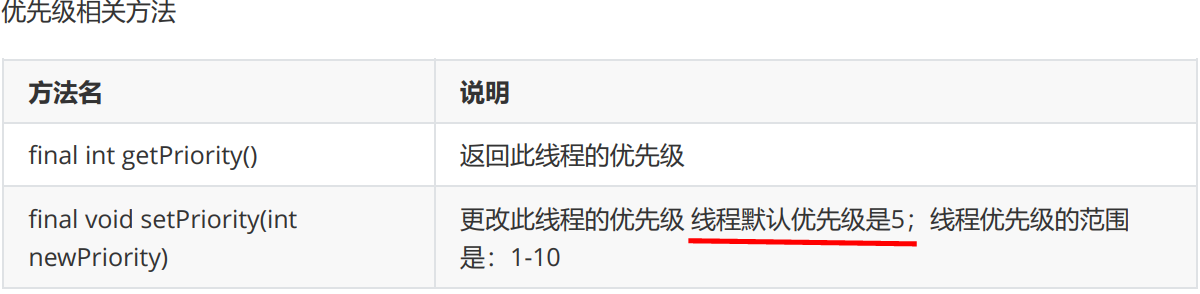
值越小,优先级越高。
示例:
//设置正确的优先级 tp1.setPriority(5); tp2.setPriority(10); tp3.setPriority(1);
3.Sleep的两种方法
/**
* Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease
* execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to
* the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers. The thread
* does not lose ownership of any monitors.
*
* @param millis
* the length of time to sleep in milliseconds
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the value of {@code millis} is negative
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is
* cleared when this exception is thrown.
*/
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease
* execution) for the specified number of milliseconds plus the specified
* number of nanoseconds, subject to the precision and accuracy of system
* timers and schedulers. The thread does not lose ownership of any
* monitors.
*
* @param millis
* the length of time to sleep in milliseconds
*
* @param nanos
* {@code 0-999999} additional nanoseconds to sleep
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the value of {@code millis} is negative, or the value of
* {@code nanos} is not in the range {@code 0-999999}
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is
* cleared when this exception is thrown.
*/
public static void sleep(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
sleep(millis);
}
4.Start:启动线程
/**
* Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine
* calls the <code>run</code> method of this thread.
* <p>
* The result is that two threads are running concurrently: the
* current thread (which returns from the call to the
* <code>start</code> method) and the other thread (which executes its
* <code>run</code> method).
* <p>
* It is never legal to start a thread more than once.
* In particular, a thread may not be restarted once it has completed
* execution.
*
* @exception IllegalThreadStateException if the thread was already
* started.
* @see #run()
* @see #stop()
*/
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
线程加锁了
5.run
/**
* If this thread was constructed using a separate
* <code>Runnable</code> run object, then that
* <code>Runnable</code> object's <code>run</code> method is called;
* otherwise, this method does nothing and returns.
* <p>
* Subclasses of <code>Thread</code> should override this method.
*
* @see #start()
* @see #stop()
* @see #Thread(ThreadGroup, Runnable, String)
*/
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}

6.SetName 和getName
/**
* Changes the name of this thread to be equal to the argument
* <code>name</code>.
* <p>
* First the <code>checkAccess</code> method of this thread is called
* with no arguments. This may result in throwing a
* <code>SecurityException</code>.
*
* @param name the new name for this thread.
* @exception SecurityException if the current thread cannot modify this
* thread.
* @see #getName
* @see #checkAccess()
*/
public final synchronized void setName(String name) {
checkAccess();
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
if (threadStatus != 0) {
setNativeName(name);
}
}
/**
* Returns this thread's name.
*
* @return this thread's name.
* @see #setName(String)
*/
public final String getName() {
return name;
}
7.守护线程
/**
* Marks this thread as either a {@linkplain #isDaemon daemon} thread
* or a user thread. The Java Virtual Machine exits when the only
* threads running are all daemon threads.
*
* <p> This method must be invoked before the thread is started.
*
* @param on
* if {@code true}, marks this thread as a daemon thread
*
* @throws IllegalThreadStateException
* if this thread is {@linkplain #isAlive alive}
*
* @throws SecurityException
* if {@link #checkAccess} determines that the current
* thread cannot modify this thread
*/
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) {
checkAccess();
if (isAlive()) {
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
}
daemon = on;
}
/**
* Tests if this thread is a daemon thread.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if this thread is a daemon thread;
* <code>false</code> otherwise.
* @see #setDaemon(boolean)
*/
public final boolean isDaemon() {
return daemon;
}
二、实现Runable接口
public class ThreadDemo1 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
}
}
Runnable接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
/**
* When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used
* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's
* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing
* thread.
* <p>
* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may
* take any action whatsoever.
*
* @see java.lang.Thread#run()
*/
public abstract void run();
}
三、Thread与Runable比较
1.效果上没区别,写法上的区别而已。
2、没有可比性,Thread实现了Runnable接口并进行了扩展,我们通常拿来进行比较只是写法上的比较,而Thread和Runnable的实质是实现的关系,不是同类东西。
2、没有可比性,Thread实现了Runnable接口并进行了扩展,我们通常拿来进行比较只是写法上的比较,而Thread和Runnable的实质是实现的关系,不是同类东西。
无论你使用Runnable还是Thread,都有一个new Thread的过程,效果上最后都是new Thread,然后执行run方法。写法上的区别无非就是你是new Thead还是new你自定义的thread,如果你有复杂的线程操作需求,那就自定义Thread,如果只是简单的在子线程run一下任务,那就自己实现runnable,当然如果自己实现runnable的话可以多一个继承(自定义Thread必须继承Thread类,java单继承规定导致不能在继承别的了)。
四、Callable接口
public class ThreadDemo2 implements Callable {
public Object call() throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
/**
* A task that returns a result and may throw an exception.
* Implementors define a single method with no arguments called
* {@code call}.
*
* <p>The {@code Callable} interface is similar to {@link
* java.lang.Runnable}, in that both are designed for classes whose
* instances are potentially executed by another thread. A
* {@code Runnable}, however, does not return a result and cannot
* throw a checked exception.
*
* <p>The {@link Executors} class contains utility methods to
* convert from other common forms to {@code Callable} classes.
*
* @see Executor
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> the result type of method {@code call}
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Callable<V> {
/**
* Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.
*
* @return computed result
* @throws Exception if unable to compute a result
*/
V call() throws Exception;
}
Runable接口与Callable接口都有注解@FunctionalInterface