一般都是用机器学习、梯度下降或sklearn、pytorch来做函数拟合运算,今天介绍遗传编程,或称基因编程/GP,来做这个计算
最终就是构造一棵树AST,来表示运算的先后、权重:
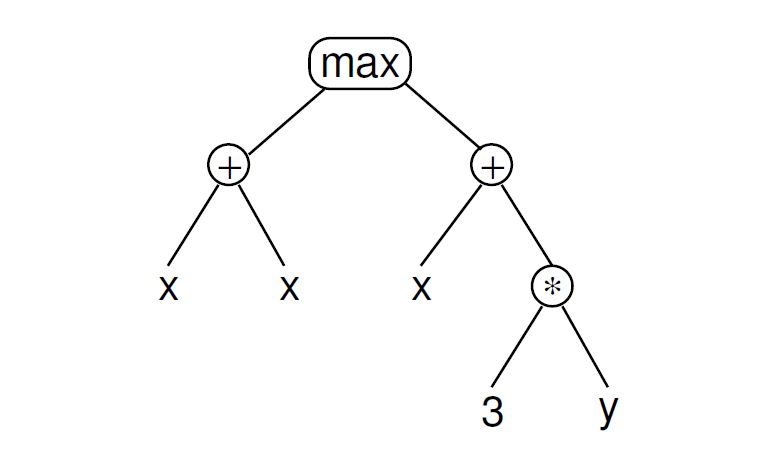
具体原理可以参考这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/ocd_with_naming/article/details/98901749
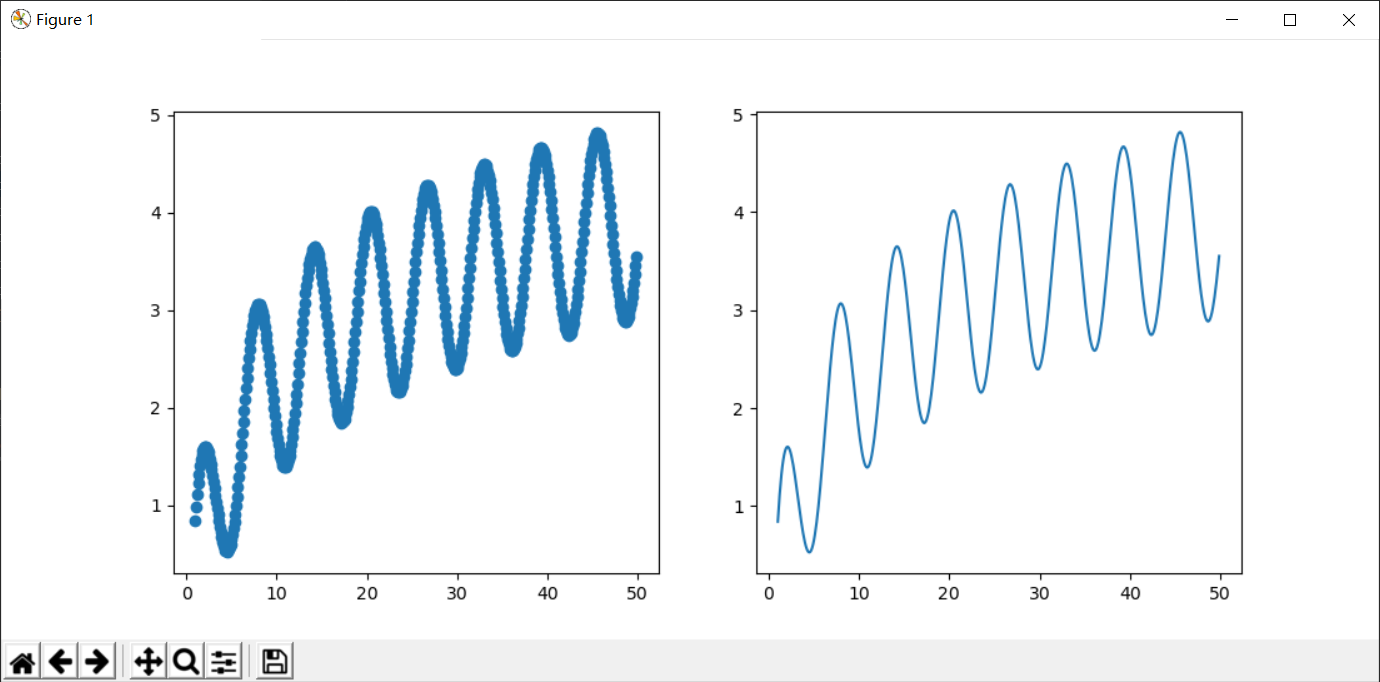
我们的目标是拟合这个函数:
np.sin(x) + np.log(x)
图像为:
先来一段java代码,是加载训练数据的,x、y的一个list;
private static List<Sample<Double>> load训练数据()
{
List<Sample<Double>> samples=new ArrayList<>();
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.0 , 0.8414709848078965 })); //第一个为x,第二个为y
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.1 , 0.9865175398657604 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.2000000000000002 , 1.1143606427611812 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.3000000000000003 , 1.2259224498846844 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.4000000000000004 , 1.3219219666096733 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.5000000000000004 , 1.4029600947122192 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.6000000000000005 , 1.4695772322872411 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.7000000000000006 , 1.5222930615146393 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.8000000000000007 , 1.5616342957803144 }));
samples.add(new DoubleDataSample(new Double[]{ 1.9000000000000008 , 1.5881539738598094 }));
//省略很多x/y对
return samples;
}
下面就是整个算法的架子了:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Op<Double>> terminals=new ArrayList<>();
terminals.add(Var.of("x", 0)); //由于只有1个自变量,所以这里只有x
//0代表第一个自变量
//如果是向量,则此处可以为x1/0, x2/1, x3/2 以此类推
List<Sample<Double>> samples=load训练数据();
final ISeq<Op<Double>> OPS = ISeq.of(MathOp.ADD, MathOp.SUB, MathOp.MUL, MathOp.SIN,MathOp.COS, MathOp.LOG); //这些是算法允许使用的操作算子
final ISeq<Op<Double>> TMS = ISeq.of(terminals); //上面的自变量在此处挂接上
final Regression<Double> REGRESSION =
Regression.of(
Regression.codecOf(
OPS, TMS, 5,
t -> t.getGene().size() < 30
),
Error.of(LossFunction::mse), //MSE计算误差
samples
);
final Engine<ProgramGene<Double>, Double> engine = Engine
.builder(REGRESSION)
.minimizing()
.alterers(
new SingleNodeCrossover<>(0.1),
new Mutator<>())
.build();
final EvolutionResult<ProgramGene<Double>, Double> er =
engine.stream()
.limit(Limits.byExecutionTime(Duration.ofSeconds(5)))
.collect(EvolutionResult.toBestEvolutionResult());
final ProgramGene<Double> program = er.getBestPhenotype()
.getGenotype()
.getGene();
final TreeNode<Op<Double>> tree = program.toTreeNode();
MathExpr.rewrite(tree);
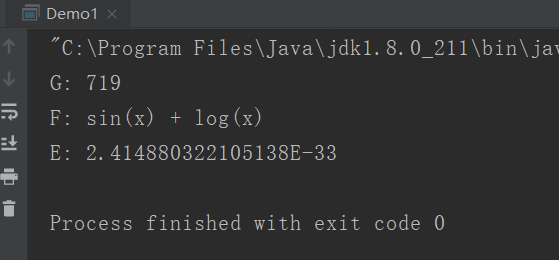
System.out.println("G: " + er.getTotalGenerations());
System.out.println("F: " + new MathExpr(tree));
System.out.println("E: " + REGRESSION.error(tree));
}