How far away ?
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 25408 Accepted Submission(s): 10111
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.
LCA_Tarjan
TarjanTarjan 算法求 LCA 的时间复杂度为 O(n+q)O(n+q) ,是一种离线算法,要用到并查集。(注:这里的复杂度其实应该不是 O(n+q)O(n+q) ,还需要考虑并查集操作的复杂度 ,但是由于在多数情况下,路径压缩并查集的单次操作复杂度可以看做 O(1)O(1),所以写成了 O(n+q)O(n+q) 。)
TarjanTarjan 算法基于 dfs ,在 dfs 的过程中,对于每个节点位置的询问做出相应的回答。
dfs 的过程中,当一棵子树被搜索完成之后,就把他和他的父亲合并成同一集合;在搜索当前子树节点的询问时,如果该询问的另一个节点已经被访问过,那么该编号的询问是被标记了的,于是直接输出当前状态下,另一个节点所在的并查集的祖先;如果另一个节点还没有被访问过,那么就做下标记,继续 dfs 。
当然,暂时还没那么容易弄懂,所以建议结合下面的例子和标算来看看。
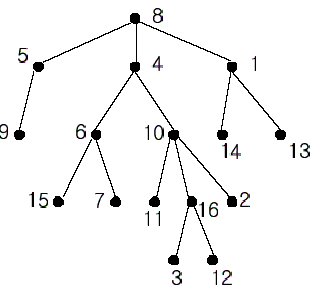
(下面的集合合并都用并查集实现)
比如:8−1−14−138−1−14−13 ,此时已经完成了对子树 11 的子树 1414 的 dfsdfs 与合并( 1414 子树的集合与 11 所代表的集合合并),如果存在询问 (13,14)(13,14) ,则其 LCA 即 getfather(14)getfather(14) ,即 11 ;如果还存在由节点 1313 与 已经完成搜索的子树中的 节点的询问,那么处理完。然后合并子树 1313 的集合与其父亲 11 当前的集合,回溯到子树 11 ,并深搜完所有 11 的其他未被搜索过的儿子,并完成子树 11 中所有节点的合并,再往上回溯,对节点 11 进行类似的操作即可。

#include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <cstring> #include <string> #include <cmath> #include <queue> #include <deque> #include <stack> #include <map> #include <set> typedef long long LL; const int MAX_N=40000; const int MAX_M=200; const int INF=1000000000; struct tedge { int to,w,next; }; tedge edge[MAX_N*2+5]; int head1[MAX_N+5],cnt1; void addedge(int a,int b,int c) { edge[cnt1]=(tedge){b,c,head1[a]};head1[a]=cnt1++; edge[cnt1]=(tedge){a,c,head1[b]};head1[b]=cnt1++; } struct tquery { int to,next; int index; }; tquery query[MAX_M*2+5]; int head2[MAX_N+5],cnt2; void addquery(int a,int b,int i) { query[cnt2]=(tquery){b,head2[a],i};head2[a]=cnt2++; query[cnt2]=(tquery){a,head2[b],i};head2[b]=cnt2++; } int fa[MAX_N]; int getf(int x) { if(fa[x]==x) return x; else return fa[x]=getf(fa[x]); } int vis[MAX_N+5]; int depth[MAX_N+5]; int ans[MAX_M+5]; void LCA(int x,int pa,int dis) { for(int i=head1[x];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next) { int l=edge[i].to; if(l!=pa) { LCA(l,x,dis+edge[i].w); } } depth[x]=dis; for(int i=head2[x];i!=-1;i=query[i].next) { int l=query[i].to; if(vis[l]) { int ancst=getf(l); ans[query[i].index]=depth[l]+depth[x]-depth[ancst]*2; //printf("%d %d %d ",l,x,ancst); } } fa[x]=pa;vis[x]=1; } void init() { memset(head1,-1,sizeof(head1));cnt1=0; memset(head2,-1,sizeof(head2));cnt2=0; memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); } int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { init(); int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1,a,b,c;i<=n-1;i++) { scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); addedge(a,b,c); } for(int i=1,a,b;i<=m;i++) { scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); addquery(a,b,i); } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) fa[i]=i; LCA(1,-1,0); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) printf("%d ",ans[i]); } return 0; }
