Spring中的Bean
1、Bean的配置:
a)、Bean的本质就是Java中的类,而Spring中的Bean其实就是对实体类的引用,来生产Java类对象,从而实现生产和管理Bean 。
b)、Spring容器支持两种格式的配置文件:Properties文件和XML文件。在实际开发中,最常使用的是XML文件格式的配置方式,这种配置方式是通过XML文件来注册并管理Bean之间的依赖关系。
c)、XML配置文件的根元素是<beans>,<beans>中包含了多个<bean>子元素,每一个<bean>子元素定义了一个Bean,并描述了该Bean如何被装配到Spring容器中。
d)、关于<beans>元素的常用属性如下表所示:
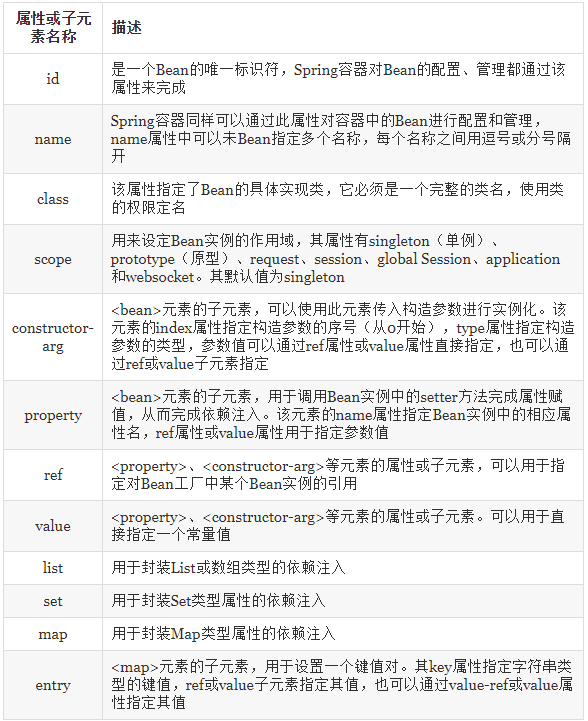
e)、如果在Bean中未指定id和name,则Spring会将class值当作id使用。
2、Bean的实例化
实例化Bean有三种方式,分别为构造器实例化、静态工厂方式实例化和实例工厂方式实例化(其中最常用的是构造器实例化)。
1)、构造器实例化:指Spring容器通过Bean对应的类中默认的构造函数来实例化Bean。
src->com.itheima.instance.constructor
①Bean1.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.constructor; 2 3 public class Bean1 { // 实例化Bean1的对象时调用其无参构造方法 4 5 }
②beans1.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 <bean id="bean1" class="com.itheima.instance.constructor.Bean1" /> 7 </beans>
③测试类:InstanceTest1.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.constructor; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 //构造器实例化Bean 7 public class InstanceTest1 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // 1、定义配置文件路径 10 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/instance/constructor/beans1.xml"; 11 // 2、ApplicationContext在加载配置文件时,对Bean进行实例化(Spring容器会通过id为bean1ID的实现类Bean1中默认的无参构造方法对Bean进行实例化) 12 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 13 // 3、通过容器获取Bean1的实例 14 Bean1 bean = (Bean1) applicationContext.getBean("bean1ID"); 15 System.out.println(bean); 16 } 17 }
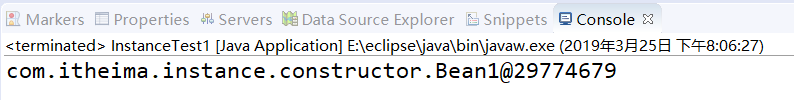
④运行结果:
2)、静态工厂:要求自己创建一个静态工厂的方法来创建Bean的实例。
src->com.itheima.instance.static_factory
①Bean2.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.static_factory; 2 3 public class Bean2 { 4 //无需添加任何方法 5 }
②MyBean2Factory.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.static_factory; 2 3 public class MyBean2Factory { // 创建工厂类MyBean2Factory 4 // 使用自己的工厂创建Bean2实例(使用静态方法创建Bean2实例) 5 public static Bean2 createBean() { 6 return new Bean2(); 7 } 8 }
③beans2.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 7 <bean id="bean2ID" class="com.itheima.instance.static_factory.MyBean2Factory" 8 factory-method="createBean" /> 9 <!-- 由于使用的是静态工厂方法,所以需要通过class属性指定其对应的工厂实现类为MyBean2Factory 10 factory-method属性来告诉Spring容器,需要createBean这个工厂方法 11 --> 12 </beans>
④测试类:InstanceTest2.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.static_factory; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 // 静态工厂实例化Bean 7 public class InstanceTest2 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/instance/static_factory/beans2.xml"; 10 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 11 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("bean2ID")); 12 } 13 }
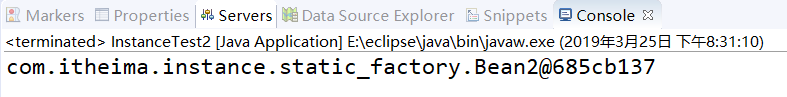
⑤运行结果:
3)、实例工厂:采用直接创建Bean实例的方式,在配置文件中,通过factory-bean属性配置一个实例工厂,然后使用factory-method属性确定使用工厂中的哪个方法。
src->com.itheima.instance.factory
①Bean3.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.factory; 2 3 public class Bean3 { 4 //无需添加任何方法 5 }
②MyBean3Factory.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.factory; 2 3 public class MyBean3Factory { // 创建工厂类MyBean3Factory 4 public MyBean3Factory() { // 默认使用无参构造方法输出语句 5 System.out.println("bean3工厂实例化中"); 6 } 7 // 创建Bean3实例的方法 8 public Bean3 createBean() { 9 return new Bean3(); 10 } 11 }
③beans3.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 <!-- 配置工厂 --> 7 <bean id="myBean3FactoryID" class="com.itheima.instance.factory.MyBean3Factory" /> 8 <!-- 使用factory-bean属性指向配置的实例工厂 (myBean3FactoryID),该属性值就是工厂Bean的id。 9 使用factory-method属性确定使用工厂中的哪个方法 (createBean) 10 --> 11 <bean id="bean3ID" factory-bean="myBean3FactoryID" factory-method="createBean" /> 12 </beans>
④测试类:InstanceTest3.java
1 package com.itheima.instance.factory; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class InstanceTest3 { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/instance/factory/beans3.xml"; 9 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 10 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("bean3ID")); 11 } 12 }
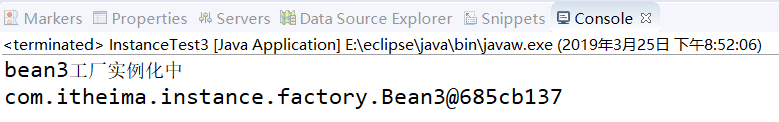
⑤运行结果:
3、Bean的作用域:
1)、作用域的种类
Spring 4.3中为Bean的实例定义了7种作用域,如下表所示:
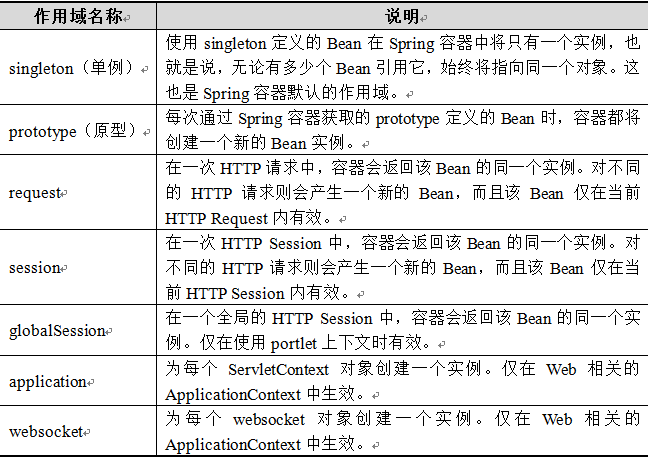
在上表7种作用域中,singleton和prototype是最常用的两种作用域。
2)、singleton作用域
a)、singleton是Spring容器默认的作用域,当Bean的作用域为singleton时,Spring容器就只会存在一个共享的Bean实例。singleton作用域对于无会话状态的Bean(如Dao 组件、Service组件)来说,是最理想的选择。
b)、在Spring配置文件中,可以使用<bean>元素的scope属性,将Bean的作用域定义成singleton。例如:
<bean id="scope" class="com.itheima.scope.Scope" scope="singleton"/>
c)、src->com.itheima.scope
①Scope.java
1 package com.itheima.scope; 2 3 public class Scope { 4 //无需写任何方法 5 }
②beans4.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 <bean id="scopeID" class="com.itheima.scope.Scope" scope="singleton"/> 7 </beans>
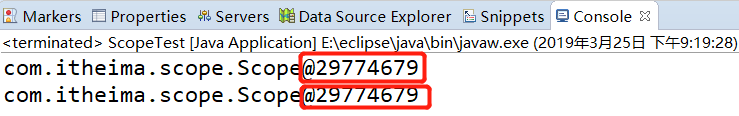
③测试类:ScopeTest.java
1 package com.itheima.scope; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class ScopeTest { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/scope/beans4.xml"; 9 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 10 // 输出获得实例 11 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scopeID")); 12 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("scopeID")); 13 // 两次输出结果相同,这说明Spring容器只创建了一个Scope类的实例 14 } 15 }
④运行结果:
3)、prototype作用域
a)、对需要保持会话状态的Bean(如Struts 2的Action类)应该使用prototype作用域。在使用prototype作用域时,Spring容器会为每个对该Bean的请求都创建一个新的实例。
b)、在Spring配置文件中,同样使用<bean>元素的scope属性,将Bean的作用域定义成prototype 。例如:
<bean id="scope" class="com.itheima.scope.Scope" scope=" prototype "/>
c)、src->com.itheima.scope
①beans4.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 <!--<bean id="scopeID" class="com.itheima.scope.Scope" scope="singleton"/> --> 7 <bean id="scopeID" class="com.itheima.scope.Scope" scope="prototype"/> 8 <!-- 在singleton作用域下,只创建一个Bean实例,而在prototype作用域下,每次创建不同的Bean实例 --> 9 </beans>
②运行结果:

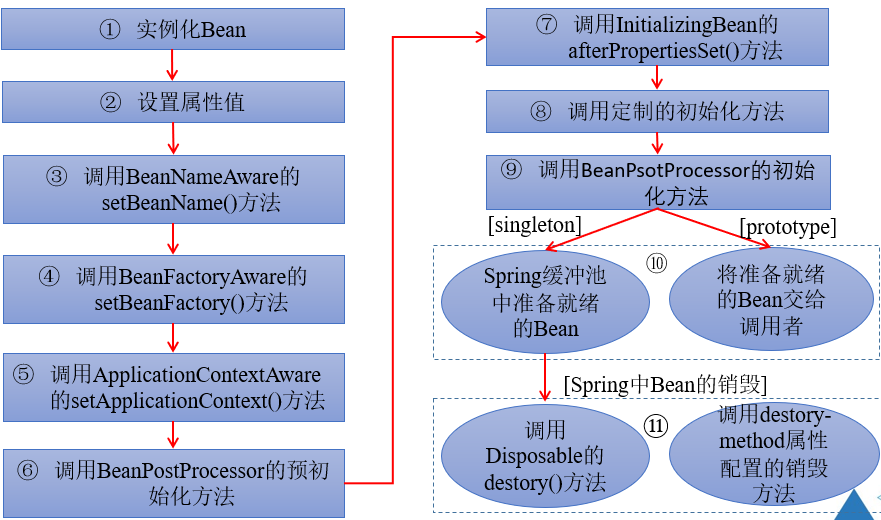
4、Bean的生命周期
1)、Spring容器可以管理Bean部分作用域的生命周期。

2)、Spring容器中Bean的生命周期流程如下图所示:
5、Bean的装配方式
Bean的装配可以理解为依赖关系注入,Bean的装配方式即Bean依赖注入的方式。Spring容器支持多种形式的Bean的装配方式,如基于XML的装配、基于注解(Annotation)的装配和自动装配(其中最常用的是基于注解的装配)。
1)、基于XML的装配
a)、2种方式:设值注入(Setter Injection)和构造注入(Constructor Injection)。
b)、设值注入要求一个bean必须满足2点要求:Bean类必须有一个默认的无参构造方法、Bean类必须为需要注入的属性提供对应的setter方法。
c)、使用设值注入时,在Spring配置文件中,需要使用<bean>元素的子元素<property>来为每个属性注入值;
d)、构造注入要求Bean类必须提供有参构造方法,配置文件中,需要使用<bean>元素的子元素<constructor-arg>来定义构造方法的参数,可以使用value属性(或子元素)来设置该参数的值。
src->com.itheima.assemble
①User.java
1 package com.itheima.assemble; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 import javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicInternalFrameTitlePane.SystemMenuBar; 5 6 public class User { 7 private String username; 8 private Integer password; 9 private List<String> list; 10 /* 11 * 1、使用构造注入 12 * 1.1、提供带所有参数的有参构造方法 13 */ 14 public User (String username, Integer passward, List<String> list) { // 有参构造方法 15 super(); // 调用父类的无参构造方法,可以不写 16 this.username = username; 17 this.password = passward; 18 this.list = list; 19 } 20 21 /* 22 * 2、使用设值注入 23 * 2.1、提供默认无参构造方法 24 * 2.2、为所有属性提供setter方法 25 */ 26 public User() { // 无参构造方法 27 super(); // 调用父类Object的无参构造方法,可以不写 28 } 29 public void setUsername(String username) { 30 this.username = username; 31 } 32 public void setPassword(Integer password) { 33 this.password = password; 34 } 35 public void setList(List<String> list) { 36 this.list = list; 37 } 38 39 @Override 40 public String toString() { // 重写父类的Object的toString方法 41 return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", list=" + list + "]"; 42 } 43 }
②beans5.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd"> 6 <!-- 1、使用构造注入方式装配User实例 --> 7 <bean id = "user1ID" class = "com.itheima.assemble.User"> 8 <!-- 9 <constructor-arg> 元素用于定义构造方法的参数, 10 其index表示其索引(从0开始),value属性用于设置注入的值, 11 其子元素<list>来为User类中对应的list集合属性注入值。 12 --> 13 <constructor-arg index = "0" value = "tom" /> 14 <constructor-arg index = "1" value = "123456" /> 15 <constructor-arg index = "2" > 16 <list> 17 <value>"constructorvalue1"</value> 18 <value>"constructorvalue2"</value> 19 </list> 20 </constructor-arg> 21 </bean> 22 23 <!-- 使用设值注入方式装配User实例 --> 24 <bean id = "user2ID" class = "com.itheima.assemble.User"> 25 <!-- 26 <property>元素用于调用Bean实例中的setter方法完成属性的赋值,从而完成依赖注入, 27 而其子元素<list>同样是为User类中对应的list集合属性注入值。 28 --> 29 <property name="username" value = "张三"></property> 30 <property name="password" value = "654321"></property> 31 <!-- 注入list集合 --> 32 <property name="list"> 33 <list> 34 <value>"setlistvalue1"</value> 35 <value>"setlistvalue2"</value> 36 </list> 37 </property> 38 </bean> 39 </beans>
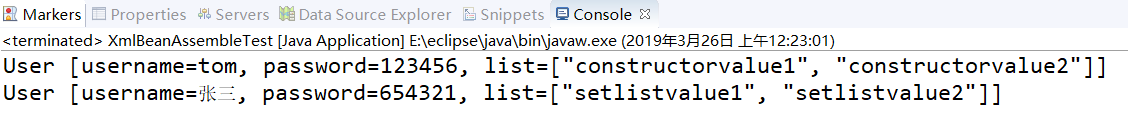
③测试类:XmlBeanAssembleTest.java
1 package com.itheima.assemble; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class XmlBeanAssembleTest { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/assemble/beans5.xml"; 9 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 10 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("user1ID")); 11 System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("user2ID")); 12 } 13 }
④运行结果:
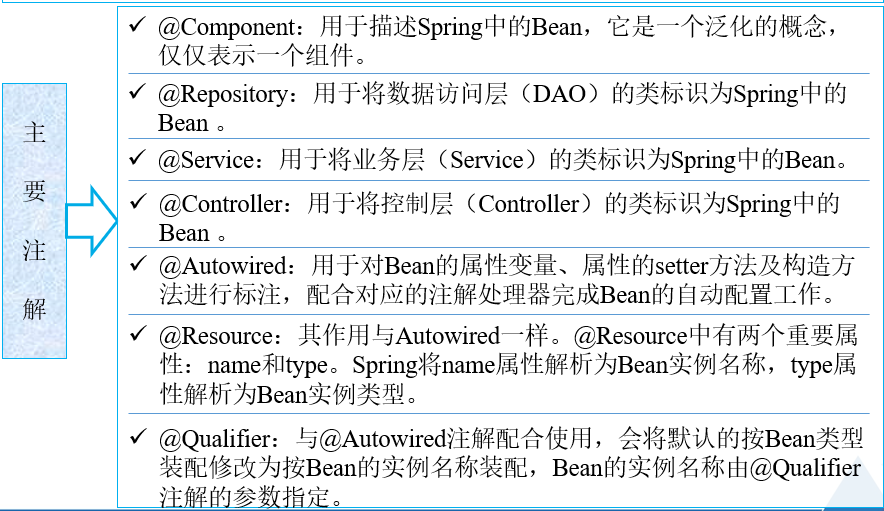
2)、基于Annotation的装配
a)、基于XML的装配可能会导致XML配置文件过于臃肿,给后续的维护和升级带来一定的困难。为此,Spring提供了对Annotation(注解)技术的全面支持。
b)、src->com.itheima.annotation
①UserDao.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 public interface UserDao { 4 public void save(); 5 }
②UserDaoImpl.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; 3 4 @Repository("userDaoID") 5 // @Repository注解将UserDaoImpl(数据访问层DAO层)的类标识为Spring中的Bean,其写法相当于配置文件中 6 // <bean id = "userDaoID" class = "com.itheima.annotation.UserDaoImpl" />的编写 7 public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ 8 public void save() { 9 System.out.println("userdaoID...save..."); 10 } 11 }
③UserService.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 public interface UserService { 4 public void save(); 5 }
④UserServiceImpl.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 import javax.annotation.Resource; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 5 6 @Service("userServiceID") 7 // @Service注解将(业务层的)UserServiceImpl类标识为Spring中的Bean,相当于配置文件中 8 // <bean id = "userServiceID" class = "com.itheima.annotation.UserServiceImpl" />的编写 9 10 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ 11 @Resource(name = "userDaoID") 12 /* 13 * @Resource注解标注在UserDao的Bean的实例上,相当于配置文件中 14 * <property name = "userDao" ref = "userDaoID" />的编写 15 * @Resource默认按照Bean实例名称进行装配,2个属性:name属性解析为Bean实例名称;type属性解析为Bean实例类型 16 * 如果都不指定,匹配过程为实例名称->实例类型,若都不匹配,则抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException异常 17 */ 18 private UserDao userDao; 19 20 public void save() { 21 // 调用成员对象userDao中的save方法 22 this.userDao.save(); 23 System.out.println("userServiceID...save..."); 24 } 25 }
⑤UserController.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 import javax.annotation.Resource; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 5 6 @Controller("userControllerID") 7 //@Controller注解标注了UserController类,这相当于配置文件中 8 //<bean id = "userControllerID" class = "com.itheima.annotation.UserController" />的编写 9 10 public class UserController { 11 @Resource(name = "userServiceID") 12 // @Resource注解标注在UserService的Bean的实例上,相当于配置文件中 13 // <property name = "userService" ref = "userServiceID" />的编写 14 private UserService userService; 15 16 public void save() { 17 this.userService.save(); 18 System.out.println("userControllerID...save..."); 19 } 20 }
⑥beans6.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> 9 <!-- 以上补充context的约束信息,使用 context 命名空间 , 10 通过配置<context:annotation-config />来开启注解处理器 --> 11 <!--分别定义3个Bean实例,这里不再需要配置子元素<property>完成setter方法依赖注入 --> 12 13 <context:annotation-config /> 14 <bean id="userDaoID" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserDaoImpl" /> 15 <bean id="userServiceID" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserServiceImpl" /> 16 <bean id="userControllerID" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserController" /> 17 </beans>
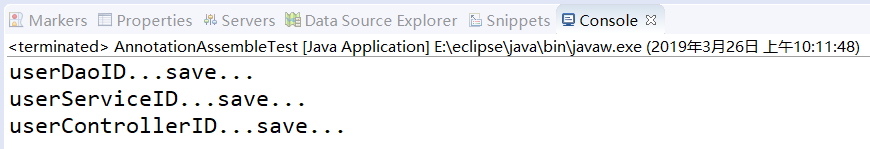
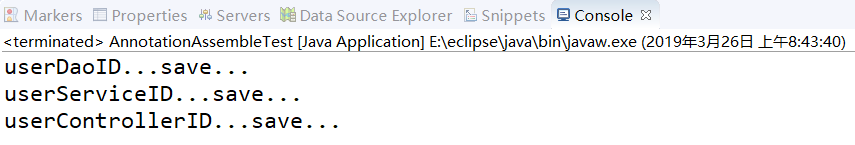
⑦AnnotationAssembleTest.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 //基于Annotation(注解)的装配 7 public class AnnotationAssembleTest { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 String xmlPath = "com/itheima/annotation/beans6.xml"; 10 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 11 // 获取UserController的Bean实例userControllerID 12 UserController userController = (UserController) applicationContext.getBean("userControllerID"); 13 userController.save(); 14 } 15 }
⑧运行结果:
c)、除了可以像示例中通过<bean>元素来配置Bean外,还可以通过包扫描的形式来配置一个包下的所有Bean:
<context:component-scan base-package="Bean所在的包路径" />
d)、将beans6.xml文件中的13~16行代码替换成下面这个,运行效果一样。
<!-- Spring注解提供了另外一种高效的注解配置方式,(对包路径下的所有Bean文件进行扫描) --> <!--使用 context 命名空间 ,通知Spring扫描指定包下所有Bean类,进行注解解析 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima.annotation" />
3)、自动装配
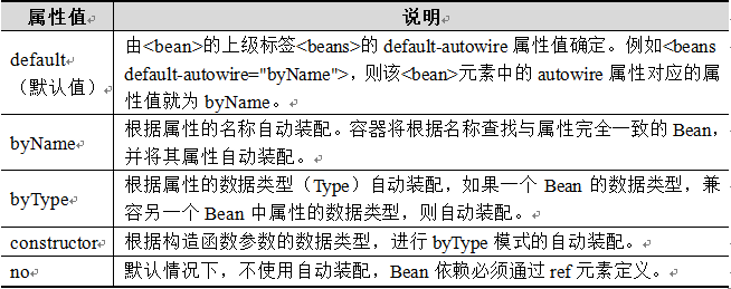
a)、所谓自动装配就是将一个Bean自动的注入到到其他Bean的Property中(也就是类成员变量赋值)。 Spring的<bean>元素中包含一个autowire属性,我们可以通过设置autowire的属性值来自动装配Bean。
b)、autowire属性有5个值,其值及说明下表所示:
c)、修改UserServiceImple.java和UserController.java,分别增加类属性的setter方法;修改Spring配置文件,使用autowire属性配置Bean;其他文件不用修改。
①UserServiceImple.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 import javax.annotation.Resource; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 5 6 @Service("userServiceID") 7 // @Service注解将(业务层的)UserServiceImpl类标识为Spring中的Bean,相当于配置文件中 8 // <bean id = "userServiceID" class = "com.itheima.annotation.UserServiceImpl" />的编写 9 10 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ 11 @Resource(name = "userDaoID") 12 /* 13 * @Resource注解标注在UserDao的Bean的实例上,相当于配置文件中 14 * <property name = "userDao" ref = "userDaoID" />的编写 15 * @Resource默认按照Bean实例名称进行装配,2个属性:name属性解析为Bean实例名称;type属性解析为Bean实例类型 16 * 如果都不指定,匹配过程为实例名称->实例类型,若都不匹配,则抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException异常 17 */ 18 private UserDao userDao; 19 20 // 添加类属性UserDao的setter方法 21 public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { 22 this.userDao = userDao; 23 } 24 25 public void save() { 26 // 调用成员对象userDao中的save方法 27 this.userDao.save(); 28 System.out.println("userServiceID...save..."); 29 } 30 }
②UserController.java
1 package com.itheima.annotation; 2 3 import javax.annotation.Resource; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; 5 6 @Controller("userControllerID") 7 //@Controller注解标注了UserController类,这相当于配置文件中 8 //<bean id = "userControllerID" class = "com.itheima.annotation.UserController" />的编写 9 10 public class UserController { 11 @Resource(name = "userServiceID") 12 // @Resource注解标注在UserService的Bean的实例上,相当于配置文件中 13 // <property name = "userService" ref = "userServiceID" />的编写 14 private UserService userService; 15 16 // 添加类属性UserService的setter方法 17 public void setUserService(UserService userService) { 18 this.userService = userService; 19 } 20 21 public void save() { 22 this.userService.save(); 23 System.out.println("userControllerID...save..."); 24 } 25 }
③beans6.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd"> 9 10 <!-- 使用bean元素的autowire属性完成自动装配,所谓自动装配,就是将一个Bean自动地注入到其他Bean的Property中 --> 11 12 <!-- 注意:这里的id(除了最后一个)名称应对应setter方法中的参数(实例化对象),即设置了autowire之后, 13 Spring会自动寻找userService Bean中的属性,并将属性名称与配置文件中定义的Bean做匹配, 14 否则会报java.lang.NullPointerException异常。 15 --> 16 <bean id="userDao" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserDaoImpl" /> 17 <bean id="userService" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserServiceImpl" autowire="byName" /> 18 <bean id="userControllerID" class="com.itheima.annotation.UserController" autowire="byName"/> 19 20 </beans>
④运行结果: