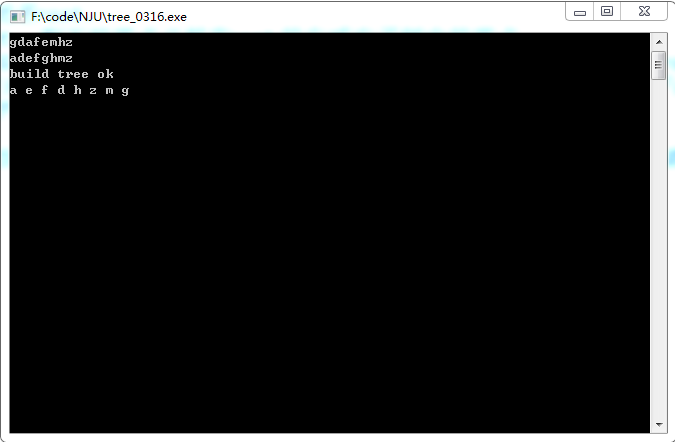
/* 现在有一个问题,已知二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历: PreOrder:GDAFEMHZ InOrder:ADEFGHMZ 我们如何还原这颗二叉树,并求出他的后序遍历 我们基于一个事实:中序遍历一定是 { 左子树中的节点集合 },root,{ 右子树中的节点集合 },前序遍历的作用就是找到每颗子树的root位置。 算法1 输入:前序遍历,中序遍历 1、寻找树的root,前序遍历的第一节点G就是root。 2、观察前序遍历GDAFEMHZ,知道了G是root,剩下的节点必然在root的左或右子树中的节点。 3、观察中序遍历ADEFGHMZ。其中root节点G左侧的ADEF必然是root的左子树中的节点,G右侧的HMZ必然是root的右子树中的节点,root不在中序遍历的末尾或开始就说明根节点的两颗子树都不为空。 4、观察左子树ADEF,按照前序遍历的顺序来排序为DAFE,因此左子树的根节点为D,并且A是左子树的左子树中的节点,EF是左子树的右子树中的节点。 5、同样的道理,观察右子树节点HMZ,前序为MHZ,因此右子树的根节点为M,左子节点H,右子节点Z。 观察发现,上面的过程是递归的。先找到当前树的根节点,然后划分为左子树,右子树,然后进入左子树重复上面的过程,然后进入右子树重复上面的过程。最后就可以还原一棵树了: PreOrder:GDAFEMHZ InOrder:ADEFGHMZ 从而得到PostOrder: AEFDHZMG */ #include<iostream> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int M=1024; char pr[M]; char in[M]; struct node { char data; node *l; node *r; }; /* void build(node * & t,int prl,int prr,int inl,int inr) { char m=pr[prl]; //printf("%c ",m); if(prl>prr||inl>inr) { t=NULL; return ; } int i1=0;// -> middle num in the pr int i2=0;// -> middle num in the in while(in[i2]!=m) i2++; i1=i2; t=new node(); t->data=m; if(prl==prr||inl==inr) { t->l=NULL; t->r=NULL; return ; } else { build(t->l,prl+1,i1,inl,i2-1);//go build left part build(t->r,i1+1,prr,i2+1,inr);//go build right part } } */ void create(node * &t, int preL, int preR, int inL,int inR) { if ( preL > preR ) { t=NULL; return ; } t = new node(); t->data = pr[preL]; int index; for ( index = inL; index <= inR; index++ ) { if ( in[index] == pr[preL] )break; } int numLeft = index - inL; create(t->l, preL+1, preL+numLeft, inL, index-1); create(t->r, preL+numLeft+1, preR, index+1, inR); } void post_display(const node *t) { if(t==NULL) return ; post_display(t->l); post_display(t->r); printf("%c ",t->data); } int main() { memset(pr,'�',sizeof(pr)); memset(in,'�',sizeof(in)); while(cin>>pr&&cin>>in) { node *tree=NULL; if(strlen(pr)==strlen(in)) { create(tree,0,strlen(pr)-1,0,strlen(pr)-1); cout<<"build tree ok"<<endl; } //cout<<tree<<endl<<tree->l<<endl<<tree->r<<endl; post_display(tree); cout<<endl; memset(pr,'�',sizeof(pr)); memset(in,'�',sizeof(in)); } return 0; } /* #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; const int maxn = 35; char in[maxn]; char pre[maxn]; struct node { char data; node *lchild; node *rchild; }; node *Create(int preL, int preR, int inL,int inR) { if ( preL > preR ) return NULL; node *root = new node(); root->data = pre[preL]; int index; for ( index = inL; index <= inR; index++ ) { if ( in[index] == pre[preL] )break; } int numLeft = index - inL; root->lchild = Create(preL+1, preL+numLeft, inL, index-1); root->rchild = Create(preL+numLeft+1, preR, index+1, inR); return root; } void PostOrderTraversal(node *root) { if ( root != NULL ) { PostOrderTraversal(root->lchild); PostOrderTraversal(root->rchild); cout << root->data << " "; } } int main() { int n; cin >> n; for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) cin >> pre[i]; for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++ ) cin >> in[i]; node *root=NULL; root = Create(0,n-1,0,n-1); PostOrderTraversal(root); return 0; } */
tz@HZAU
2019/3/16