写在前面:本博客为本人原创,严禁任何形式的转载!本博客只允许放在博客园(.cnblogs.com),如果您在其他网站看到这篇博文,请通过下面这个唯一的合法链接转到原文!
本博客全网唯一合法URL:http://www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/9107838.html
基于C++语言实现的PL/0语言的算术表达式的自下而上的语法分析程序。该语言的其他语法实现思想与此一致,故不赘述。
运行此程序前,必须先将代码通过:【编译原理】c++实现词法分析器的词法分析,生成词法表(词法表是txt文件,为了语法分析成功,务必删除文件中最后空着的一行,即文件末尾不可以留空白行)。生成的该词法表为此程序的必要输入。
产生式:
S->X(AX)*|AX(AX)*
X->Y(MY)*
Y->I|N|(S)
A->+|-
M->*|/
C->=|#|<|<=|>|>=
进行自下而上的语法分析一定比自上而下要难。我们知道,做自下而上的语法的分析的核心在于“寻找可归约串”(即术语所说的“句柄”),而且要有一定的“向前展望性”,以防止在可以归约但却不应该归约的地方进行归约动作而不是继续移进下一个终结符或者非终结符。所以编译原理的语法分析做LR分析的核心目标就是能精确地控制计算机程序对待分析、编译的程序代码语句进行正确的、无二义的、符合编程者原目的的语法分析(在自下而上的语法分析中就是“归约”)。
那么知道了为什么要构造规范项目集族、构造确定的DFA、构造LR分析表后,对于上述产生式所代表的比较简单的算术表达式语句分析,我在本篇博客中就不使用传统的“构造规范项目集族、构造确定的DFA、构造LR分析表”这样一个套路来做自下而上语法分析了。
在本篇博客中,我使用比较简单易理解的模式匹配算法,结合面向对象程序设计思想中的“策略”设计模式来完成编程。
/* this code was first initiated by TZ,COI,HZAU contact email:xmb028@163.com personal website:wnm1503303791.github.io personal blogs:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/ this code has been posted on my personal blog,checking url:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/9107838.html Copyright 2018/5/29 TZ. All Rights Reserved. */ #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<bitset> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<set> #include<list> #include<deque> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<fstream> using namespace std; //预处理函数 bool preproccess(char *a,char *b) { int i1=0,i2=1; memset(b,1024,'�'); while(a[i2]!=',') { b[i1]=a[i2]; ++i1,++i2; } b[i1]='�'; //cout<<b<<endl; return true; } fstream f2("stack.txt", ios::out);//打开文件,供写 static int mcount=1;//存储打印次数 //当移进或者归约时打印栈内情况,以供分析 bool outf(int head,char data[1024][1024],fstream &f) { f<<"times("<<mcount<<"),"; f<<"head is:"<<head<<endl; for(int i=head;i>=0;i--) { f<<data[i]<<endl; } mcount++; f<<endl; } //“策略”设计模式,面向对象方法 class presentation { private: char data[1024][1024];//栈 fstream *infile;//词法分析表 int head;//栈顶指针 public: //first initiated the object presentation(fstream *in_f) { this->infile=in_f; memset(data,sizeof(data),'�'); head=-1; } bool push() { head++; infile->getline(data[head],1024); char t[1024];//存放字符标志 preproccess(data[head],t); cout<<data[head]<<","<<t<<endl; memset(data[head],1024,'�'); strcpy(data[head],t); } /* S->X(AX)*|AX(AX)* X->Y(MY)* Y->I|N|(S) A->+|- M->*|/ C->=|#|<|<=|>|>= */ //归约函数 bool reduce() { //S->X(AX)*|AX(AX)* if( head>=4&& (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-3],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-3],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-4],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-3],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-4],1024,'�'); head=head-5+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); return true; } if( head>=2&& (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); return true; } if( head>=2&& (!strcmp(data[head],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-2],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-3],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-3],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); return true; } if( head>=1&& (!strcmp(data[head],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); head=head-2+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); return true; } //X->Y(MY)* if( head>=4&& (!strcmp(data[head],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-3],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-3],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-4],"Y")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); head=head-5+1; strcpy(data[head],"X"); return true; } if( head>=2&& (!strcmp(data[head],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"Y")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"X"); return true; } if( head>=0&&(!strcmp(data[head],"Y")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); head=head-1+1; strcpy(data[head],"X"); return true; } //Y->I|N|(S) if( head>=0&&(!strcmp(data[head],"ident")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); head=head-1+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); return true; } if( head>=0&&(!strcmp(data[head],"number")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); head=head-1+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); return true; } if( head>=2&& (!strcmp(data[head],"rparen"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"S"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"lparen")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); return true; } return false; } //遍历栈 bool visit_data() { cout<<"current stack:"<<endl; for(int i=head;i>=0;i--) { cout<<data[i]<<endl; } } //主控函数 bool mainf() { while(!infile->eof()) { push(); bool t=reduce(); outf(head,data,f2); //每当移进结束时就检查一下是否有可规约串 while(t)//防止规约嵌套 { t=reduce(); outf(head,data,f2); } //visit_data(); } visit_data(); bool flag=false; for(int i=head;i>=0;i--) { if(!strcmp(data[i],"S")) { flag=true; } if( strcmp(data[i],"S")&& strcmp(data[i],"X")&& strcmp(data[i],"A")&& strcmp(data[i],"Y")&& strcmp(data[i],"M")&& strcmp(data[i],"C") ) { return false; } } return flag; /* while(head>0) { bool t=reduce(); //每当移进结束时就检查一下是否有可规约串 while(t)//防止规约嵌套 { t=reduce(); } //visit_data(); outf(head,data,f2); } */ } }; int main() { fstream f1; f1.open("lexical.txt", ios::in);//打开词法分析表,供读 presentation* s1=new presentation(&f1); bool result=s1->mainf(); if(result) cout<<"ACCEPTED!"<<endl; else cout<<"ERROR!"<<endl; f1.close(); f2.close(); return 0; }
当然了,对于不喜欢看面向对象设计模式的同学,我还写了另外一个面向过程的代码,这个更易理解。而且我在程序中已经将一张特定的词法分析表给出。
/*
this code was first initiated by TZ,COI,HZAU
contact email:xmb028@163.com
personal website:wnm1503303791.github.io
personal blogs:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/
this code has been posted on my personal blog,checking url:www.cnblogs.com/acm-icpcer/p/9107838.html
Copyright 2018/5/29 TZ.
All Rights Reserved.
*/
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<bitset> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<set> #include<list> #include<deque> #include<map> #include<queue> #include<fstream> using namespace std; char mdata[1024][1024]={ "ident", "times", "rparen", "number", "plus", "ident", "lparen" /* "lparen", "ident", "plus", "number", "rparen", "times", "ident" */ }; char data[1024][1024]; int head=0; bool reduce() { //S->X(AX)*|AX(AX)* if( (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-4],"X")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-3],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-4],1024,'�'); head=head-5+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); head=head-2+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus"))&& (!strcmp(data[head],"X"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"plus")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"minus")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-3],1024,'�'); head=head-4+1; strcpy(data[head],"S"); head++; return true; } //X->Y(MY)* if( (!strcmp(data[head],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head],"Y")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"X"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"Y"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"times")||!strcmp(data[head-1],"slash"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-4],"Y")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); head=head-5+1; strcpy(data[head],"X"); head++; return true; } //Y->I|N|(S) if( (!strcmp(data[head],"ident")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); head=head-1+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"number")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); head=head-1+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); head++; return true; } if( (!strcmp(data[head],"rparen"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-1],"S"))&& (!strcmp(data[head-2],"lparen")) ) { memset(data[head],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-1],1024,'�'); memset(data[head-2],1024,'�'); head=head-3+1; strcpy(data[head],"Y"); head++; return true; } return false; } bool visit_data() { cout<<"current stack:"<<endl; for(int i=head;i>=0;i--) { cout<<data[i]<<endl; } } int main() { int i=0; while(i<=6) { strcpy(data[head],mdata[i]); head++; bool t=reduce(); //每当移进结束时就检查一下是否有可规约串 while(t)//防止规约嵌套 { t=reduce(); } visit_data(); i++; } visit_data(); /* int i=0; while(i<=6) { strcpy(data[head],mdata[i]); head++; i++; } visit_data(); */ }
运行示例:
(1)合法的语句:
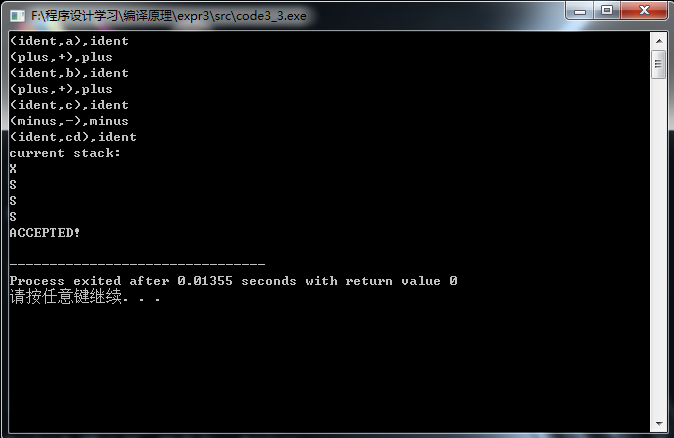
(2)不合法的语句:
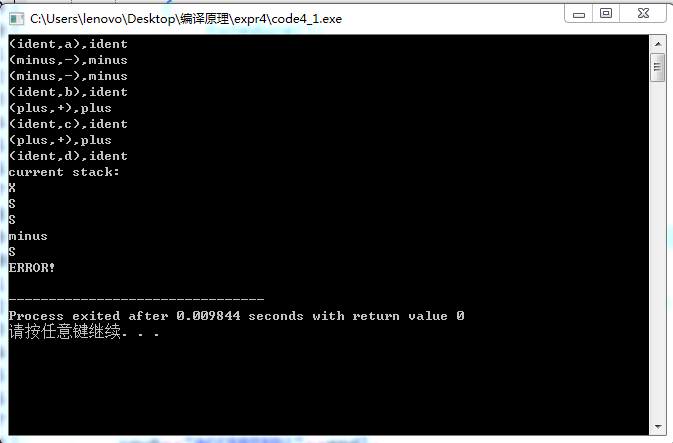
tz@dormitory HZAU
2018/5/30
last updated@COI HZAU
2018/6/12