延迟执行
IQueryable query = from c in North.Customers select c;
这样的查询句法不会导致语句立即执行,它仅仅是一个描述,对应一个SQL。仅仅在需要使用的时候才会执行语句.比如:
IQueryable query = from c in North.Customers select c; foreach (Customers c in query) Response.Write(c.CustomerID);
如果你执行两次foreach操作,将会捕获到两次SQL语句的执行:
NorthWindDataContext North = new NorthWindDataContext(); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("Log.txt"), true); North.Log = sw; IQueryable query = from c in North.Customers select c; foreach (Customers c in query) Response.Write(c.CustomerID); foreach (Customers c in query) Response.Write(c.ContactName); sw.Close();
对应SQL:

对于这样的需求,建议你先使用ToList()等方法把查询结果先进行保存,然后再对集合进行查询:
IEnumerable<Customers> customers = (from c in North.Customers select c).ToList(); foreach (Customers c in customers) Response.Write(c.CustomerID); foreach (Customers c in customers) Response.Write(c.ContactName);
那么这样只会捕获到一次SQL语句的执行:
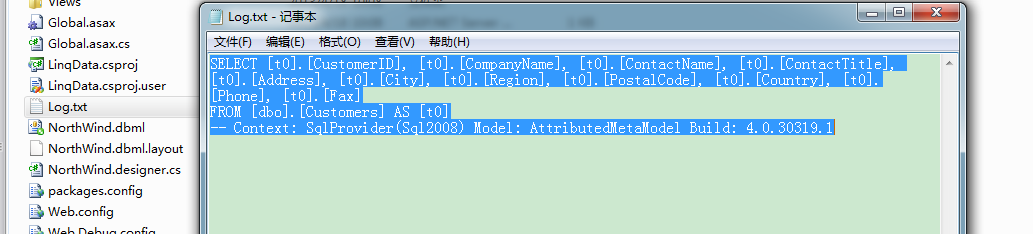
延迟执行的优点在于我们可以像拼接SQL那样拼接查询句法,然后再执行:
var query = from c in North.Customers select c; var newquery = (from c in query select c).OrderBy(c => c.CustomerID);
DataLoadOptions
NorthWindDataContext North = new NorthWindDataContext(); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("Log.txt"), true); North.Log = sw; var products = from p in North.Products select p; foreach (var p in products) { if (p.UnitPrice > 10) ShowDetail(p.Order_Details); } sw.Close();
private void ShowDetail(EntitySet<Order_Details> orderdetails) { foreach (var o in orderdetails) { Response.Write(o.Quantity + "<br>"); } }
你会发现Linq to sql对每个价格大于10的产品都根据产品号进行了一次查询:
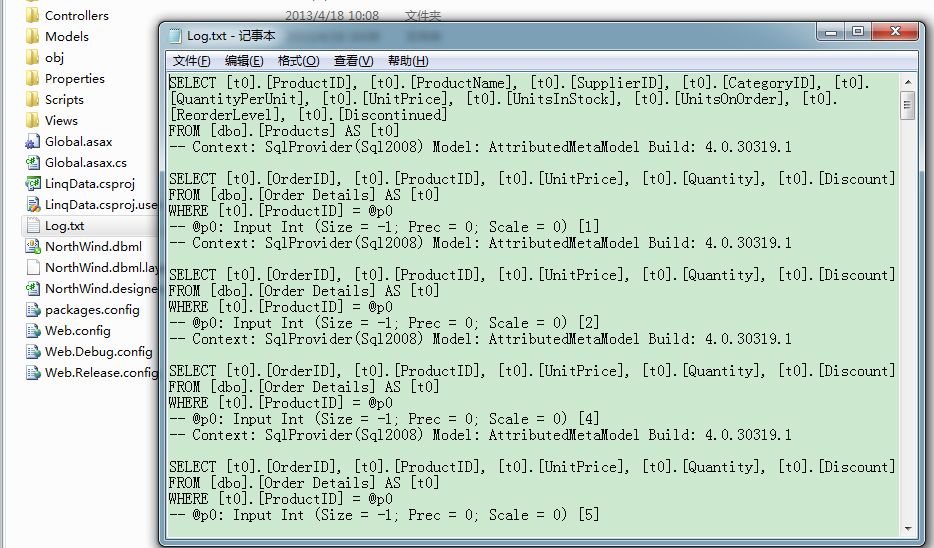
这样的语句查询了N次。这样的查询不是很合理,我们可以通过设置DataContext的DataLoadOption,来指示 DataContext再加载产品信息的同时把对应的产品订单信息一起加载:
NorthWindDataContext ctx = new NorthWindDataContext(); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("Log.txt"), true); ctx.Log = sw; DataLoadOptions options = new DataLoadOptions(); options.LoadWith<Products>(p => p.Order_Details); ctx.LoadOptions = options; var products = from p in ctx.Products select p; foreach (var p in products) { if (p.UnitPrice > 10) ShowDetail(p.Order_Details); } sw.Close();
执行上面的查询会发现Linq to sql进行了左连接:
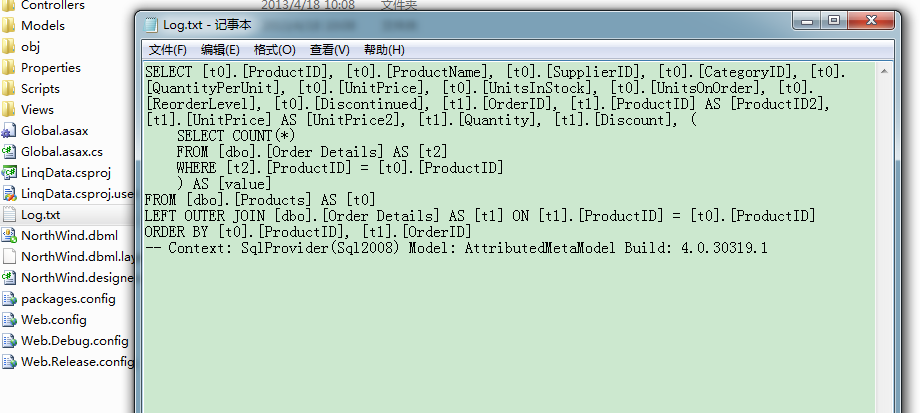
那么,我们怎么限制订单详细表的加载条件那?
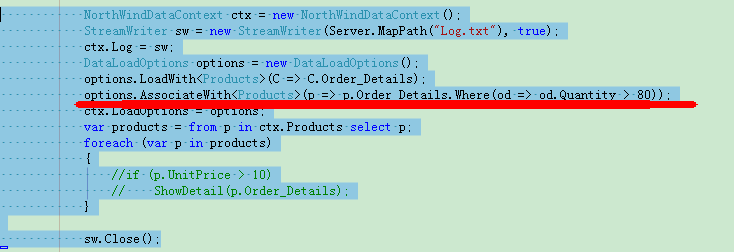
加上这句
options.AssociateWith<Products>(p => p.Order_Details.Where(od => od.Quantity > 80));
这样,就只会有数量大于80的订单详细信息会和产品一起加载。
DataLoadOptions限制
Linq to sql对DataLoadOptions的使用是有限制的,它只支持1个1对多的关系。一个顾客可能有多个订单,一个订单可能有多个详细订单:
这样的语句执行后会导致查询详细订单的SQL执行N次。而对于多对1的关系,Linq to sql对于DataLoadOptions没有限制。
主键缓存
Linq to sql对查询过的对象进行缓存,之后的如果只根据主键查询一条记录的话会直接从缓存中读取。比如下面的代码:
NorthWindDataContext ctx = new NorthWindDataContext(); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("Log.txt"), true); ctx.Log = sw; Customers c1 = ctx.Customers.Single(customer => customer.CustomerID == "ANATR"); c1.ContactName = "zhuye"; Customers c2 = ctx.Customers.Single(customer => customer.CustomerID == "ANATR"); Response.Write(c2.ContactName); sw.Close();
执行后只会产生一条SQL:

由于没有提交修改,所以数据库中的记录还是没有更新。由于这个特性,我们在使用存储过程作为实体更新方法的时候就要当心了,存储过程书写错误,即使你提交了修改也很可能导致缓存中的数据和数据库中的数据不一致,引起不必要的麻烦。
DataContext隔离
有的时候我们会把对象从外部传入DataContext,要求它更新,由于不同的DataContext是相对独立的。由于新的DataContext中还没有获取实体,我们只能通过附加方式更新数据。
首先把Customer表的主键字段加上IsVersion标识:

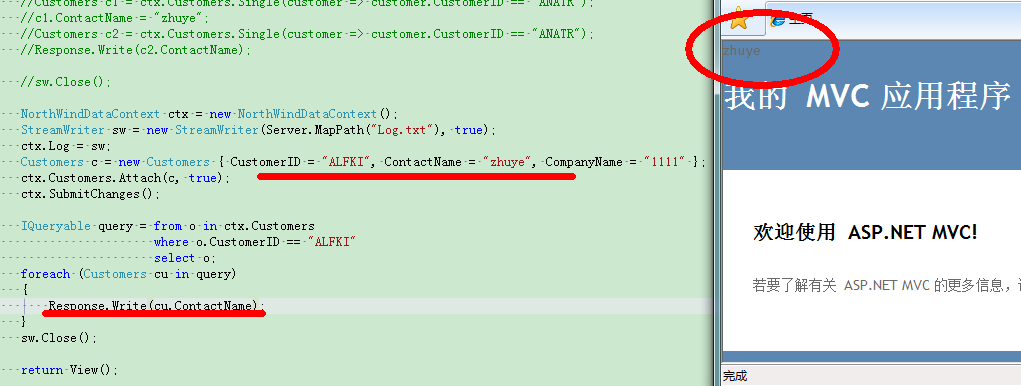
NorthWindDataContext ctx = new NorthWindDataContext(); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("Log.txt"), true); ctx.Log = sw; Customers c = new Customers { CustomerID = "ALFKI", ContactName = "zhuye", CompanyName = "1111" }; ctx.Customers.Attach(c, true); ctx.SubmitChanges(); IQueryable query = from o in ctx.Customers where o.CustomerID == "ALFKI" select o; foreach (Customers cu in query) { Response.Write(cu.ContactName); } sw.Close();
运行如上测试代码,查看结果如下
示例代码下载地址 https://files.cnblogs.com/aehyok/LinqData.zip