一、jdbc中使用行级锁的步骤
1.1必须将自动提交方式改为手动提交
1.2查询语句后面使用for update(引起事务、启动行级锁) 比如: select * from user where userid in(10001,10002) for update;的意思是启动行级锁,锁住userid为10001和10002的这两条数据。
1.3启动行级锁的目的是只有当前事务才能修改锁住的数据。
1.4结束事务(提交|回滚)的时候释放行级锁。
二、jdbc中使用行级锁的示例
package edu.aeon.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; import edu.aeon.aeonutils.AeonJdbcUtils; /** * [说明]:修改jdbc中事务的提交方式 * @author aeon */ public class TestJDBC { /** * @throws SQLException */ public static void jdbc_insert() throws SQLException{ Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; try { connection = AeonJdbcUtils.getMySqlConnection(); //设置事务的提交方式为手动提交 connection.setAutoCommit(false); String sql="select userid,username,userpw from user where userid in(?,?) for update"; //将sql语句进行预编译然后保存到preparedStatement对象中 preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10001); preparedStatement.setInt(2, 10002); preparedStatement.executeQuery(); sql="update user set username='hjs' where userid in(?,?)"; preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); preparedStatement.setInt(1, 10001); preparedStatement.setInt(2, 10002); int rowCount=preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); connection.commit(); System.out.println("成功修改了"+rowCount+"条数据!"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { connection.rollback(); System.out.println("本次操作失败!"); e.printStackTrace(); }finally { AeonJdbcUtils.closeDB(null, preparedStatement, connection); } } public static void main(String[] args) { try { jdbc_insert(); } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("本次操作失败!"); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果截图:
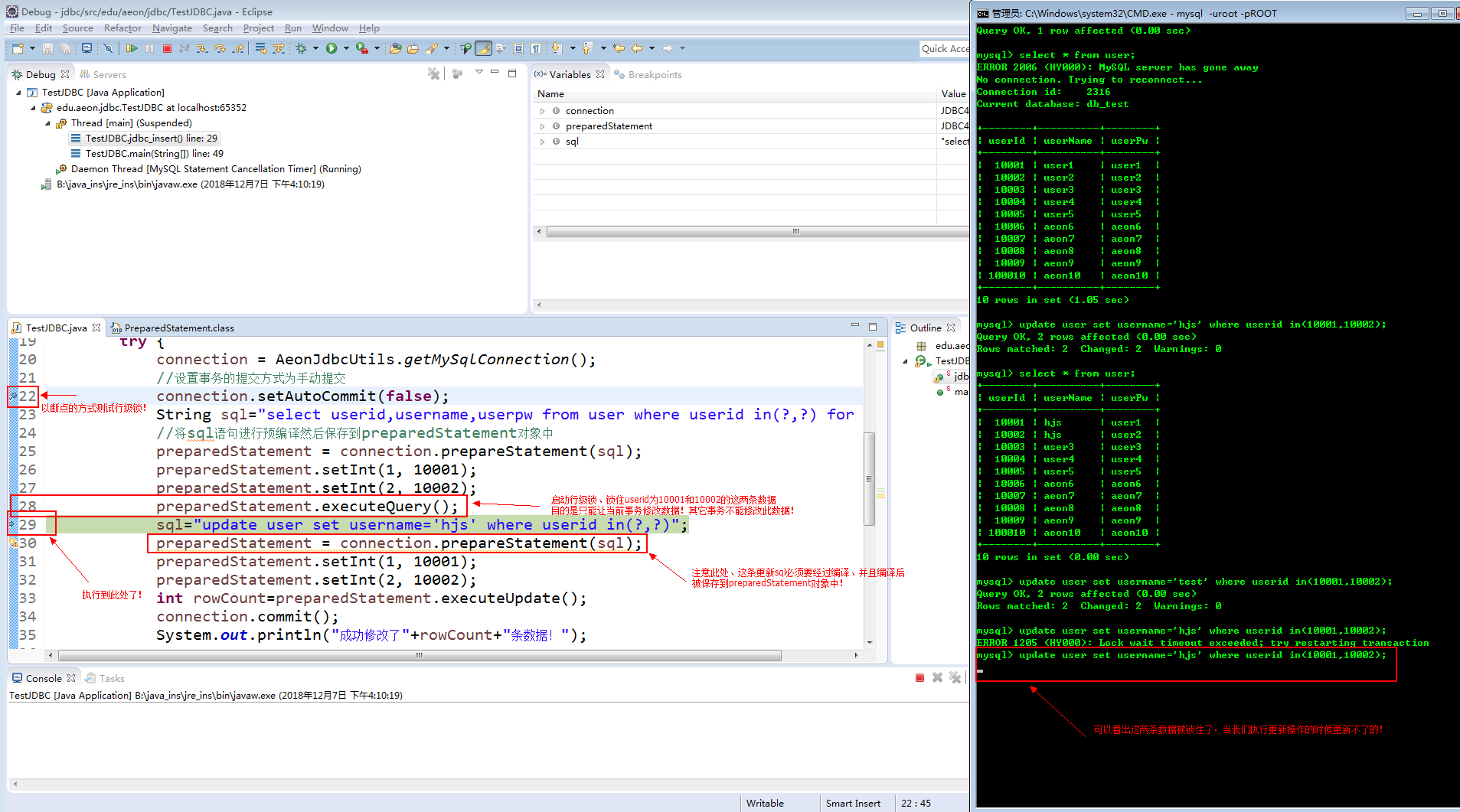
启动行级锁的目的是只能让当前事务修改数据、其它事务不能对锁住的数据做修改操作!
