实现网络中的主机互相通信
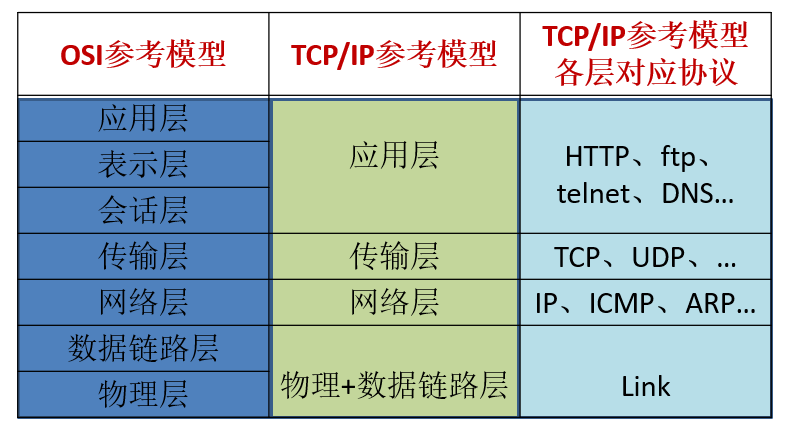
OSI参考模型:模型过于理想化,未能在因特网上进行广泛推广
TCP/IP参考模型(或TCP/IP协议):事实上的国际标准
IP 地址:InetAddress
① 唯一的标识 Internet 上的计算机
②本地回环地址(hostAddress):127.0.0.1 主机名(hostName):localhost
端口号标识正在计算机上运行的进程(程序)
①不同的进程有不同的端口号
②被规定为一个 16 位的整数 0~65535。
其中,0~1023被预先定义的服务通信占用(如MySql占用端口3306,http占用端口80等)。
除非我们需要访问这些特定服务,否则,就应该使用 1024~65535 这些端口中的某一个进行通信,
以免发生端口冲突。
端口号与IP地址的组合得出一个网络套接字。
TestInetAddress
package com.aff.internet; import java.net.InetAddress; /* * 网络通信第一个要素:通过IP地址,唯一的定位互联网上的一台主机 InetAddress:位于java.net包下 1.InetAddress代表IP地址,一个InetAddress的对象就代表一个IP地址 2.如何创建InetAddress的对象:getByName(String host) 3.getHostAddress: 获取IP地址对应的域名 getHostName:获取IP地址 */ public class TestInetAddress { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建一个InetAddress对象:getByName InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com"); inet = InetAddress.getByName("14.215.177.38"); System.out.println(inet); // System.out.println(inet.getHostAddress()); System.out.println(inet.getHostName()); // 获取本地的主机 getLocalHost InetAddress inet1 = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); System.out.println(inet1);// LZ/192.168.3.10 System.out.println(inet1.getHostAddress());// 192.168.3.10 } }
网络通信协议
TCP协议:
① 使用TCP协议前,须先建立TCP连接,形成传输数据通道
②传输前,采用“三次握手”方式,是可靠的
③ TCP协议进行通信的两个应用进程:客户端、服务端
④在连接中可进行大数据量的传输
⑤传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低
UDP协议:
①将数据、源、目的封装成数据包,不需要建立连接
②每个数据报的大小限制在64K内
③因无需连接,故是不可靠的
④发送数据结束时无需释放资源,速度快
Socket
① 利用套接字(Socket)开发网络应用程序早已被广泛的采用,以至于成为事实上的标准。
②通信的两端都要有Socket,是两台机器间通信的端点
③网络通信其实就是Socket间的通信。
④Socket允许程序把网络连接当成一个流,数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输。
⑤一般主动发起通信的应用程序属客户端,等待通信请求的
为服务端
TCP编程三例
TestTCP1
package com.aff.internet; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import org.junit.Test; //TCP编程1 //客户端给服务端发送信息,服务端输出信息到控制台上 //网络编程实际上就是Socket编程 //得先开服务端, 由于服务端等待客户端发送信息 public class TestTCP1 { // 客户端 @Test public void client() { Socket socket = null; OutputStream os = null; try { // 1.创建一个socket的对象,通过构造器指明服务端的ip地址,以及接收程序的端口号 socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.10"), 9090); // 2.getOutputStream:发送数据,方法返回getOutputStream的对象 os = socket.getOutputStream(); // 3.具体输出过程 os.write("我是客户端".getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭相应的流和socket if (os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (socket != null) { try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 服务端 @Test public void server() { ServerSocket ss = null; Socket s = null; InputStream is = null; try { // 1.创建一个ServerSocket的对象,通过构造器指明自身的端口号 ss = new ServerSocket(9090); // 2.调用其accept()方法,返回一个Socket对象 s = ss.accept(); // 3.调用Socket对象的getInputStream()获取一个从客户端发送过来的输入流 is = s.getInputStream(); // 4.对获取的流进行操作 byte[] b = new byte[20]; int len; while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) { String str = new String(b, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } System.out.println("收到来自于" + s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的信息"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { // 关闭相应的流以及Socket, ServerSocket对象 if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 从后往前关闭,先关闭流 } if (s != null) { try { s.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ss != null) { try { ss.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
TestTCP2
package com.aff.internet; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import org.junit.Test; //TCP编程2:客户端给服务端发送信息,服务端将信息到控制台上,同时发送"已收到信息"给客户端 public class TestTCP2 { // 客户端 @Test public void client() { Socket socket = null; OutputStream os = null; InputStream is = null; try { // 1.创建一个socket的对象,通过构造器指明服务端的ip地址,以及接收程序的端口号 socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("192.168.3.10"), 9090); // 2.getOutputStream:发送数据,方法返回getOutputStream的对象 os = socket.getOutputStream(); // 3.具体输出过程 os.write("我是客户端".getBytes()); // socket.shutdownOutput(); is = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] b = new byte[20]; int len; while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) { String str = new String(b, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 关闭相应的流和socket if (os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (socket != null) { try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } // 服务端 @Test public void server() { ServerSocket ss = null; Socket s = null; InputStream is = null; OutputStream os = null; try { // 1.创建一个ServerSocket的对象,通过构造器指明自身的端口号 ss = new ServerSocket(9090); // 2.调用其accept()方法,返回一个Socket对象 s = ss.accept(); // 3.调用Socket对象的getInputStream()获取一个从客户端发送过来的输入流 is = s.getInputStream(); // 4.对获取的流进行操作 byte[] b = new byte[20]; int len; while ((len = is.read(b)) != -1) { String str = new String(b, 0, len); System.out.println(str); } os = s.getOutputStream(); os.write("我已收到信息".getBytes()); System.out.println("收到来自于" + s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的信息"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (os != null) { try { os.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // 关闭相应的流以及Socket, ServerSocket对象 if (is != null) { try { is.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // 从后往前关闭,先关闭流 } if (s != null) { try { s.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (ss != null) { try { ss.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }