近来参与一个Java的web办公系统,碰到一个bug,开始猜测是线程池管理的问题,最后发现是单例模式的问题。
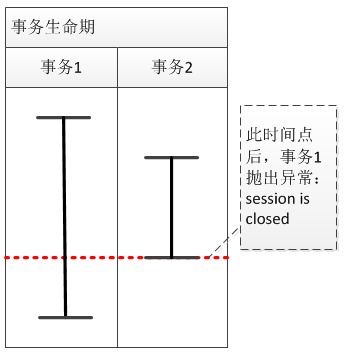
即,当同时发起两个事务请求时,当一个事务完成后,另一个事务会抛出session is closed异常。具体见下图:
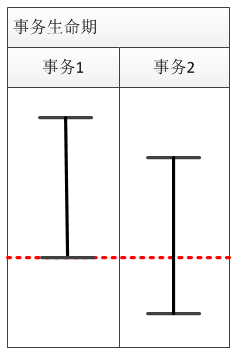
至于,下面这种情况,当时也测试过,但问题情形忘了,手上没有数据库环境,无法进行测试:
最开始,个人认为是session管理的问题,比如,在关闭session的时候,会同时关闭先前打开的session。由于下面采用的是其他公司的框架,所以就反馈给了技术总监。后来,反馈给我,竟然是单例的问题。
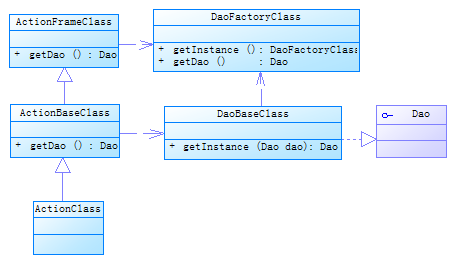
简单看了一下本系统,其在框架基础上又封装了一层,涉及这个bug的类关系如下:
发现原来设想复杂了,本框架并没有一个session的线程池管理,仅仅是对每个请求新建一个ThreadLocal对象(在DaoFactoryClass中实现),其中的initValue方法中新建了一个session对象。
问题出现在自己封装的DaoBaseClass类中,此类实现了一个单例模式,需要一个Dao参数,这个参数是通过ActionFrameClass的方法getDao()获得的,于是乎,原来实现的每个线程一个session变量,现在又被单例模式给破坏了。
附注:
ThreadLocal和Synchonized都用于解决多线程并发访问。但是ThreadLocal与synchronized有本质的区别。synchronized是利用锁的机制,使变量或代码块在某一时该只能被一个线程访问。而ThreadLocal为每一个线程都提供了变量的副本,使得每个线程在某一时间访问到的并不是同一个对象,这样就隔离了多个线程对数据的数据共享。而Synchronized却正好相反,它用于在多个线程间通信时能够获得数据共享。
Synchronized用于线程间的数据共享,而ThreadLocal则用于线程间的数据隔离。
一、ThreadLocal使用一般步骤:
1、在多线程的类(如ThreadDemo类)中,创建一个ThreadLocal对象threadXxx,用来保存线程间需要隔离处理的对象xxx。
2、在ThreadDemo类中,创建一个获取要隔离访问的数据的方法getXxx(),在方法中判断,若ThreadLocal对象为null时候,应该new()一个隔离访问类型的对象,并强制转换为要应用的类型。
3、在ThreadDemo类的run()方法中,通过getXxx()方法获取要操作的数据,这样可以保证每个线程对应一个数据对象,在任何时刻都操作的是这个对象。
二、Hibernate中的使用:
private static final ThreadLocal threadSession = new ThreadLocal();
public static Session getSession() throws InfrastructureException {
Session s = (Session) threadSession.get();
try {
if (s == null) {
s = getSessionFactory().openSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
} catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new InfrastructureException(ex);
}
return s;
}
三、ThreadLocal实现原理(JDK1.5中)
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread hash maps attached to each thread
* (Thread.threadLocals and inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal
* objects act as keys, searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a
* custom hash code (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates
* collisions in the common case where consecutively constructed
* ThreadLocals are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved
* in less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Accessed only by like-named method.
*/
private static int nextHashCode = 0;
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
/**
* Compute the next hash code. The static synchronization used here
* should not be a performance bottleneck. When ThreadLocals are
* generated in different threads at a fast enough rate to regularly
* contend on this lock, memory contention is by far a more serious
* problem than lock contention.
*/
private static synchronized int nextHashCode() {
int h = nextHashCode;
nextHashCode = h + HASH_INCREMENT;
return h;
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable.
*/
public ThreadLocal() {
}
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this thread-local
* variable. Creates and initializes the copy if this is the first time
* the thread has called this method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
return (T)map.get(this);
// Maps are constructed lazily. if the map for this thread
// doesn't exist, create it, with this ThreadLocal and its
// initial value as its only entry.
T value = initialValue();
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Many applications will have no need for
* this functionality, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current threads' copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
* @param map the map to store.
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
.......
/**
* ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for
* maintaining thread local values. No operations are exported
* outside of the ThreadLocal class. The class is package private to
* allow declaration of fields in class Thread. To help deal with
* very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use
* WeakReferences for keys. However, since reference queues are not
* used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when
* the table starts running out of space.
*/
static class ThreadLocalMap {
........
}
}
public class Thread implements Runnable {
......
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
......
}
- by 一个农夫 -