一、基础语法
每行代码分号结束
注释
// 单行代码 /* 多行注释 */ /// <summary> /// 文档注释 /// </summary>
变量
计算机中存储数据
变量类型 变量名;
变量名 = 值;
变量的类型
整形 int
浮点型 float
浮点型 double 小数点后面的位数15-16位
decimal 比浮点型有更高的精度和更小的范围,适合于财务和货币计算。使用后缀m或M。
字符 char ''单引号,不能多于一个字符,也不能存空
字符串 string ""双引号
变量的使用规则
先声明,再赋值,再使用
变量的命名规范
字母数字下划线
大小写敏感
不用关键字
不要重复定义同名变量
驼峰命名法
接收输入
Console.WriteLine("请输入num1:"); int num1 = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
交换两个变量不使用第三个变量
n1 = n1 - n2;
n2 = n1 + n2;
n1 = n2 - n1;
字符转义和不转义
转义
@ 不转义 @"C:user1.txt"
类型转换
显示
隐式
C# using语句的使用
使用时注意事项
①using只能用于实现了IDisposable接口的类型,禁止为不支持IDisposable接口的类型使用using语句,否则会出现编译错误;
②using语句适用于清理单个非托管资源的情况,而多个非托管对象的清理最好以try-finnaly来实现,因为嵌套的using语句可能存在隐藏的Bug。内层using块引发异常时,将不能释放外层using块的对象资源;
③using语句支持初始化多个变量,但前提是这些变量的类型必须相同,例如:
using(Pen p1 = new Pen(Brushes.Black), p2 = new Pen(Brushes.Blue)) { // }
④针对初始化对个不同类型的变量时,可以都声明为IDisposable类型,例如:
using (IDisposable font = new Font("Verdana", 12), pen = new Pen(Brushes.Black)) { float size = (font as Font).Size; Brush brush = (pen as Pen).Brush; }
using实质
在程序编译阶段,编译器会自动将using语句生成为try-finally语句,并在finally块中调用对象的Dispose方法,来清理资源。所以,using语句等效于try-finally语句,例如:
Font f2 = new Font("Arial", 10, FontStyle.Bold); try { //执行文本绘制操作 } finally { if (f2 != null) ((IDisposable)f2).Dispose(); }
二、运算符
赋值运算符 =
+的作用:两边数值相加;一边是字符串连接
占位符 {数字}
- 算术运算符
- 关系运算符
- 逻辑运算符
- 位运算符
- 赋值运算符
- 其他运算符
算术运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| + | 把两个操作数相加 | A + B 将得到 30 |
| - | 从第一个操作数中减去第二个操作数 | A - B 将得到 -10 |
| * | 把两个操作数相乘 | A * B 将得到 200 |
| / | 分子除以分母 | B / A 将得到 2 |
| % | 取模运算符,整除后的余数 | B % A 将得到 0 |
| ++ | 自增运算符,整数值增加 1 | A++ 将得到 11 |
| -- | 自减运算符,整数值减少 1 | A-- 将得到 9 |
关系运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| == | 检查两个操作数的值是否相等,如果相等则条件为真。 | (A == B) 不为真。 |
| != | 检查两个操作数的值是否相等,如果不相等则条件为真。 | (A != B) 为真。 |
| > | 检查左操作数的值是否大于右操作数的值,如果是则条件为真。 | (A > B) 不为真。 |
| < | 检查左操作数的值是否小于右操作数的值,如果是则条件为真。 | (A < B) 为真。 |
| >= | 检查左操作数的值是否大于或等于右操作数的值,如果是则条件为真。 | (A >= B) 不为真。 |
| <= | 检查左操作数的值是否小于或等于右操作数的值,如果是则条件为真。 | (A <= B) 为真。 |
逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| && | 称为逻辑与运算符。如果两个操作数都非零,则条件为真。 | (A && B) 为假。 |
| || | 称为逻辑或运算符。如果两个操作数中有任意一个非零,则条件为真。 | (A || B) 为真。 |
| ! | 称为逻辑非运算符。用来逆转操作数的逻辑状态。如果条件为真则逻辑非运算符将使其为假。 |
位运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| & | 如果同时存在于两个操作数中,二进制 AND 运算符复制一位到结果中。 | (A & B) 将得到 12,即为 0000 1100 |
| | | 如果存在于任一操作数中,二进制 OR 运算符复制一位到结果中。 | (A | B) 将得到 61,即为 0011 1101 |
| ^ | 如果存在于其中一个操作数中但不同时存在于两个操作数中,二进制异或运算符复制一位到结果中。 | (A ^ B) 将得到 49,即为 0011 0001 |
| ~ | 按位取反运算符是一元运算符,具有"翻转"位效果,即0变成1,1变成0,包括符号位。 | (~A ) 将得到 -61,即为 1100 0011,一个有符号二进制数的补码形式。 |
| << | 二进制左移运算符。左操作数的值向左移动右操作数指定的位数。 | A << 2 将得到 240,即为 1111 0000 |
| >> | 二进制右移运算符。左操作数的值向右移动右操作数指定的位数。 | A >> 2 将得到 15,即为 0000 1111 |
赋值运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| = | 简单的赋值运算符,把右边操作数的值赋给左边操作数 | C = A + B 将把 A + B 的值赋给 C |
| += | 加且赋值运算符,把右边操作数加上左边操作数的结果赋值给左边操作数 | C += A 相当于 C = C + A |
| -= | 减且赋值运算符,把左边操作数减去右边操作数的结果赋值给左边操作数 | C -= A 相当于 C = C - A |
| *= | 乘且赋值运算符,把右边操作数乘以左边操作数的结果赋值给左边操作数 | C *= A 相当于 C = C * A |
| /= | 除且赋值运算符,把左边操作数除以右边操作数的结果赋值给左边操作数 | C /= A 相当于 C = C / A |
| %= | 求模且赋值运算符,求两个操作数的模赋值给左边操作数 | C %= A 相当于 C = C % A |
| <<= | 左移且赋值运算符 | C <<= 2 等同于 C = C << 2 |
| >>= | 右移且赋值运算符 | C >>= 2 等同于 C = C >> 2 |
| &= | 按位与且赋值运算符 | C &= 2 等同于 C = C & 2 |
| ^= | 按位异或且赋值运算符 | C ^= 2 等同于 C = C ^ 2 |
| |= | 按位或且赋值运算符 | C |= 2 等同于 C = C | 2 |
其他运算符
| 运算符 | 描述 | 实例 |
|---|---|---|
| sizeof() | 返回数据类型的大小。 | sizeof(int),将返回 4. |
| typeof() | 返回 class 的类型。 | typeof(StreamReader); |
| & | 返回变量的地址。 | &a; 将得到变量的实际地址。 |
| * | 变量的指针。 | *a; 将指向一个变量。 |
| ? : | 条件表达式 | 如果条件为真 ? 则为 X : 否则为 Y |
| is | 判断对象是否为某一类型。 | If( Ford is Car) // 检查 Ford 是否是 Car 类的一个对象。 |
| as | 强制转换,即使转换失败也不会抛出异常。 | Object obj = new StringReader("Hello"); StringReader r = obj as StringReader; |
三、流程控制
顺序结构
分支结构
if
if(判断条件){ 要执行的语句 }
if-else
if(条件1){ 语句1; }else{ 语句2; }
选择结构
if else-if
if(判断条件){ 要执行的代码; } else if(判断条件){ 要执行的代码; } else if(判断条件){ 要执行的代码; } ... else{ 要执行的代码; }
switch-case
switch(expression){ case constant-expression : statement(s); break; case constant-expression : statement(s); break; /* 您可以有任意数量的 case 语句 */ default : /* 可选的 */ statement(s); break; }
switch 语句必须遵循下面的规则:
- switch 语句中的 expression 必须是一个整型或枚举类型,或者是一个 class 类型,其中 class 有一个单一的转换函数将其转换为整型或枚举类型。
- 在一个 switch 中可以有任意数量的 case 语句。每个 case 后跟一个要比较的值和一个冒号。
- case 的 constant-expression 必须与 switch 中的变量具有相同的数据类型,且必须是一个常量。
- 当被测试的变量等于 case 中的常量时,case 后跟的语句将被执行,直到遇到 break 语句为止。
- 当遇到 break 语句时,switch 终止,控制流将跳转到 switch 语句后的下一行。
- 不是每一个 case 都需要包含 break。如果 case 语句为空,则可以不包含 break,控制流将会 继续 后续的 case,直到遇到 break 为止。
- C# 不允许从一个开关部分继续执行到下一个开关部分。如果 case 语句中有处理语句,则必须包含 break 或其他跳转语句。
- 一个 switch 语句可以有一个可选的 default case,出现在 switch 的结尾。default case 可用于在上面所有 case 都不为真时执行一个任务。default case 中的 break 语句不是必需的。
- C# 不支持从一个 case 标签显式贯穿到另一个 case 标签。如果要使 C# 支持从一个 case 标签显式贯穿到另一个 case 标签,可以使用 goto 一个 switch-case 或 goto default。
using System; namespace DecisionMaking { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { /* 局部变量定义 */ char grade = 'B'; switch (grade) { case 'A': Console.WriteLine("很棒!"); break; case 'B': case 'C': Console.WriteLine("做得好"); break; case 'D': Console.WriteLine("您通过了"); break; case 'F': Console.WriteLine("最好再试一下"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("无效的成绩"); break; } Console.WriteLine("您的成绩是 {0}", grade); Console.ReadLine(); } } }
循环结构
while
while(condition) { statement(s); }
do-while
do { statement(s); }while( condition );
for
for ( init; condition; increment ) { statement(s); }
foreach
int[] fibarray = new int[] { 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 }; foreach (int element in fibarray) { System.Console.WriteLine(element); } System.Console.WriteLine();
循环控制语句
| 控制语句 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| break 语句 | 终止 loop 或 switch 语句,程序流将继续执行紧接着 loop 或 switch 的下一条语句。 |
| continue 语句 | 引起循环跳过主体的剩余部分,立即重新开始测试条件。 |
异常捕获
try{ 可能会出现异常的代码; } catch{ 出现异常后要执行的代码; }
四、复杂数据类型
枚举
常量
const 变量类型 变量名 = 值;
枚举是一组命名整型常量。枚举类型是使用 enum 关键字声明的。
C# 枚举是值类型。换句话说,枚举包含自己的值,且不能继承或传递继承。
[public] enum <enum_name> { enumeration list };
- public:访问修饰符
- enum:关键字
- enum_name 指定枚举的类型名称。
- enumeration list 是一个用逗号分隔的标识符列表。
枚举列表中的每个符号代表一个整数值,一个比它前面的符号大的整数值。默认情况下,第一个枚举符号的值是 0.例如:
using System; public class EnumTest { enum Day { Sun, Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat }; static void Main() { int x = (int)Day.Sun; int y = (int)Day.Fri; Console.WriteLine("Sun = {0}", x); Console.WriteLine("Fri = {0}", y); } }
结果:
Sun = 0 Fri = 5
结构
一次性声明不同数据类型的变量(不是变量,是字段)
[public] struct 结构名 { 成员; }
规范上,和变量区别,字段前面要加下划线
struct Person{ public string _name; public int _age; }
在 C# 中,结构体是值类型数据结构。它使得一个单一变量可以存储各种数据类型的相关数据。struct 关键字用于创建结构体。
结构体是用来代表一个记录。假设您想跟踪图书馆中书的动态。您可能想跟踪每本书的以下属性:
- Title
- Author
- Subject
- Book ID
using System; using System.Text; struct Books { public string title; public string author; public string subject; public int book_id; }; public class testStructure { public static void Main(string[] args) { Books Book1; /* 声明 Book1,类型为 Book */ Books Book2; /* 声明 Book2,类型为 Book */ /* book 1 详述 */ Book1.title = "C Programming"; Book1.author = "Nuha Ali"; Book1.subject = "C Programming Tutorial"; Book1.book_id = 6495407; /* book 2 详述 */ Book2.title = "Telecom Billing"; Book2.author = "Zara Ali"; Book2.subject = "Telecom Billing Tutorial"; Book2.book_id = 6495700; /* 打印 Book1 信息 */ Console.WriteLine( "Book 1 title : {0}", Book1.title); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 author : {0}", Book1.author); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 subject : {0}", Book1.subject); Console.WriteLine("Book 1 book_id :{0}", Book1.book_id); /* 打印 Book2 信息 */ Console.WriteLine("Book 2 title : {0}", Book2.title); Console.WriteLine("Book 2 author : {0}", Book2.author); Console.WriteLine("Book 2 subject : {0}", Book2.subject); Console.WriteLine("Book 2 book_id : {0}", Book2.book_id); Console.ReadKey(); } }
C# 结构的特点
您已经用了一个简单的名为 Books 的结构。在 C# 中的结构与传统的 C 或 C++ 中的结构不同。C# 中的结构有以下特点:
- 结构可带有方法、字段、索引、属性、运算符方法和事件。
- 结构可定义构造函数,但不能定义析构函数。但是,您不能为结构定义无参构造函数。无参构造函数(默认)是自动定义的,且不能被改变。
- 与类不同,结构不能继承其他的结构或类。
- 结构不能作为其他结构或类的基础结构。
- 结构可实现一个或多个接口。
- 结构成员不能指定为 abstract、virtual 或 protected。
- 当您使用 New 操作符创建一个结构对象时,会调用适当的构造函数来创建结构。与类不同,结构可以不使用 New 操作符即可被实例化。
- 如果不使用 New 操作符,只有在所有的字段都被初始化之后,字段才被赋值,对象才被使用。
类 vs 结构
类和结构有以下几个基本的不同点:
- 类是引用类型,结构是值类型。
- 结构不支持继承。
- 结构不能声明默认的构造函数。
数组
数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组是用来存储数据的集合,通常认为数组是一个同一类型变量的集合。
声明数组变量并不是声明 number0、number1、...、number99 一个个单独的变量,而是声明一个就像 numbers 这样的变量,然后使用 numbers[0]、numbers[1]、...、numbers[99] 来表示一个个单独的变量。数组中某个指定的元素是通过索引来访问的。
所有的数组都是由连续的内存位置组成的。最低的地址对应第一个元素,最高的地址对应最后一个元素。
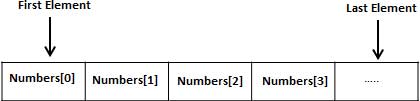
声明数组
在 C# 中声明一个数组,您可以使用下面的语法:
datatype[] arrayName;
其中,
- datatype 用于指定被存储在数组中的元素的类型。
- [ ] 指定数组的秩(维度)。秩指定数组的大小。
- arrayName 指定数组的名称。
例如:
double[] balance;
初始化数组
声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组。当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组。
数组是一个引用类型,所以您需要使用 new 关键字来创建数组的实例。
例如:
double[] balance = new double[10];
赋值给数组
您可以通过使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素,比如:
double[] balance = new double[10]; balance[0] = 4500.0;
您可以在声明数组的同时给数组赋值,比如:
double[] balance = { 2340.0, 4523.69, 3421.0};
您也可以创建并初始化一个数组,比如:
int [] marks = new int[5] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
在上述情况下,你也可以省略数组的大小,比如:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
您也可以赋值一个数组变量到另一个目标数组变量中。在这种情况下,目标和源会指向相同的内存位置:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95}; int[] score = marks;
当您创建一个数组时,C# 编译器会根据数组类型隐式初始化每个数组元素为一个默认值。例如,int 数组的所有元素都会被初始化为 0。
访问数组元素
元素是通过带索引的数组名称来访问的。这是通过把元素的索引放置在数组名称后的方括号中来实现的。例如:
double salary = balance[9];
五、string
在 C# 中,您可以使用字符数组来表示字符串,但是,更常见的做法是使用 string 关键字来声明一个字符串变量。string 关键字是 System.String 类的别名。
创建 String 对象
您可以使用以下方法之一来创建 string 对象:
- 通过给 String 变量指定一个字符串
- 通过使用 String 类构造函数
- 通过使用字符串串联运算符( + )
- 通过检索属性或调用一个返回字符串的方法
- 通过格式化方法来转换一个值或对象为它的字符串表示形式
下面的实例演示了这点:
实例
using System; namespace StringApplication { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //字符串,字符串连接 string fname, lname; fname = "Rowan"; lname = "Atkinson"; string fullname = fname + lname; Console.WriteLine("Full Name: {0}", fullname); //通过使用 string 构造函数 char[] letters = { 'H', 'e', 'l', 'l','o' }; string greetings = new string(letters); Console.WriteLine("Greetings: {0}", greetings); //方法返回字符串 string[] sarray = { "Hello", "From", "Tutorials", "Point" }; string message = String.Join(" ", sarray); Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", message); //用于转化值的格式化方法 DateTime waiting = new DateTime(2012, 10, 10, 17, 58, 1); string chat = String.Format("Message sent at {0:t} on {0:D}", waiting); Console.WriteLine("Message: {0}", chat); Console.ReadKey() ; } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Full Name: RowanAtkinson
Greetings: Hello
Message: Hello From Tutorials Point
Message: Message sent at 17:58 on Wednesday, 10 October 2012
String 类的属性
String 类有以下两个属性:
| 序号 | 属性名称 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Chars 在当前 String 对象中获取 Char 对象的指定位置。 |
| 2 | Length 在当前的 String 对象中获取字符数。 |
String 类的方法
String 类有许多方法用于 string 对象的操作。下面的表格提供了一些最常用的方法:
| 序号 | 方法名称 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public static int Compare( string strA, string strB ) 比较两个指定的 string 对象,并返回一个表示它们在排列顺序中相对位置的整数。该方法区分大小写。 |
| 2 | public static int Compare( string strA, string strB, bool ignoreCase ) 比较两个指定的 string 对象,并返回一个表示它们在排列顺序中相对位置的整数。但是,如果布尔参数为真时,该方法不区分大小写。 |
| 3 | public static string Concat( string str0, string str1 ) 连接两个 string 对象。 |
| 4 | public static string Concat( string str0, string str1, string str2 ) 连接三个 string 对象。 |
| 5 | public static string Concat( string str0, string str1, string str2, string str3 ) 连接四个 string 对象。 |
| 6 | public bool Contains( string value ) 返回一个表示指定 string 对象是否出现在字符串中的值。 |
| 7 | public static string Copy( string str ) 创建一个与指定字符串具有相同值的新的 String 对象。 |
| 8 | public void CopyTo( int sourceIndex, char[] destination, int destinationIndex, int count ) 从 string 对象的指定位置开始复制指定数量的字符到 Unicode 字符数组中的指定位置。 |
| 9 | public bool EndsWith( string value ) 判断 string 对象的结尾是否匹配指定的字符串。 |
| 10 | public bool Equals( string value ) 判断当前的 string 对象是否与指定的 string 对象具有相同的值。 |
| 11 | public static bool Equals( string a, string b ) 判断两个指定的 string 对象是否具有相同的值。 |
| 12 | public static string Format( string format, Object arg0 ) 把指定字符串中一个或多个格式项替换为指定对象的字符串表示形式。 |
| 13 | public int IndexOf( char value ) 返回指定 Unicode 字符在当前字符串中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 14 | public int IndexOf( string value ) 返回指定字符串在该实例中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 15 | public int IndexOf( char value, int startIndex ) 返回指定 Unicode 字符从该字符串中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 16 | public int IndexOf( string value, int startIndex ) 返回指定字符串从该实例中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 17 | public int IndexOfAny( char[] anyOf ) 返回某一个指定的 Unicode 字符数组中任意字符在该实例中第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 18 | public int IndexOfAny( char[] anyOf, int startIndex ) 返回某一个指定的 Unicode 字符数组中任意字符从该实例中指定字符位置开始搜索第一次出现的索引,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 19 | public string Insert( int startIndex, string value ) 返回一个新的字符串,其中,指定的字符串被插入在当前 string 对象的指定索引位置。 |
| 20 | public static bool IsNullOrEmpty( string value ) 指示指定的字符串是否为 null 或者是否为一个空的字符串。 |
| 21 | public static string Join( string separator, string[] value ) 连接一个字符串数组中的所有元素,使用指定的分隔符分隔每个元素。 |
| 22 | public static string Join( string separator, string[] value, int startIndex, int count ) 连接接一个字符串数组中的指定位置开始的指定元素,使用指定的分隔符分隔每个元素。 |
| 23 | public int LastIndexOf( char value ) 返回指定 Unicode 字符在当前 string 对象中最后一次出现的索引位置,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 24 | public int LastIndexOf( string value ) 返回指定字符串在当前 string 对象中最后一次出现的索引位置,索引从 0 开始。 |
| 25 | public string Remove( int startIndex ) 移除当前实例中的所有字符,从指定位置开始,一直到最后一个位置为止,并返回字符串。 |
| 26 | public string Remove( int startIndex, int count ) 从当前字符串的指定位置开始移除指定数量的字符,并返回字符串。 |
| 27 | public string Replace( char oldChar, char newChar ) 把当前 string 对象中,所有指定的 Unicode 字符替换为另一个指定的 Unicode 字符,并返回新的字符串。 |
| 28 | public string Replace( string oldValue, string newValue ) 把当前 string 对象中,所有指定的字符串替换为另一个指定的字符串,并返回新的字符串。 |
| 29 | public string[] Split( params char[] separator ) 返回一个字符串数组,包含当前的 string 对象中的子字符串,子字符串是使用指定的 Unicode 字符数组中的元素进行分隔的。 |
| 30 | public string[] Split( char[] separator, int count ) 返回一个字符串数组,包含当前的 string 对象中的子字符串,子字符串是使用指定的 Unicode 字符数组中的元素进行分隔的。int 参数指定要返回的子字符串的最大数目。 |
| 31 | public bool StartsWith( string value ) 判断字符串实例的开头是否匹配指定的字符串。 |
| 32 | public char[] ToCharArray() 返回一个带有当前 string 对象中所有字符的 Unicode 字符数组。 |
| 33 | public char[] ToCharArray( int startIndex, int length ) 返回一个带有当前 string 对象中所有字符的 Unicode 字符数组,从指定的索引开始,直到指定的长度为止。 |
| 34 | public string ToLower() 把字符串转换为小写并返回。 |
| 35 | public string ToUpper() 把字符串转换为大写并返回。 |
| 36 | public string Trim() 移除当前 String 对象中的所有前导空白字符和后置空白字符。 |
上面的方法列表并不详尽,请访问 MSDN 库,查看完整的方法列表和 String 类构造函数。
实例
下面的实例演示了上面提到的一些方法:
比较字符串
实例
using System; namespace StringApplication { class StringProg { static void Main(string[] args) { string str1 = "This is test"; string str2 = "This is text"; if (String.Compare(str1, str2) == 0) { Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are equal."); } else { Console.WriteLine(str1 + " and " + str2 + " are not equal."); } Console.ReadKey() ; } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
This is test and This is text are not equal.
字符串包含字符串:
实例
using System; namespace StringApplication { class StringProg { static void Main(string[] args) { string str = "This is test"; if (str.Contains("test")) { Console.WriteLine("The sequence 'test' was found."); } Console.ReadKey() ; } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
The sequence 'test' was found.
获取子字符串:
实例
using System; namespace StringApplication { class StringProg { static void Main(string[] args) { string str = "Last night I dreamt of San Pedro"; Console.WriteLine(str); string substr = str.Substring(23); Console.WriteLine(substr); Console.ReadKey() ; } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Last night I dreamt of San Pedro
San Pedro
连接字符串:
实例
using System; namespace StringApplication { class StringProg { static void Main(string[] args) { string[] starray = new string[]{"Down the way nights are dark", "And the sun shines daily on the mountain top", "I took a trip on a sailing ship", "And when I reached Jamaica", "I made a stop"}; string str = String.Join(" ", starray); Console.WriteLine(str); Console.ReadKey() ; } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Down the way nights are dark
And the sun shines daily on the mountain top
I took a trip on a sailing ship
And when I reached Jamaica
I made a stop
六、方法(函数)
函数就是将一堆代码进行重用的一种机制。函数就是一段代码,这段代码可能有输入的值(参数),可能会返回值。
还没有接触到创建对象,这里的方法都是静态方法。
[public] static 返回值类型 方法名([参数列表]) { 方法体; }
调用
类名.方法名([参数]);
如果写的放给Main()函数同在一个类中,类名可以省略。
例子
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace HelloWorld { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int max = Program.getMax(5, 6); // 类名可以省略 Console.WriteLine(max); Console.ReadKey(); } public static int getMax(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a: b ; } } }
委托
为什么使用委托
将方法作为参数
修饰符 delegate 返回值类型 委托名 ( 参数列表 );
委托指向要委托的方法,参数和返回值类型要一样
实例化
委托名 委托对象名 = new 委托名 ( 方法名 );
也可以
委托名 委托对象名 = 方法名 ;
例子
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public delegate void DelSay(string name); // 参数和要委托的方法参数一致 public static void SayChinese(string name) { Console.WriteLine("吃了吗? " + name); } public static void SayEnglish(string name) { Console.WriteLine("Nice to meet you, " + name); } public static void Test(string name, DelSay del) { del(name); } static void Main(string[] args) {
DelSay del = SayChinese;
del("李");
DelSay del2 = new DelSay(SayChinese);
del2("钱");
Test("王", SayChinese); Test("Jhon", SayEnglish); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
需求:字符串中的字母全转为大写;字符串中的字母全转为小写;字符串中的字母两边加引号。
不使用委托
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public static void toUpper(string[] str) { for(int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++) { str[i] = str[i].ToUpper(); } } public static void toLower(string[] str) { for(int i=0; i<str.Length; i++) { str[i] = str[i].ToLower(); } } public static void toSYH(string[] str) { for(int i=0; i<str.Length; i++) { str[i] = """ + str[i] + """; } } static void Main(string[] args) { string[] str = { "aSAPGHllds", "faHDohHS", "SOHadf" }; toLower(str); foreach (string s in str) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.WriteLine("Hello World!"); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
使用委托
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public delegate string DelTo(string str); public static string toUpper(string str) { return str.ToUpper(); } public static string toLower(string str) { return str.ToLower(); } public static string toSYH(string str) { return """ + str + """; } public static void ProStr(string[] str, DelTo del) { for(int i=0; i<str.Length; i++) { str[i] = del(str[i]); } } static void Main(string[] args) { string[] str = { "aSAPGHllds", "faHDohHS", "SOHadf" }; ProStr(str, toSYH); foreach(string s in str) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
匿名方法
可以使用匿名函数,不必再定义三个字符串转换方法
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public delegate string DelTo(string str); public static void ProStr(string[] str, DelTo del) { for(int i=0; i<str.Length; i++) { str[i] = del(str[i]); } } static void Main(string[] args) { string[] str = { "aSAPGHllds", "faHDohHS", "SOHadf" }; ProStr(str, delegate(string name) { return name.ToLower(); }); foreach(string s in str) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
我们已经提到过,委托是用于引用与其具有相同标签的方法。换句话说,您可以使用委托对象调用可由委托引用的方法。
匿名方法(Anonymous methods) 提供了一种传递代码块作为委托参数的技术。匿名方法是没有名称只有主体的方法。
在匿名方法中您不需要指定返回类型,它是从方法主体内的 return 语句推断的。
编写匿名方法的语法
匿名方法是通过使用 delegate 关键字创建委托实例来声明的。例如:
delegate void NumberChanger(int n); ... NumberChanger nc = delegate(int x) { Console.WriteLine("Anonymous Method: {0}", x); };
代码块 Console.WriteLine("Anonymous Method: {0}", x); 是匿名方法的主体。
委托可以通过匿名方法调用,也可以通过命名方法调用,即,通过向委托对象传递方法参数。
例如:
nc(10);
实例
下面的实例演示了匿名方法的概念:
using System; delegate void NumberChanger(int n); namespace DelegateAppl { class TestDelegate { static int num = 10; public static void AddNum(int p) { num += p; Console.WriteLine("Named Method: {0}", num); } public static void MultNum(int q) { num *= q; Console.WriteLine("Named Method: {0}", num); } static void Main(string[] args) { // 使用匿名方法创建委托实例 NumberChanger nc = delegate(int x) { Console.WriteLine("Anonymous Method: {0}", x); }; // 使用匿名方法调用委托 nc(10); // 使用命名方法实例化委托 nc = new NumberChanger(AddNum); // 使用命名方法调用委托 nc(5); // 使用另一个命名方法实例化委托 nc = new NumberChanger(MultNum); // 使用命名方法调用委托 nc(2); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果:
Anonymous Method: 10
Named Method: 15
Named Method: 30
匿名函数更进一步可以写为lambda表达式
NumberChanger nc = (int x) =》 { Console.WriteLine("Anonymous Method: {0}", x); };
练习
使用委托求数组的最大值
不使用委托
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public static int GetMax(int[] arr) { int max = arr[0]; for(int i=0; i<arr.Length; i++) { if(max < arr[i]) { max = arr[i]; } } return max; } public static string GetMax(string[] arr) { string max = arr[0]; for(int i=0; i<arr.Length; i++) { if(max.Length < arr[i].Length) { max = arr[i]; } } return max; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 5, 2, 8, 3, 9 }; Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr)); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
使用委托
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public delegate int DelCompare(object o1, object o2); public static object GetMax(object[] obj, DelCompare del) { object max = obj[0]; for(int i=0; i<obj.Length; i++) { if (del(max, obj[i]) < 0) { max = obj[i]; } } return max; } public static int CompareInt(object o1, object o2) { return (int)o1 - (int)o2; } public static int CompareString(object o1, object o2) { return ((string)o1).Length - ((string)o2).Length; } static void Main(string[] args) { object[] arr = { 1, 5, 2, 8, 3, 9 }; Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr, CompareInt)); object[] arr1 = { "abc", "ertrwtw", "fggewhewhew" }; Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr1, delegate (object o1, object o2) { return ((string)o1).Length - ((string)o2).Length; })); Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr1, (object o1, object o2) => { return ((string)o1).Length - ((string)o2).Length; })); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
泛型委托
使用委托求任意数组的最大值
上面使用object,涉及到拆装箱,写起来也不简洁,使用泛型
namespace ConsoleApp1 { class Program { public delegate int DelCompare<T>(T o1, T o2); public static T GetMax<T>(T[] obj, DelCompare<T> del) { T max = obj[0]; for(int i=0; i<obj.Length; i++) { if (del(max, obj[i]) < 0) { max = obj[i]; } } return max; } public static int CompareInt(int o1, int o2) { return o1 - o2; } public static int CompareString(string o1, string o2) { return o1.Length - o2.Length; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 5, 2, 8, 3, 9 }; Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr, CompareInt)); string[] arr1 = { "abc", "ertrwtw", "fggewhewhew" }; Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr1, delegate (string o1, string o2) { return o1.Length - o2.Length; })); Console.WriteLine(GetMax(arr1, (string o1, string o2) => { return o1.Length - o2.Length; })); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
使用委托进行窗体传值
新建两个窗体
Form1窗体添加label和button

Form2窗体添加文本框和button
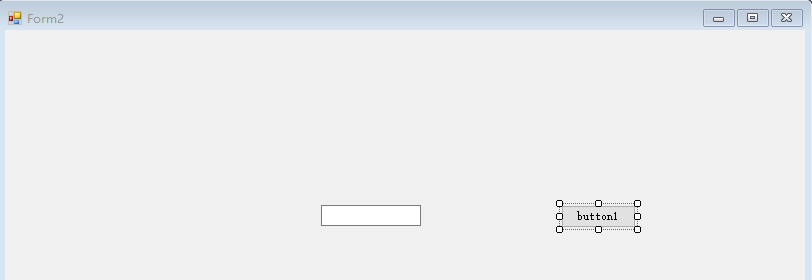
点击Form1的button弹出Form2
在Form2的文本框中输入文字,点击button,文字传给Form1的label
Form1的label显示值的方法在Form1中,但是需要被Form2调用,使用委托,即将Form1的方法传给Form2让Form2调用
namespace 窗体传值 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Form2 form2 = new Form2(ShowMsg); form2.Show(); } public void ShowMsg(string str) { label1.Text = str; } } }
namespace 窗体传值 { public partial class Form2 : Form { public delegate void DelMsg(string msg); DelMsg _del; public Form2(DelMsg del) { InitializeComponent(); this._del = del; } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Form1 form1 = new Form1(); this._del(textBox1.Text); } private void textBox1_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { } } }
多播委托
{ class Program { delegate void DelTest(); static void Test1() { Console.WriteLine("This is test1."); } static void Test2() { Console.WriteLine("This is test2."); } static void Test3() { Console.WriteLine("This is test3."); } static void Main(string[] args) { DelTest del = Test1; del += Test2; del += Test3; del(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
事件
无论是企业中使用的大型应用程序还是手机中安装的一个 App 都与事件密不可分。
例如在登录 QQ 软件时需要输入用户名和密码,然后单击“登录”按钮来登录 QQ,此时单击按钮的动作会触发一个按钮的单击事件来完成执行相应的代码实现登录的功能。
在 C# 语言中,Windows 应用程序、 ASP.NET 网站程序等类型的程序都离不开事件的应用。
事件是一种引用类型,实际上也是一种特殊的委托。
通常,每一个事件的发生都会产生发送方和接收方,发送方是指引发事件的对象,接收方则是指获取、处理事件。事件要与委托一起使用。
事件定义的语法形式如下。
访问修饰符 event 委托名 事件名 ;
在这里,由于在事件中使用了委托,因此需要在定义事件前先定义委托。
在定义事件后需要定义事件所使用的方法,并通过事件来调用委托。
下面通过实例来演示事件的应用。
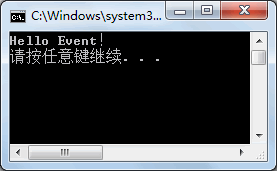
【实例 1】通过事件完成在控制台上输岀“Hello Event!”的操作。
根据题目要求,代码如下。
class Program { //定义委托 public delegate void SayDelegate(); //定义事件 public event SayDelegate SayEvent; //定义委托中调用的方法 public void SayHello() { Console.WriteLine("Hello Event!"); } //创建触发事件的方法 public void SayEventTrigger() { //触发事件,必须与事件是同名方法 SayEvent(); } static void Main(string[] args) { //创建Program类的实例 Program program = new Program(); //实例化事件,使用委托指向处理方法 program.SayEvent = new SayDelegate(program.SayHello); //调用触发事件的方法 program.SayEventTrigger(); } }
执行上面的代码,效果如下图所示。
【实例 2】在事件中使用多播委托完成预定不同商品的操作。
根据题目要求,代码如下。
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //创建MyEvent类的实例 MyEvent myEvent = new MyEvent(); //实例化事件,使用委托指向处理方法 myEvent.BuyEvent += new MyEvent.BuyDelegate(MyEvent.BuyFood); myEvent.BuyEvent += new MyEvent.BuyDelegate(MyEvent.BuyCake); myEvent.BuyEvent += new MyEvent.BuyDelegate(MyEvent.BuyFlower); //调用触发事件的方法 myEvent.InvokeEvent(); } } class MyEvent { //定义委托 public delegate void BuyDelegate(); //定义事件 public event BuyDelegate BuyEvent; //定义委托中使用的方法 public static void BuyFood() { Console.WriteLine("购买快餐!"); } public static void BuyCake() { Console.WriteLine("购买蛋糕!"); } public static void BuyFlower() { Console.WriteLine("购买鲜花!"); } //创建触发事件的方法 public void InvokeEvent() { //触发事件,必须和事件是同名方法 BuyEvent(); } }
执行上面的代码,效果与实例 1 效果一致。
需要注意的是,在使用事件时如果事件的定义和调用不在同一个类中,实例化的事件只能出现在+=或者-=操作符的左侧。
在上面的代码中,实例化事件的代码只能写成myEvent.BuyEvent += new MyEvent.BuyDelegate(MyEvent.BuyFood)的形式,而不能使用myEvent.BuyEvent = new MyEvent.BuyDelegate(MyEvent.BuyFood)的形式。
事件是每一个 Windows 应用程序中必备的,很多事件的操作都是自动生成的。