本系列主要讲解kafka基本设计和原理分析,分如下内容:
- 基本概念
- 消息模型
- kafka副本同步机制
- kafka文件存储机制
- kafka数据可靠性和一致性保证
- kafka leader选举
- kafka消息传递语义
- Kafka集群partitions/replicas默认分配解析
Kafka集群partitions/replicas默认分配解析
kafka在创建topic,需要指定分区数和副本的数量,本节探讨分区、副本在broker上的分配情况。
目标
replica assignment有三个目标:
- 在brokers之间均分replicas
- partition与它的其他replicas不再同一个broker上
- 如果broker有rack信息,则partition的replicas尽量分配在不同rack上面
kafka0.10版本支持了2种replica assignment策略(对于partition来说,它也是由n个replica组成的),一种是rack unware,一种是rack-ware,这里的rack就是机架的意思。
rack unaware
- 随机从broker list选一个开始,然后对每个partition的第一个replica进行round-robin分配
- 之后对每个partition的其余replicas进行递增1位错位开来
这种策略分配算法核心代码如下:
private def assignReplicasToBrokersRackUnaware(nPartitions: Int,
replicationFactor: Int,
brokerList: Seq[Int],
fixedStartIndex: Int,
startPartitionId: Int): Map[Int, Seq[Int]] = {
val ret = mutable.Map[Int, Seq[Int]]()
val brokerArray = brokerList.toArray
val startIndex = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(brokerArray.length)
var currentPartitionId = math.max(0, startPartitionId)
var nextReplicaShift = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(brokerArray.length)
for (_ <- 0 until nPartitions) {
if (currentPartitionId > 0 && (currentPartitionId % brokerArray.length == 0))
nextReplicaShift += 1
val firstReplicaIndex = (currentPartitionId + startIndex) % brokerArray.length
val replicaBuffer = mutable.ArrayBuffer(brokerArray(firstReplicaIndex))
for (j <- 0 until replicationFactor - 1)
replicaBuffer += brokerArray(replicaIndex(firstReplicaIndex, nextReplicaShift, j, brokerArray.length))
ret.put(currentPartitionId, replicaBuffer)
currentPartitionId += 1
}
ret
}
private def replicaIndex(firstReplicaIndex: Int, secondReplicaShift: Int, replicaIndex: Int, nBrokers: Int): Int = {
val shift = 1 + (secondReplicaShift + replicaIndex) % (nBrokers - 1)
(firstReplicaIndex + shift) % nBrokers
}
上述代码含义大致如下先分配分区,再分配该分区的副本
假设我们现在有5个broker,对topic1设置10个分区,三个副本。即
nPartitions=10,replicationFactor=3,brokerList={0,1,2,3,4},nBrokers=5
假设从broker-0开始,有10个partition,每个partition有3个replica
则可以看到p0在broker-0,p1在broker-1,依次round下来。
到了第二个replica的时候,可以看到p0在broker-1,p1在broker-2,这样递增1位错开。
通过继承RackAwareTest类的测试代码如下:
package unit.kafka.admin
import kafka.admin.{BrokerMetadata, AdminUtils, RackAwareTest}
import kafka.utils.Logging
import org.junit.Assert._
import org.junit.Test
import scala.collection.Map
class AdminRackUnAwareTest extends RackAwareTest with Logging {
@Test
def testReplicaAssignment() {
val brokerMetadatas = (0 to 4).map(new BrokerMetadata(_, None))
val actualAssignment = AdminUtils.assignReplicasToBrokers(brokerMetadatas, 10, 3, 0)
println(actualAssignment)
}
}
输出结果为:
Map(8 -> ArrayBuffer(3, 0, 1), 2 -> ArrayBuffer(2, 3, 4), 5 -> ArrayBuffer(0, 2, 3), 4 -> ArrayBuffer(4, 0, 1), 7 -> ArrayBuffer(2, 4, 0), 1 -> ArrayBuffer(1, 2, 3), 9 -> ArrayBuffer(4, 1, 2), 3 -> ArrayBuffer(3, 4, 0), 6 -> ArrayBuffer(1, 3, 4), 0 -> ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 2))
为方便查看,绘图如下:
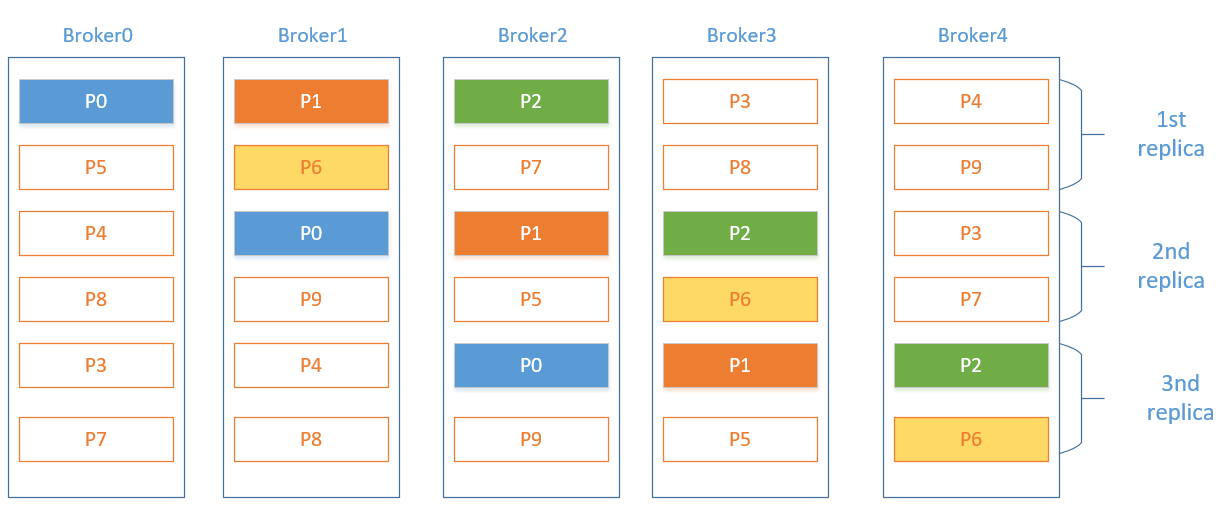
分配策略:
首分区
broker=i%nBrokers
副本分区
shift=1+(i/nBrokers+j)%(nBrokers-1)
broker=[i+shift]%nBrokers
针对本文情况,i取值{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},j取值{0,1}
i=0
首分区
broker=0
副本分区
i=0,j=0:shift=1,broker=1
i=0,j=1:shift=2,broker=2
i=3
首分区
broker=3
副本分区
i=3,j=0:shift=1,broker=4
i=3,j=1:shift=2,broker=0
i=6
首分区
broker=1
副本分区
i=6,j=0:shift=2,broker=3
i=6,j=1:shift=3,broker=4
rack aware
- 首先对broker list跟rack进行一次映射
- 按rack顺序round起来得到一个新的broker-list
- 使用round-robbin对parition跟broker进行映射
核心代码如下:
private def assignReplicasToBrokersRackAware(nPartitions: Int,
replicationFactor: Int,
brokerMetadatas: Seq[BrokerMetadata],
fixedStartIndex: Int,
startPartitionId: Int): Map[Int, Seq[Int]] = {
val brokerRackMap = brokerMetadatas.collect { case BrokerMetadata(id, Some(rack)) =>
id -> rack
}.toMap
val numRacks = brokerRackMap.values.toSet.size
val arrangedBrokerList = getRackAlternatedBrokerList(brokerRackMap)
val numBrokers = arrangedBrokerList.size
val ret = mutable.Map[Int, Seq[Int]]()
val startIndex = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(arrangedBrokerList.size)
var currentPartitionId = math.max(0, startPartitionId)
var nextReplicaShift = if (fixedStartIndex >= 0) fixedStartIndex else rand.nextInt(arrangedBrokerList.size)
for (_ <- 0 until nPartitions) {
if (currentPartitionId > 0 && (currentPartitionId % arrangedBrokerList.size == 0))
nextReplicaShift += 1
val firstReplicaIndex = (currentPartitionId + startIndex) % arrangedBrokerList.size
val leader = arrangedBrokerList(firstReplicaIndex)
val replicaBuffer = mutable.ArrayBuffer(leader)
val racksWithReplicas = mutable.Set(brokerRackMap(leader))
val brokersWithReplicas = mutable.Set(leader)
var k = 0
for (_ <- 0 until replicationFactor - 1) {
var done = false
while (!done) {
val broker = arrangedBrokerList(replicaIndex(firstReplicaIndex, nextReplicaShift * numRacks, k, arrangedBrokerList.size))
val rack = brokerRackMap(broker)
// Skip this broker if
// 1. there is already a broker in the same rack that has assigned a replica AND there is one or more racks
// that do not have any replica, or
// 2. the broker has already assigned a replica AND there is one or more brokers that do not have replica assigned
if ((!racksWithReplicas.contains(rack) || racksWithReplicas.size == numRacks)
&& (!brokersWithReplicas.contains(broker) || brokersWithReplicas.size == numBrokers)) {
replicaBuffer += broker
racksWithReplicas += rack
brokersWithReplicas += broker
done = true
}
k += 1
}
}
ret.put(currentPartitionId, replicaBuffer)
currentPartitionId += 1
}
ret
}
假设有6个broker,3个rack,6个partition,每个partition有3个replica
broker和rack映射如下:
0 -> "rack1", 1 -> "rack3", 2 -> "rack3", 3 -> "rack2", 4 -> "rack2", 5 -> "rack1"
按rack顺序round起来得到一个新的broker-list,
0(rack1),3(rack2),1(rack3),5(rack1),4(rack2),2(rack3)
最后使用round-robbin对parition跟broker进行映射
0 -> 0,3,1
1 -> 3,1,5
2 -> 1,5,4
3 -> 5,4,2
4 -> 4,2,0
5 -> 2,0,3
关于作者
爱编程、爱钻研、爱分享、爱生活
关注分布式、高并发、数据挖掘
如需捐赠,请扫码
