一、cuda简介
CUDA是支持c++/c语言,一般我喜欢用c来写,他的编译是gpu部分由nvcc来进行的
一般的函数定义 void function();
cuda的函数定义 __global__ void function();
解释:在这里,这个global前缀表明这个函数在哪里执行,可以由谁来呼叫
global:主机呼叫,设备执行
host:主机呼叫,主机执行
device:设备呼叫,设备执行
执行一般c函数 funtion();
执行cuda函数 function<<>> ();
解释:在GPU上面执行函数可以自定分配grid和线程,grid包含线程,因为是并列执行,因此如果内容一样数据的生成很多是不分前后的。
二、运行例子的方法:
建立一个CUDA8.0 Runtim模版为基础的工程,
或建立一个c++工程,将cpp后缀改为.cu

建完工程后会有一部分代码

在主函数return 0 之前加入getchar();即可运行,关于此代码后期可慢慢研究,这里不做讲解。
源码为:

#include "cuda_runtime.h" #include "device_launch_parameters.h" #include <stdio.h> cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size); __global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b) { int i = threadIdx.x; c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; } int main() { const int arraySize = 5; const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; int c[arraySize] = { 0 }; // Add vectors in parallel. cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!"); return 1; } printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d} ", c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]); // cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and // tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces. cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!"); return 1; } getchar(); return 0; } // Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel. cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size) { int *dev_a = 0; int *dev_b = 0; int *dev_c = 0; cudaError_t cudaStatus; // Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system. cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?"); goto Error; } // Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) . cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } // Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers. cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } // Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element. addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b); // Check for any errors launching the kernel cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s ", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus)); goto Error; } // cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns // any errors encountered during the launch. cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel! ", cudaStatus); goto Error; } // Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory. cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } Error: cudaFree(dev_c); cudaFree(dev_a); cudaFree(dev_b); return cudaStatus; }
三、实战代码:
例一:第一个程序hello world
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
__global__ void helloFromGPU(void)
{
printf("Hello World from GPU!
");
}
int main(void)
{
// hello from cpu
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
printf("Hello World from CPU!
");
helloFromGPU << <1, 10 >> > ();
cudaDeviceReset();//重置CUDA设备释放程序占用的资源
system("pause");
return 0;
}
无视所有错误直接运行即可。
在这里 helloFromGPU << <1, 10 >> >();
表示这一函数将有十个一样的线程,也就是这个函数总计会被执行十次。
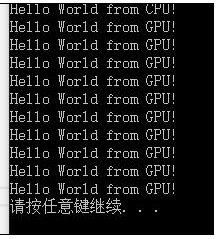
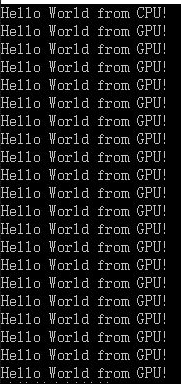
改为helloFromGPU << <2, 10 >> >();
例二:参数的传入
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
__global__ void Add(int i, int j)
{
int count;
count = i + j;
printf("
Num is %d
", count);
}
int main(void)
{
Add << <1, 1 >> >(10, 15);
cudaDeviceReset();//重置CUDA设备释放程序占用的资源
system("pause");
return 0;
}
传入参数与一般的c没有什么不一样之处
例三:数据的传入和传出
从这里开始要用到显存分配,在这一段中,我们的数据要从内存copy到显存上面,然后现在又要从显存上面copy回来
这次我们定一个减法函数,在设备上执行
__global__ void Decrease(int a, int b, int *c)
{
*c = a - b;
}
我的要传的数为一个整数型的c,一般会定义一个全局的以cuda错误处理返回值为类型的函数,在这一函数内执行数据的传输,及时返回错误
cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c);
在例子中我省略了这个直接用void类型
void addWithCuda(int *c);
代码:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
void addWithCuda(int *c);//1.定义传入的函数c
int main(void)
{
int c;
c = 10;
addWithCuda(&c);//2.传入参数变量(地址)
cudaDeviceReset();//6.重置CUDA设备释放程序占用的资源
printf("Value is %d", c);//7.主机上打印显示数据
system("pause");
return 0;
}
__global__ void Decrease(int a, int b, int *c)
{
*c = a - b;
}
void addWithCuda(int *c)
{
int *dev_c = 0;//这个相当于内存和显存有一样的
//3.请求CUDA设备的内存(显存),执行CUDA函数
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, sizeof(int));
Decrease << <1, 1 >> >(15, 30, dev_c);
//4.等待设备所有线程任务执行完毕
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
//5.数据复制到主机,释放占用空间
cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_c);
}
例四:数据的传入和传出Ⅱ
如果要复制数据进去,那么我们先要修改下上一个例子的函数
1.传入的数值全改为指针类型
__global__ void Decrease(int *a, int *b, int *c)
{
*c = *a - *b;
}
2.修改函数的传入参数
void addWithCuda(int *c,int *a,int *b);//1.定义传入的函数c
3.增加处理函数中对于相应存储空间的的申请和释放
void addWithCuda(int *c, int *a, int *b)
{
int *dev_c = 0;
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
//3.请求CUDA设备的内存(显存),执行CUDA函数
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, sizeof(int));
//4.从主机复制数据到设备上
cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Decrease << < 1, 1 >> >(dev_a, dev_b, dev_c);
//5.等待设备所有线程任务执行完毕
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
//6.数据复制到主机,释放占用空间
cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
}
4.最后是主函数
int main(void)
{
int c;
int a, b;
c = 10;
a = 30;
b = 15;
addWithCuda(&c, &a, &b);//2.传入参数变量(地址)
cudaDeviceReset();//7.重置CUDA设备释放程序占用的资源
printf("Value is %d", c);//8.主机上打印显示数据
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.代码:
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <Windows.h>
__global__ void Decrease(int *a, int *b, int *c)
{
*c = *a - *b;
}
void addWithCuda(int *c, int *a, int *b)
{
int *dev_c = 0;
int *dev_a = 0;
int *dev_b = 0;
//3.请求CUDA设备的内存(显存),执行CUDA函数
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, sizeof(int));
//4.从主机复制数据到设备上
cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
Decrease << < 1, 1 >> >(dev_a, dev_b, dev_c);
//5.等待设备所有线程任务执行完毕
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
//6.数据复制到主机,释放占用空间
cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaFree(dev_c);
cudaFree(dev_a);
cudaFree(dev_b);
}
int main(void)
{
int c;
int a, b;
c = 10;
a = 30;
b = 15;
addWithCuda(&c, &a, &b);//2.传入参数变量(地址)
cudaDeviceReset();//7.重置CUDA设备释放程序占用的资源
printf("Value is %d", c);//8.主机上打印显示数据
system("pause");
return 0;
}
最后再放一个程序关于循环可以自行理解
程序实现向量的加法操作,使用了一个block内部的512个线程。
#include <stdio.h> #include<cuda_runtime.h> //__global__声明的函数,告诉编译器这段代码交由CPU调用,由GPU执行 __global__ void add(const int *dev_a,const int *dev_b,int *dev_c) { int i=threadIdx.x; dev_c[i]=dev_a[i]+dev_b[i]; } int main(void) { //申请主机内存,并进行初始化 int host_a[512],host_b[512],host_c[512]; for(int i=0;i<512;i++) { host_a[i]=i; host_b[i]=i<<1; } //定义cudaError,默认为cudaSuccess(0) cudaError_t err = cudaSuccess; //申请GPU存储空间 int *dev_a,*dev_b,*dev_c; err=cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_a, sizeof(int)*512); err=cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_b, sizeof(int)*512); err=cudaMalloc((void **)&dev_c, sizeof(int)*512); if(err!=cudaSuccess) { printf("the cudaMalloc on GPU is failed"); return 1; } printf("SUCCESS"); //将要计算的数据使用cudaMemcpy传送到GPU cudaMemcpy(dev_a,host_a,sizeof(host_a),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); cudaMemcpy(dev_b,host_b,sizeof(host_b),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); //调用核函数在GPU上执行。数据较少,之使用一个Block,含有512个线程 add<<<1,512>>>(dev_a,dev_b,dev_c); cudaMemcpy(&host_c,dev_c,sizeof(host_c),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); for(int i=0;i<512;i++) printf("host_a[%d] + host_b[%d] = %d + %d = %d ",i,i,host_a[i],host_b[i],host_c[i]); cudaFree(dev_a);//释放GPU内存 cudaFree(dev_b);//释放GPU内存 cudaFree(dev_c);//释放GPU内存 return 0 ; }
