文字描述:
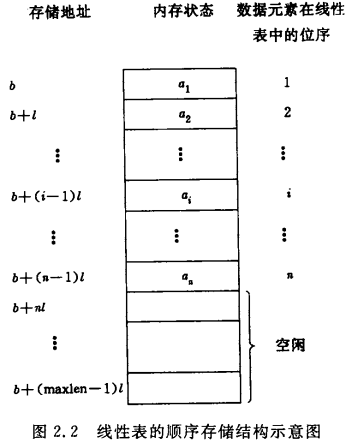
用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素,只要确定了存储线性表的起始位置,线性表中任一数据元素都可随机存取,所以线性表的顺序存储结构是一种随机存取的存储结构。
即是,线性表的顺序存储结构的特定是逻辑关系上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻,因此可以随机存取表中任一元素,它的存储位置可用一个简单、直观的公式来表示。但是这也导致了它的一个弱点,在作插入或删除操作时,需移动大量元素。
示意图
算法分析
在顺序存储结构的线性表中某个位置上插入或删除一个数据元素,其时间主要耗费在移动元素上,而移动的元素个数取决于插入或删除的位置。故其插入和删除的时间复杂度为n。
在顺序存储结构的线性表中求“表长”和“取第i个数据元素”的时间复杂度为1。
在顺序存储结构的线性表中,union算法(将所有在线性表Lb但不在线性表La中的数据元素插入到La,即La=La U Lb), 其时间复杂度为La.length X Lb.length; 但是如果La,Lb是有序的,另外新建Lc存放结果,其时间复杂度将变为MAX(La.length+Lb.length).
代码实现

1 // 2 // Created by lady on 19-1-26. 3 // 4 5 /* 6 现性表的顺序表示和实现 7 现性表的顺序表示:用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的数据元素。 8 */ 9 #include <stdio.h> 10 #include <stdlib.h> 11 12 //-------------线性表的动态分配顺序存储结构------------------ 13 #define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100 //线性表存储空间的初始分配量 14 #define LIST_INCREMENT 10 //线性表存储空间的分配增量 15 typedef int ElemType; 16 typedef struct{ 17 ElemType *elem; //存储空间基址 18 int length; //当前长度 19 int listsize; //当前分配的存储容量(以sizeof(ElemType)为单位) 20 }SqList; 21 22 /*构造一个空的线性表*/ 23 static int InitList_Sq(SqList *L) 24 { 25 if(L==NULL){ 26 return -1; 27 } 28 if((L->elem=(ElemType*)malloc(LIST_INIT_SIZE*sizeof(ElemType))) == NULL){ 29 //存储分配失败 30 return -1; 31 } 32 //空表长度为0 33 L->length = 0; 34 //初始存储容量 35 L->listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE; 36 return 0; 37 } 38 39 /*在L中第i个位置之前插入新的数据元素e,L的长度增1*/ 40 static int ListInsert_Sq(SqList *L, int i, ElemType e) 41 { 42 //i的合法值为1 <= i <= ListLength_Sq(L)+1 43 if((i<1) || (i>L->length+1)) 44 return -1; 45 if(L->length >= L->listsize){ 46 //当前存储空间已满,增加分配 47 ElemType *newbase = NULL; 48 if((newbase=(ElemType*)realloc(L->elem, (L->listsize+LIST_INCREMENT)*sizeof(ElemType))) == NULL){ 49 //存储分配失败 50 return -1; 51 } 52 //新的基址 53 L->elem = newbase; 54 //增加存储容量 55 L->listsize += LIST_INCREMENT; 56 } 57 //q为插入位置 58 ElemType *q = (L->elem+i-1); 59 ElemType *p; 60 for(p=(L->elem+L->length-1); p>=q; --p){ 61 //插入位置及之后的元素右移 62 *(p+1) = *p; 63 } 64 //插入e 65 *q = e; 66 //表长增1 67 L->length += 1; 68 return 0; 69 } 70 71 /*删除L中的第i个数据元素,并用e返回其值, L的长度减1*/ 72 static int ListDelete_Sq(SqList *L, int i, ElemType *e) 73 { 74 //i的合法值为1 <= i <= ListLength_Sq(L) 75 if((i<1) || (i>L->length)){ 76 return -1; 77 } 78 ElemType *p; 79 ElemType *q; 80 //p为被删除元素的位置 81 p = L->elem+i-1; 82 //被删除元素的值赋给e 83 *e = *p; 84 //表尾元素的位置 85 q = L->elem+L->length-1; 86 for(++p;p<=q;++p){ 87 //被删除元素之后的元素坐移 88 *(p-1) = *p; 89 } 90 //表长减1 91 L->length -= 1; 92 return 0; 93 } 94 95 /*依次对L的每个数据元素调用函数fun。一旦fun失败,则操作失败*/ 96 static int ListTraverse_Sq(SqList L, int (*fun)(ElemType,int), char info[]) 97 { 98 printf("顺序存储的线性表%s", info); 99 int i = 0; 100 for(i=0; i<L.length; i++) 101 { 102 if(fun(L.elem[i],i+1) < 0){ 103 printf("Err:when traverse(e,%d) wrong! ",i); 104 return -1; 105 } 106 } 107 printf(" "); 108 return 0; 109 } 110 111 /* 112 * 在顺序表L中查找第1个值与e满足fun的元素的位序 113 * 若找到, 则返回其在L中的位置, 否则返回0 114 */ 115 static int LocateElem_Sq(SqList L, ElemType e, int (*fun)(ElemType,ElemType)) 116 { 117 //i的初值为第一个元素的位置 118 int i = 1; 119 ElemType *p; 120 //p的初值为第一个元素的存储位置 121 p = L.elem; 122 while(i<=L.length && (fun(*p++,e))) 123 ++i; 124 if(i<=L.length) 125 return i; 126 return 0; 127 } 128 129 /*销毁线性表L*/ 130 static int DestroyList_Sq(SqList *L) 131 { 132 if(L == NULL) 133 return -1; 134 if(L->elem){ 135 free(L->elem); 136 L->elem = NULL; 137 } 138 L->length = 0; 139 L->listsize = 0; 140 return 0; 141 } 142 143 /* 144 * 已知顺序线性表La和Lb的元素按照非递减排列 145 * 归并La和Lb得到新的顺序线性表Lc,Lc的元素也按值非递减排列 146 * 时间复杂度为MAX(La.length, Lb.length) 147 */ 148 static int MergeList_Sq(SqList La, SqList Lb, SqList *Lc) 149 { 150 if(Lc == NULL){ 151 return -1; 152 } 153 154 ElemType *pa = La.elem, *pa_last; 155 ElemType *pb = Lb.elem, *pb_last; 156 157 Lc->length = La.length + Lb.length; 158 Lc->listsize = La.length + Lb.length; 159 160 if((Lc->elem = (ElemType*)malloc(Lc->listsize * sizeof(ElemType))) == NULL){ 161 //存储分配失败 162 Lc->length = 0; 163 Lc->listsize = 0; 164 return -1; 165 } 166 ElemType *pc = Lc->elem; 167 168 pa_last = La.elem+La.length-1; 169 pb_last = Lb.elem+Lb.length-1; 170 while((pa<=pa_last) && (pb<=pb_last)){ 171 //归并 172 if(*pa <= *pb){ 173 *pc++ = *pa++; 174 }else{ 175 *pc++ = *pb++; 176 } 177 } 178 while(pa<=pa_last){ 179 //插入La的剩余部分 180 *pc++ = *pa++; 181 } 182 while(pb<=pb_last){ 183 //插入Lb的剩余部分 184 *pc++ = *pb++; 185 } 186 return 0; 187 } 188 189 //打印位置loc和其数据元素e 190 static int printE(ElemType e, int loc) 191 { 192 printf("%3d=%-3d", loc, e); 193 return 0; 194 } 195 196 //比较元素e1和e2是否相等, 相等返回0,否则返回-1 197 static int equal(ElemType e1, ElemType e2) 198 { 199 if(e1==e2){ 200 return 0; 201 }else{ 202 return -1; 203 } 204 } 205 206 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 207 { 208 SqList L; 209 if(InitList_Sq((&L)) < 0){ 210 printf("Err:init sqList wrong! "); 211 goto End; 212 } 213 214 ElemType e; 215 int location; 216 int data; 217 218 //以插入法构造一个线性表·[12,13,21,24,28,30,42,77] 219 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 1, 12); 220 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 2, 13); 221 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 3, 21); 222 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 4, 24); 223 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 5, 28); 224 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 6, 30); 225 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 7, 42); 226 ListInsert_Sq(&L, 8, 77); 227 ListTraverse_Sq(L, printE, "L:"); 228 printf(" "); 229 230 //insert a data and print 231 printf("insert a data and print, please input (locatioon, data):"); 232 scanf("%d,%d", &location, &data); 233 ListInsert_Sq(&L, location, data); 234 ListTraverse_Sq(L, printE, "L:"); 235 printf(" "); 236 237 //delete a data and print 238 printf("delete a data and print, please input (location):"); 239 scanf("%d", &location); 240 ListDelete_Sq(&L, location, &e); 241 ListTraverse_Sq(L, printE, "L:"); 242 printf(" "); 243 244 //locate a data and print 245 printf("locata a data and print, please input (data):"); 246 scanf("%d", &data); 247 location = LocateElem_Sq(L, data, equal); 248 printf("the location of the first data who equals to %d is %d! ", data, location); 249 250 printf("Merge LA and LB to LC! "); 251 SqList La, Lb, Lc; 252 if(InitList_Sq(&La) || InitList_Sq(&Lb)){ 253 printf("Err:init sqList wrong! "); 254 goto End; 255 } 256 //构造一个值非递减的线性表:LA [3,5,8,11] 257 ListInsert_Sq(&La, 1, 3); 258 ListInsert_Sq(&La, 2, 5); 259 ListInsert_Sq(&La, 3, 8); 260 ListInsert_Sq(&La, 4, 11); 261 ListTraverse_Sq(La, printE, "LA"); 262 263 //构造一个值非递减的线性表:LB [2,6,8,9,11,15,20] 264 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 1, 2); 265 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 2, 6); 266 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 3, 8); 267 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 4, 9); 268 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 5, 11); 269 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 6, 15); 270 ListInsert_Sq(&Lb, 7, 20); 271 ListTraverse_Sq(Lb, printE, "LB"); 272 273 //将线性表La和Lb按照非递减形式归并成线性表Lc 274 if(MergeList_Sq(La, Lb, &Lc)) 275 { 276 printf("Err:when merge(La,Lb) wrong! "); 277 goto End; 278 } 279 ListTraverse_Sq(Lc, printE, "LC"); 280 281 End: 282 DestroyList_Sq(&L); 283 DestroyList_Sq(&La); 284 DestroyList_Sq(&Lb); 285 DestroyList_Sq(&Lc); 286 return 0; 287 }
代码运行
/home/lady/CLionProjects/untitled/cmake-build-debug/untitled 顺序存储的线性表L: 1=12 2=13 3=21 4=24 5=28 6=30 7=42 8=77 insert a data and print, please input (locatioon, data):5,25 顺序存储的线性表L: 1=12 2=13 3=21 4=24 5=25 6=28 7=30 8=42 9=77 delete a data and print, please input (location):5 顺序存储的线性表L: 1=12 2=13 3=21 4=24 5=28 6=30 7=42 8=77 locata a data and print, please input (data):42 the location of the first data who equals to 42 is 7! Merge LA and LB to LC! 顺序存储的线性表LA 1=3 2=5 3=8 4=11 顺序存储的线性表LB 1=2 2=6 3=8 4=9 5=11 6=15 7=20 顺序存储的线性表LC 1=2 2=3 3=5 4=6 5=8 6=8 7=9 8=11 9=11 10=15 11=20 Process finished with exit code 0
