在说jdk动态代理之前先讲一下代理模式,以下内容引用自[菜鸟教程]:
在代理模式(Proxy Pattern)中,一个类代表另一个类的功能。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式。
在代理模式中,我们创建具有现有对象的对象,以便向外界提供功能接口。
介绍
意图:为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。
主要解决:在直接访问对象时带来的问题,比如说:要访问的对象在远程的机器上。在面向对象系统中,有些对象由于某些原因(比如对象创建开销很大,或者某些操作需要安全控制,或者需要进程外的访问),直接访问会给使用者或者系统结构带来很多麻烦,我们可以在访问此对象时加上一个对此对象的访问层。
何时使用:想在访问一个类时做一些控制。
如何解决:增加中间层。
关键代码:实现与被代理类组合。
应用实例: 1、Windows 里面的快捷方式。 2、猪八戒去找高翠兰结果是孙悟空变的,可以这样理解:把高翠兰的外貌抽象出来,高翠兰本人和孙悟空都实现了这个接口,猪八戒访问高翠兰的时候看不出来这个是孙悟空,所以说孙悟空是高翠兰代理类。 3、买火车票不一定在火车站买,也可以去代售点。 4、一张支票或银行存单是账户中资金的代理。支票在市场交易中用来代替现金,并提供对签发人账号上资金的控制。 5、spring aop。
优点: 1、职责清晰。 2、高扩展性。 3、智能化。
缺点: 1、由于在客户端和真实主题之间增加了代理对象,因此有些类型的代理模式可能会造成请求的处理速度变慢。 2、实现代理模式需要额外的工作,有些代理模式的实现非常复杂。
使用场景:按职责来划分,通常有以下使用场景: 1、远程代理。 2、虚拟代理。 3、Copy-on-Write 代理。 4、保护(Protect or Access)代理。 5、Cache代理。 6、防火墙(Firewall)代理。 7、同步化(Synchronization)代理。 8、智能引用(Smart Reference)代理。
注意事项: 1、和适配器模式的区别:适配器模式主要改变所考虑对象的接口,而代理模式不能改变所代理类的接口。 2、和装饰器模式的区别:装饰器模式为了增强功能,而代理模式是为了加以控制。
以Image接口为例,类图如下:
- 创建一个接口。
public interface Image { void display(); }
2. 创建实现接口的实体类。
public class RealImage implements Image { private String fileName; public RealImage(String fileName){ this.fileName = fileName; loadFromDisk(fileName); } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("Displaying " + fileName); } private void loadFromDisk(String fileName){ System.out.println("Loading " + fileName); } }
3. 创建代理类
1 public class ProxyImage implements Image{ 2 3 private RealImage realImage; 4 private String fileName; 5 6 public ProxyImage(String fileName){ 7 this.fileName = fileName; 8 } 10 @Override 11 public void display() { 12 if(realImage == null){ 13 realImage = new RealImage(fileName); 14 } 15 realImage.display(); 16 } 17 }
4. 当被请求时,使用 ProxyImage 来获取 RealImage 类的对象。
1 public class ProxyPatternDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Image image = new ProxyImage("test_10mb.jpg"); 5 6 // 图像将从磁盘加载 7 image.display(); 8 System.out.println(""); 9 // 图像不需要从磁盘加载 10 image.display(); 11 } 12 }
5. 执行程序,输出结果:
Loading test_10mb.jpg Displaying test_10mb.jpg Displaying test_10mb.jpg
以上代码就是基于实现同一个接口将目标对象作为依赖,然后在代理对象中实现需要增强的方法并在该方法中调用目标对象的方法实现对目标对象的增强,也是静态代理的实现方式。但是这种方法在面对多个对象需要被代理的情况下就需要大量的实现类,而且在目标类的接口修改以后,代理类也必须做出相应的修改,编码和代码维护成本很高。所以JDK为我们提供了动态代理的编码方式,这种方式实现的代理类都是在程序运行时动态生成,而且一种增强可用于多个目标类,减少编码复杂度和代码维护难度。
JDK动态代理的实现用到的主要类或者接口:
- InvocationHandler
1 /* 2 * Copyright (c) 1999, 2006, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. 3 * ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.24 */ 25 26 package java.lang.reflect; 27 28 /** 29 * {@code InvocationHandler} is the interface implemented by 30 * the <i>invocation handler</i> of a proxy instance. 31 * 32 * <p>Each proxy instance has an associated invocation handler. 33 * When a method is invoked on a proxy instance, the method 34 * invocation is encoded and dispatched to the {@code invoke} 35 * method of its invocation handler. 36 * 37 * @author Peter Jones 38 * @see Proxy 39 * @since 1.3 40 */ 41 public interface InvocationHandler { 42 43 /** 44 * Processes a method invocation on a proxy instance and returns 45 * the result. This method will be invoked on an invocation handler 46 * when a method is invoked on a proxy instance that it is 47 * associated with. 48 * 49 * @param proxy the proxy instance that the method was invoked on 50 * 51 * @param method the {@code Method} instance corresponding to 52 * the interface method invoked on the proxy instance. The declaring 53 * class of the {@code Method} object will be the interface that 54 * the method was declared in, which may be a superinterface of the 55 * proxy interface that the proxy class inherits the method through. 56 * 57 * @param args an array of objects containing the values of the 58 * arguments passed in the method invocation on the proxy instance, 59 * or {@code null} if interface method takes no arguments. 60 * Arguments of primitive types are wrapped in instances of the 61 * appropriate primitive wrapper class, such as 62 * {@code java.lang.Integer} or {@code java.lang.Boolean}. 63 * 64 * @return the value to return from the method invocation on the 65 * proxy instance. If the declared return type of the interface 66 * method is a primitive type, then the value returned by 67 * this method must be an instance of the corresponding primitive 68 * wrapper class; otherwise, it must be a type assignable to the 69 * declared return type. If the value returned by this method is 70 * {@code null} and the interface method's return type is 71 * primitive, then a {@code NullPointerException} will be 72 * thrown by the method invocation on the proxy instance. If the 73 * value returned by this method is otherwise not compatible with 74 * the interface method's declared return type as described above, 75 * a {@code ClassCastException} will be thrown by the method 76 * invocation on the proxy instance. 77 * 78 * @throws Throwable the exception to throw from the method 79 * invocation on the proxy instance. The exception's type must be 80 * assignable either to any of the exception types declared in the 81 * {@code throws} clause of the interface method or to the 82 * unchecked exception types {@code java.lang.RuntimeException} 83 * or {@code java.lang.Error}. If a checked exception is 84 * thrown by this method that is not assignable to any of the 85 * exception types declared in the {@code throws} clause of 86 * the interface method, then an 87 * {@link UndeclaredThrowableException} containing the 88 * exception that was thrown by this method will be thrown by the 89 * method invocation on the proxy instance. 90 * 91 * @see UndeclaredThrowableException 92 */ 93 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 94 throws Throwable; 95 }
2. Proxy
package java.lang.reflect; import java.lang.ref.WeakReference; import java.security.AccessController; import java.security.PrivilegedAction; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.IdentityHashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Objects; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong; import java.util.function.BiFunction; import sun.misc.ProxyGenerator; import sun.misc.VM; import sun.reflect.CallerSensitive; import sun.reflect.Reflection; import sun.reflect.misc.ReflectUtil; import sun.security.util.SecurityConstants; public class Proxy implements java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -2222568056686623797L; /** parameter types of a proxy class constructor */ private static final Class<?>[] constructorParams = { InvocationHandler.class }; /** * a cache of proxy classes */ private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory()); /** * the invocation handler for this proxy instance. * @serial */ protected InvocationHandler h; /** * Prohibits instantiation. */ private Proxy() { } /** * Constructs a new {@code Proxy} instance from a subclass * (typically, a dynamic proxy class) with the specified value * for its invocation handler. * * @param h the invocation handler for this proxy instance * * @throws NullPointerException if the given invocation handler, {@code h}, * is {@code null}. */ protected Proxy(InvocationHandler h) { Objects.requireNonNull(h); this.h = h; } /** * Returns the {@code java.lang.Class} object for a proxy class * given a class loader and an array of interfaces. The proxy class * will be defined by the specified class loader and will implement * all of the supplied interfaces. If any of the given interfaces * is non-public, the proxy class will be non-public. If a proxy class * for the same permutation of interfaces has already been defined by the * class loader, then the existing proxy class will be returned; otherwise, * a proxy class for those interfaces will be generated dynamically * and defined by the class loader. * * <p>There are several restrictions on the parameters that may be * passed to {@code Proxy.getProxyClass}: * * <ul> * <li>All of the {@code Class} objects in the * {@code interfaces} array must represent interfaces, not * classes or primitive types. * * <li>No two elements in the {@code interfaces} array may * refer to identical {@code Class} objects. * * <li>All of the interface types must be visible by name through the * specified class loader. In other words, for class loader * {@code cl} and every interface {@code i}, the following * expression must be true: * <pre> * Class.forName(i.getName(), false, cl) == i * </pre> * * <li>All non-public interfaces must be in the same package; * otherwise, it would not be possible for the proxy class to * implement all of the interfaces, regardless of what package it is * defined in. * * <li>For any set of member methods of the specified interfaces * that have the same signature: * <ul> * <li>If the return type of any of the methods is a primitive * type or void, then all of the methods must have that same * return type. * <li>Otherwise, one of the methods must have a return type that * is assignable to all of the return types of the rest of the * methods. * </ul> * * <li>The resulting proxy class must not exceed any limits imposed * on classes by the virtual machine. For example, the VM may limit * the number of interfaces that a class may implement to 65535; in * that case, the size of the {@code interfaces} array must not * exceed 65535. * </ul> * * <p>If any of these restrictions are violated, * {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} will throw an * {@code IllegalArgumentException}. If the {@code interfaces} * array argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, a * {@code NullPointerException} will be thrown. * * <p>Note that the order of the specified proxy interfaces is * significant: two requests for a proxy class with the same combination * of interfaces but in a different order will result in two distinct * proxy classes. * * @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class * @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class * to implement * @return a proxy class that is defined in the specified class loader * and that implements the specified interfaces * @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the * parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass} * are violated * @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present * and any of the following conditions is met: * <ul> * <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and * the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} with * {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission * denies access.</li> * <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf}, * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf}.</li> * </ul> * @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array * argument or any of its elements are {@code null} */ @CallerSensitive public static Class<?> getProxyClass(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) throws IllegalArgumentException { final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs); } return getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); } /* * Check permissions required to create a Proxy class. * * To define a proxy class, it performs the access checks as in * Class.forName (VM will invoke ClassLoader.checkPackageAccess): * 1. "getClassLoader" permission check if loader == null * 2. checkPackageAccess on the interfaces it implements * * To get a constructor and new instance of a proxy class, it performs * the package access check on the interfaces it implements * as in Class.getConstructor. * * If an interface is non-public, the proxy class must be defined by * the defining loader of the interface. If the caller's class loader * is not the same as the defining loader of the interface, the VM * will throw IllegalAccessError when the generated proxy class is * being defined via the defineClass0 method. */ private static void checkProxyAccess(Class<?> caller, ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader(); if (VM.isSystemDomainLoader(loader) && !VM.isSystemDomainLoader(ccl)) { sm.checkPermission(SecurityConstants.GET_CLASSLOADER_PERMISSION); } ReflectUtil.checkProxyPackageAccess(ccl, interfaces); } } /** * Generate a proxy class. Must call the checkProxyAccess method * to perform permission checks before calling this. */ private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) { if (interfaces.length > 65535) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded"); } // If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing // the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy; // otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces); } /* * a key used for proxy class with 0 implemented interfaces */ private static final Object key0 = new Object(); /* * Key1 and Key2 are optimized for the common use of dynamic proxies * that implement 1 or 2 interfaces. */ /* * a key used for proxy class with 1 implemented interface */ private static final class Key1 extends WeakReference<Class<?>> { private final int hash; Key1(Class<?> intf) { super(intf); this.hash = intf.hashCode(); } @Override public int hashCode() { return hash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { Class<?> intf; return this == obj || obj != null && obj.getClass() == Key1.class && (intf = get()) != null && intf == ((Key1) obj).get(); } } /* * a key used for proxy class with 2 implemented interfaces */ private static final class Key2 extends WeakReference<Class<?>> { private final int hash; private final WeakReference<Class<?>> ref2; Key2(Class<?> intf1, Class<?> intf2) { super(intf1); hash = 31 * intf1.hashCode() + intf2.hashCode(); ref2 = new WeakReference<Class<?>>(intf2); } @Override public int hashCode() { return hash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { Class<?> intf1, intf2; return this == obj || obj != null && obj.getClass() == Key2.class && (intf1 = get()) != null && intf1 == ((Key2) obj).get() && (intf2 = ref2.get()) != null && intf2 == ((Key2) obj).ref2.get(); } } /* * a key used for proxy class with any number of implemented interfaces * (used here for 3 or more only) */ private static final class KeyX { private final int hash; private final WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") KeyX(Class<?>[] interfaces) { hash = Arrays.hashCode(interfaces); refs = (WeakReference<Class<?>>[])new WeakReference<?>[interfaces.length]; for (int i = 0; i < interfaces.length; i++) { refs[i] = new WeakReference<>(interfaces[i]); } } @Override public int hashCode() { return hash; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { return this == obj || obj != null && obj.getClass() == KeyX.class && equals(refs, ((KeyX) obj).refs); } private static boolean equals(WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs1, WeakReference<Class<?>>[] refs2) { if (refs1.length != refs2.length) { return false; } for (int i = 0; i < refs1.length; i++) { Class<?> intf = refs1[i].get(); if (intf == null || intf != refs2[i].get()) { return false; } } return true; } } /** * A function that maps an array of interfaces to an optimal key where * Class objects representing interfaces are weakly referenced. */ private static final class KeyFactory implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Object> { @Override public Object apply(ClassLoader classLoader, Class<?>[] interfaces) { switch (interfaces.length) { case 1: return new Key1(interfaces[0]); // the most frequent case 2: return new Key2(interfaces[0], interfaces[1]); case 0: return key0; default: return new KeyX(interfaces); } } } /** * A factory function that generates, defines and returns the proxy class given * the ClassLoader and array of interfaces. */ private static final class ProxyClassFactory implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> { // prefix for all proxy class names private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy"; // next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong(); @Override public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) { Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length); for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) { /* * Verify that the class loader resolves the name of this * interface to the same Class object. */ Class<?> interfaceClass = null; try { interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { } if (interfaceClass != intf) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( intf + " is not visible from class loader"); } /* * Verify that the Class object actually represents an * interface. */ if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface"); } /* * Verify that this interface is not a duplicate. */ if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName()); } } String proxyPkg = null; // package to define proxy class in int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL; /* * Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the * proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that * all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package. */ for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) { int flags = intf.getModifiers(); if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) { accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL; String name = intf.getName(); int n = name.lastIndexOf('.'); String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1)); if (proxyPkg == null) { proxyPkg = pkg; } else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "non-public interfaces from different packages"); } } } if (proxyPkg == null) { // if no non-public proxy interfaces, use com.sun.proxy package proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + "."; } /* * Choose a name for the proxy class to generate. */ long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement(); String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num; /* * Generate the specified proxy class. */ byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass( proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags); try { return defineClass0(loader, proxyName, proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length); } catch (ClassFormatError e) { /* * A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the * proxy class generation code) there was some other * invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy * class creation (such as virtual machine limitations * exceeded). */ throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString()); } } } /** * Returns an instance of a proxy class for the specified interfaces * that dispatches method invocations to the specified invocation * handler. * * <p>{@code Proxy.newProxyInstance} throws * {@code IllegalArgumentException} for the same reasons that * {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} does. * * @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class * @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class * to implement * @param h the invocation handler to dispatch method invocations to * @return a proxy instance with the specified invocation handler of a * proxy class that is defined by the specified class loader * and that implements the specified interfaces * @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the * parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass} * are violated * @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present * and any of the following conditions is met: * <ul> * <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and * the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission * s.checkPermission} with * {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission * denies access;</li> * <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf}, * the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and * invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf};</li> * <li> any of the given proxy interfaces is non-public and the * caller class is not in the same {@linkplain Package runtime package} * as the non-public interface and the invocation of * {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission s.checkPermission} with * {@code ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage.{package name}")} * permission denies access.</li> * </ul> * @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array * argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, or * if the invocation handler, {@code h}, is * {@code null} */ @CallerSensitive public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException { Objects.requireNonNull(h); final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs); } /* * Look up or generate the designated proxy class. */ Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); /* * Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler. */ try { if (sm != null) { checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl); } final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); final InvocationHandler ih = h; if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { cons.setAccessible(true); return null; } }); } return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h}); } catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { Throwable t = e.getCause(); if (t instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) t; } else { throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } } private static void checkNewProxyPermission(Class<?> caller, Class<?> proxyClass) { SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { if (ReflectUtil.isNonPublicProxyClass(proxyClass)) { ClassLoader ccl = caller.getClassLoader(); ClassLoader pcl = proxyClass.getClassLoader(); // do permission check if the caller is in a different runtime package // of the proxy class int n = proxyClass.getName().lastIndexOf('.'); String pkg = (n == -1) ? "" : proxyClass.getName().substring(0, n); n = caller.getName().lastIndexOf('.'); String callerPkg = (n == -1) ? "" : caller.getName().substring(0, n); if (pcl != ccl || !pkg.equals(callerPkg)) { sm.checkPermission(new ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage." + pkg)); } } } } /** * Returns true if and only if the specified class was dynamically * generated to be a proxy class using the {@code getProxyClass} * method or the {@code newProxyInstance} method. * * <p>The reliability of this method is important for the ability * to use it to make security decisions, so its implementation should * not just test if the class in question extends {@code Proxy}. * * @param cl the class to test * @return {@code true} if the class is a proxy class and * {@code false} otherwise * @throws NullPointerException if {@code cl} is {@code null} */ public static boolean isProxyClass(Class<?> cl) { return Proxy.class.isAssignableFrom(cl) && proxyClassCache.containsValue(cl); } /** * Returns the invocation handler for the specified proxy instance. * * @param proxy the proxy instance to return the invocation handler for * @return the invocation handler for the proxy instance * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the argument is not a * proxy instance * @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present * and the caller's class loader is not the same as or an * ancestor of the class loader for the invocation handler * and invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess * s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to the invocation * handler's class. */ @CallerSensitive public static InvocationHandler getInvocationHandler(Object proxy) throws IllegalArgumentException { /* * Verify that the object is actually a proxy instance. */ if (!isProxyClass(proxy.getClass())) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a proxy instance"); } final Proxy p = (Proxy) proxy; final InvocationHandler ih = p.h; if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { Class<?> ihClass = ih.getClass(); Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); if (ReflectUtil.needsPackageAccessCheck(caller.getClassLoader(), ihClass.getClassLoader())) { ReflectUtil.checkPackageAccess(ihClass); } } return ih; } private static native Class<?> defineClass0(ClassLoader loader, String name, byte[] b, int off, int len); }
下面基于这两个类/接口来实现JDK动态代理编码:
1. 实现InvocationHandler接口来做增强
2.创建代理工厂方法调用Proxy的 public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h) 方法
package com.vincent.fat.core.proxy; import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse; import com.vincent.fat.core.service.HttpService; import com.vincent.fat.core.service.impl.HttpServiceImpl; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; @Slf4j public class JdkDynamicProxy { static class InvocationHandlerImpl implements InvocationHandler{ private final Object target; InvocationHandlerImpl(Object target) { this.target = target; }
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, @NotNull Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { log.info("before the method {} EXE。。。",method.getName()); Object res = method.invoke(this.target, args); log.info("after the method {} EXE。。。",method.getName()); return res; } } static class JdkProxyFactory{ public static Object getProxy(Object target){ return Proxy.newProxyInstance( target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandlerImpl(target) ); } } public static void main(String[] args) { HttpService service = (HttpService)JdkProxyFactory.getProxy(new HttpServiceImpl()); log.warn(service.getClass().getName()); String s = service.testMethod(" vincent!"); } }
HTTPService 接口:
package com.vincent.fat.core.service; import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse; import cn.hutool.http.Method; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Map; public interface HttpService extends Serializable { HttpResponse doRequest(String url, Map<String,Object> params, Method method); default String testMethod(final String name){ String hi= "hello"+name; System.out.println(hi); return hi; } }
HTTPService 实现类:
import cn.hutool.http.HttpRequest; import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse; import cn.hutool.http.Method; import com.vincent.fat.core.service.HttpService; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Map; @Service public class HttpServiceImpl implements HttpService, Serializable { @Override public HttpResponse doRequest(String url, Map<String, Object> params, Method method) { return new HttpRequest(url) .method(method) .form(params) .timeout(2000) .execute(); } }
最终执行结果:
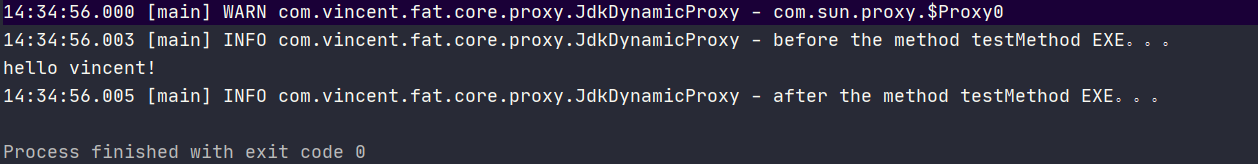
可以看到 JDK在运行过程中动态生成了一个叫做:com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 的代理类,执行代理类的say()方法代理类就会调用 InvocationHandlerImpl的invoke()方法完成增强;
PS:想要获取动态生成的代理类可以在代理对象生成之前的代码中设置系统属性,这样就可以保存下动态生成的class文件: System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0经过反编译得到的代码如下:
// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.sun.proxy; import cn.hutool.http.HttpResponse; import com.vincent.fat.core.service.HttpService; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException; import java.util.Map; public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements HttpService, Serializable { private static Method m1; private static Method m2; private static Method m4; private static Method m3; private static Method m0; public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler var1) throws { super(var1); } public final boolean equals(Object var1) throws { try { return (Boolean)super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } } public final String toString() throws { try { return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m2, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } } public final HttpResponse doRequest(String var1, Map var2, cn.hutool.http.Method var3) throws { try { return (HttpResponse)super.h.invoke(this, m4, new Object[]{var1, var2, var3}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var5) { throw var5; } catch (Throwable var6) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var6); } } public final String testMethod(String var1) throws { try { return (String)super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var4); } } public final int hashCode() throws { try { return (Integer)super.h.invoke(this, m0, (Object[])null); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var3); } } static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", Class.forName("java.lang.Object")); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString"); m4 = Class.forName("com.vincent.fat.core.service.HttpService").getMethod("doRequest", Class.forName("java.lang.String"), Class.forName("java.util.Map"), Class.forName("cn.hutool.http.Method")); m3 = Class.forName("com.vincent.fat.core.service.HttpService").getMethod("testMethod", Class.forName("java.lang.String")); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode"); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(var2.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(var3.getMessage()); } } }
从代码中可以看到,$Proxy0 继承了Proxy类和实现了目标对象的接口,在static块中使用反射得到了目标对象接口中的所有方法对象,在调用代理对象的方法时,代理对象调用传入Proxy类的 InvocationHandler实现类的invoke方法完成增强。