1、算法模型
算法模型对象:特殊的对象.在该对象中已经集成好个一个方程(还没有求出解的方程).
- 模型对象的作用:通过方程实现预测或者分类
- 样本数据(df,np):
- 特征数据:自变量
- 目标数据:因变量
2、模型对象的分类
- 有监督学习:模型需要的样本数据中存在特征数据和目标数据
- 无监督学习:模型需要的样本数据中存在特征数据
- 半监督学习:模型需要的样本数据部分需要有特征数据和目标数据,部分只需要特征数据
3、sklearn模块
sklearn模块封装了多种算法模型对象.
导入sklearn,建立线性回归算法模型对象
sklearn 模块开发流程:
1、实例模型对象
2、获取样本数据
3、训练模型
4、测试结果
利用sklearn模块 实现预测,处理流程如下:
注意: .reshape(-1,1) 将一维数组变为二维数组(将行变为列)
plt.scatter() 绘图
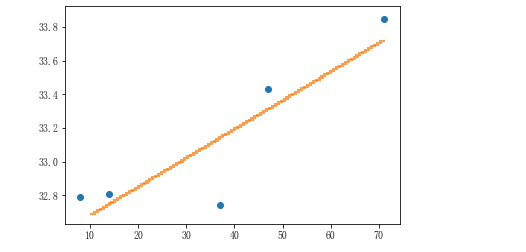
#1.导包 from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline #2.实例化模型对象 linner = LinearRegression() #3.提取样本数据:必须是二维数组 numpy或dataFrame #4.训练模型:往方程里带数据求出方程式 linner.fit(x[],y[]) linner.fit(near_city_dist.reshape(-1,1),near_city_max_temp) #5.实现预测:带入x求y linner.predict(38) #array([33.16842645]) #6.给模型打分--大概值 linner.score(near_city_dist.reshape(-1,1),near_city_max_temp) 0.77988083971852 # 7.绘制回归曲线 x = np.linspace(10,70,num=100) y = linner.predict(x.reshape(-1,1)) plt.scatter(near_city_dist,near_city_max_temp)# plt.scatter(x,y,s=0.2)
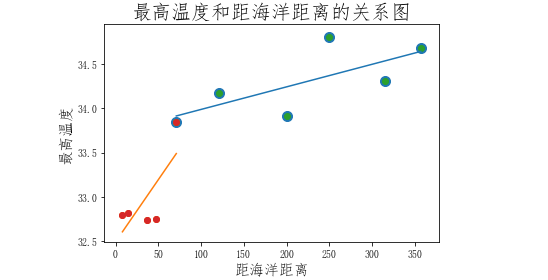
#将近海和远海的散点图合并显示 plt.scatter(far_city_dists,far_max_temps,s=100) plt.scatter(near_city_dists,near_max_temps) plt.scatter(far_city_dists,far_max_temps) plt.plot(x,y) plt.scatter(near_city_dists,near_max_temps) plt.plot(x1,y1) plt.title('最高温度和距海洋距离的关系图',fontsize=20) plt.xlabel('距海洋距离',fontsize=15) plt.ylabel('最高温度',fontsize=15)
scatter函数的用法:绘制散点图
plot() 函数的用法:画线图
未完待续.........
相关文章:
对于线性回归通俗理解的笔记 https://www.cnblogs.com/aitree/p/14324669.html