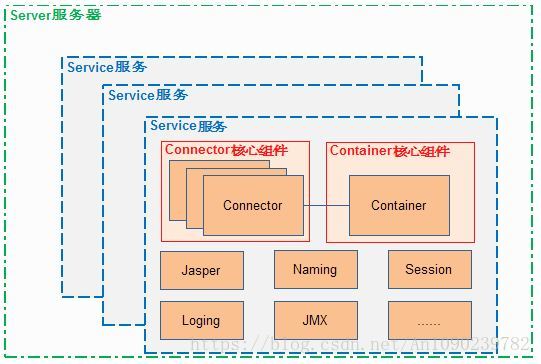
Connector是Tomcat的连接器,其主要任务是负责处理浏览器发送过来的请求,并创建一个Request和Response的对象用于和浏览器交换数据,然后产生一个线程用于处理请求,Connector会把Request和Response对象传递给该线程,该线程的具体的处理过程是Container容器的事了。执行过程分为以下几个步骤:
- 实例化Connector,构造一个Connector对象。
- 调用Connector的initIntenal方法,初始化Connetor。
- 调用ProtocolHanlder的init方法,完成ProtocolHanlder的初始化。这个过程包括了创建线程池并创建一个线程处理浏览器请求。
- 调用Connector的startIntenal方法,启动Connector。
- 调用ProtocolHandler的start方法,启动Protocolhanlder。
- 调用MapperListener的start方法,启动监听器程序。
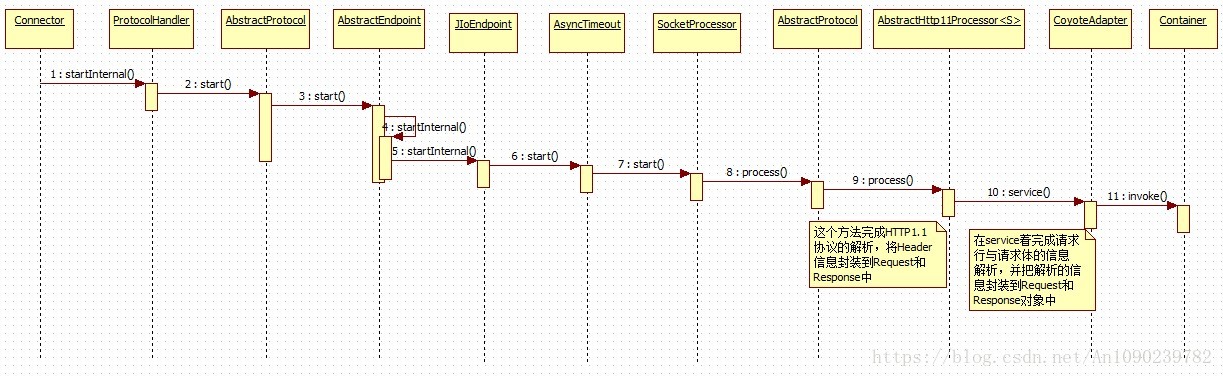
Connect执行过程的时序图:
注意:由于Tomcat还支持AJP协议,但为了简化,我画的这个序列图是基于Http协议的,这也是我们在Web开发中接触最多的协议了。
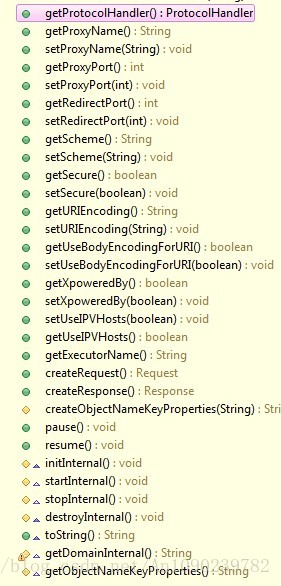
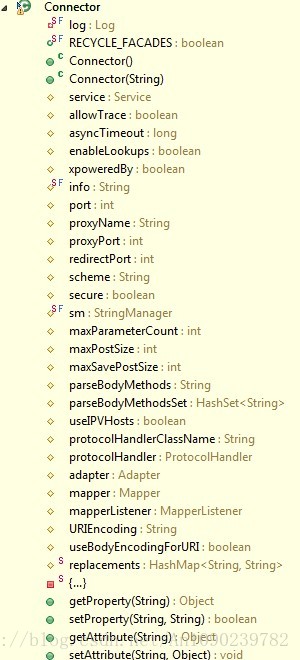
在深入Connector之前我们先看看Connector类的结构:
既然是处理浏览器请求,那么需要支持http协议,在Tomcat中有两种协议处理器:HTTP/1.1与AJP/1.3协议处理器。在server.xml中已经指明tomcat所支持的两种协议:
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" />
<Connector port="8009" protocol="AJP/1.3" redirectPort="8443" />在tomcat中是怎么样分别处理这两种协议的呢,我们可以ProtocolHanlder类中找到答案:
图中被选中的就是Tomcat默认使用协议处理器,其实现过程与Java标准Socket编程是一样的,在tomcat中可以使用Connetor类的setProtocol方法,看看源码就知道了:
public void setProtocol(String protocol) {
if (AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) {
if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol)) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName
("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol");
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName
("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpAprProtocol");
} else if (protocol != null) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName(protocol);
} else {
setProtocolHandlerClassName
("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11AprProtocol");
}
} else {
if ("HTTP/1.1".equals(protocol)) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName
("org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11Protocol");
} else if ("AJP/1.3".equals(protocol)) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName
("org.apache.coyote.ajp.AjpProtocol");
} else if (protocol != null) {
setProtocolHandlerClassName(protocol);
}
}
}从第2个if子句的最后一个else可以知道tomcat默认使用的是http1.1协议。
我们再看看Connector的初始化过程:
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
super.initInternal();
// Initialize adapter
adapter = new CoyoteAdapter(this);
protocolHandler.setAdapter(adapter);
// Make sure parseBodyMethodsSet has a default
if( null == parseBodyMethodsSet ) {
setParseBodyMethods(getParseBodyMethods());
}
if (protocolHandler.isAprRequired() &&
!AprLifecycleListener.isAprAvailable()) {
throw new LifecycleException(
sm.getString("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerNoApr",
getProtocolHandlerClassName()));
}
try {
protocolHandler.init();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new LifecycleException
(sm.getString
("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerInitializationFailed"), e);
}
// Initialize mapper listener
mapperListener.init();
}从这段代码中可以看到:首先调用父类org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleMBeanBase的初始化方法,然后创建一个Adapter,然后设置protocolHanlder(协议处理器)的Adapter,同时判断传过来的请求的请求方法(比如get或者post),如果没有指明请求方法,默认使用post处理,然后调用protocolHanlder的初始化方法,最后调用mapperListener的初始化方法,而mapperListener的初始化方法调用的是org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase的init方法,我们重点关注protocolHanlder的初始化方法,具体是实现在AbstractProtocol抽象类中,其直接子类有AbstractAjpProtocol和AbstractHttp11Protocol,分别对应的是两种不同的处理协议,所以协议处理器的初始化方法是在其子抽象类(实现ProtocolHanlder接口的抽象类)来实现的,这里看看AbstractHttp11Protocol的初始化方法:
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled())
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.init",
getName()));
if (oname == null) {
// Component not pre-registered so register it
oname = createObjectName();
if (oname != null) {
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(this, oname,
null);
}
}
if (this.domain != null) {
try {
tpOname = new ObjectName(domain + ":" +
"type=ThreadPool,name=" + getName());
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(endpoint,
tpOname, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
getLog().error(sm.getString(
"abstractProtocolHandler.mbeanRegistrationFailed",
tpOname, getName()), e);
}
rgOname=new ObjectName(domain +
":type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=" + getName());
Registry.getRegistry(null, null).registerComponent(
getHandler().getGlobal(), rgOname, null );
}
String endpointName = getName();
endpoint.setName(endpointName.substring(1, endpointName.length()-1));
try {
endpoint.init();
} catch (Exception ex) {
getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.initError",
getName()), ex);
throw ex;
}
}打断点调试可以知道oname的值是Tomcat:type=ProtocolHandler,port=auto-1,address=”127.0.0.1”,tpOname是Tomcat:type=ProtocolHandler,port=auto-1,address=”127.0.0.1”,rOname是Tomcat:type=GlobalRequestProcessor,name=”http-bio-127.0.0.1-auto-1”,我们重点关注endpoint的init方法,主要完成以下几个过程:
- 设置线程接收数和最大连接数
- 创建线程池,启动监听的线程监听用户请求
- 启动一个线程处理请求
初始化完成Connector就可以启动了,启动阶段调用startInternal方法:
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Validate settings before starting
if (getPort() < 0) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString(
"coyoteConnector.invalidPort", Integer.valueOf(getPort())));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
String errPrefix = "";
if(this.service != null) {
errPrefix += "service.getName(): "" + this.service.getName() + ""; ";
}
throw new LifecycleException
(errPrefix + " " + sm.getString
("coyoteConnector.protocolHandlerStartFailed"), e);
}
mapperListener.start();
}可以看出Connector调用protocolHandler.start()方法,继续看看这个方法的源码:
@Override
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled())
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start",
getName()));
try {
endpoint.start();
} catch (Exception ex) {
getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.startError",
getName()), ex);
throw ex;
}
}这个方法又调用了endpoint.start()方法:
public final void start() throws Exception {
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bind();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
startInternal();
}然后又调用了org.apache.tomcat.util.net.AbstractEndpoint.startInternal()方法:
@Override
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
// Create worker collection
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
startAcceptorThreads();
// Start async timeout thread
Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(new AsyncTimeout(),
getName() + "-AsyncTimeout");
timeoutThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
timeoutThread.setDaemon(true);
timeoutThread.start();
}
}- 设置线程接收数和最大连接数
- 创建线程池,启动监听的线程监听用户请求
- 启动一个线程处理异步请求
这个异步线程是如何执行的呢?
/**
* Async timeout thread
*/
protected class AsyncTimeout implements Runnable {
/**
* The background thread that checks async requests and fires the
* timeout if there has been no activity.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (running) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Iterator<SocketWrapper<Socket>> sockets =
waitingRequests.iterator();
while (sockets.hasNext()) {
SocketWrapper<Socket> socket = sockets.next();
long access = socket.getLastAccess();
if (socket.getTimeout() > 0 &&
(now-access)>socket.getTimeout()) {
processSocketAsync(socket,SocketStatus.TIMEOUT);
}
}
// Loop if endpoint is paused
while (paused && running) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
}
}
}
//processSocket
public boolean processSocketAsync(SocketWrapper<Socket> socket,
SocketStatus status) {
try {
synchronized (socket) {
if (waitingRequests.remove(socket)) {
SocketProcessor proc = new SocketProcessor(socket,status);
ClassLoader loader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
try {
//threads should not be created by the webapp classloader
if (Constants.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(
getClass().getClassLoader());
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
// During shutdown, executor may be null - avoid NPE
if (!running) {
return false;
}
getExecutor().execute(proc);
//TODO gotta catch RejectedExecutionException and properly handle it
} finally {
if (Constants.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
PrivilegedAction<Void> pa = new PrivilegedSetTccl(loader);
AccessController.doPrivileged(pa);
} else {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(loader);
}
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.SocketProcessor的职责是把具体的请求处理过程委派给org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint.Handler,然后根据handler返回的不同SocketState,来决定是否关闭连接或者进行下一轮处理。
public void run() {
boolean launch = false;
synchronized (socket) {
try {
SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;
try {
// SSL handshake
serverSocketFactory.handshake(socket.getSocket());
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("endpoint.err.handshake"), t);
}
// Tell to close the socket
state = SocketState.CLOSED;
}
if ((state != SocketState.CLOSED)) {
if (status == null) {
state = handler.process(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN_READ);
} else {
state = handler.process(socket,status);
}
}
if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {
// Close socket
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Closing socket:"+socket);
}
countDownConnection();
try {
socket.getSocket().close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
}
} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADING ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADING_TOMCAT ||
state == SocketState.UPGRADED){
socket.setKeptAlive(true);
socket.access();
launch = true;
} else if (state == SocketState.LONG) {
socket.access();
waitingRequests.add(socket);
}
} finally {
if (launch) {
try {
getExecutor().execute(new SocketProcessor(socket, SocketStatus.OPEN_READ));
} catch (RejectedExecutionException x) {
log.warn("Socket reprocessing request was rejected for:"+socket,x);
try {
//unable to handle connection at this time
handler.process(socket, SocketStatus.DISCONNECT);
} finally {
countDownConnection();
}
} catch (NullPointerException npe) {
if (running) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.launch.fail"),
npe);
}
}
}
}
}
socket = null;
// Finish up this request
}
}其中的process方法主要完成对request的解析,包括请求头、请求行和请求体 :
//process method of org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor<S>.HttpProcessor extends org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor<S>
@Override
public SocketState process(SocketWrapper<S> socketWrapper)
throws IOException {
RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);
// Setting up the I/O
setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);
getInputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
getOutputBuffer().init(socketWrapper, endpoint);
// Flags
error = false;
keepAlive = true;
comet = false;
openSocket = false;
sendfileInProgress = false;
readComplete = true;
if (endpoint.getUsePolling()) {
keptAlive = false;
} else {
keptAlive = socketWrapper.isKeptAlive();
}
if (disableKeepAlive()) {
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(0);
}
while (!error && keepAlive && !comet && !isAsync() &&
upgradeInbound == null &&
httpUpgradeHandler == null && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// Parsing the request header
try {
setRequestLineReadTimeout();
if (!getInputBuffer().parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {
if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {
break;
}
}
if (endpoint.isPaused()) {
// 503 - Service unavailable
response.setStatus(503);
error = true;
} else {
// Make sure that connectors that are non-blocking during
// header processing (NIO) only set the start time the first
// time a request is processed.
if (request.getStartTime() < 0) {
request.setStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
keptAlive = true;
// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX
request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());
// Currently only NIO will ever return false here
if (!getInputBuffer().parseHeaders()) {
// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it
// instead associate it with the socket
openSocket = true;
readComplete = false;
break;
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
setSocketTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(
sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);
}
error = true;
break;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();
if (logMode != null) {
String message = sm.getString(
"http11processor.header.parse");
switch (logMode) {
case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:
message += sm.getString(
"http11processor.fallToDebug");
//$FALL-THROUGH$
case INFO:
getLog().info(message);
break;
case DEBUG:
getLog().debug(message);
}
}
// 400 - Bad Request
response.setStatus(400);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
if (!error) {
// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);
try {
prepareRequest();
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {
getLog().debug(sm.getString(
"http11processor.request.prepare"), t);
}
// 400 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(400);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
}
if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {
keepAlive = false;
} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&
socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {
keepAlive = false;
}
// Process the request in the adapter
if (!error) {
try {
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);
adapter.service(request, response);
if(keepAlive && !error) { // Avoid checking twice.
error = response.getErrorException() != null ||
(!isAsync() &&
statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus()));
}
setCometTimeouts(socketWrapper);
} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {
error = true;
} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {
error = true;
// The response should not have been committed but check it
// anyway to be safe
if (!response.isCommitted()) {
response.reset();
response.setStatus(500);
response.setHeader("Connection", "close");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
getLog().error(sm.getString(
"http11processor.request.process"), t);
// 500 - Internal Server Error
response.setStatus(500);
adapter.log(request, response, 0);
error = true;
}
}
// Finish the handling of the request
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);
if (!isAsync() && !comet) {
if (error) {
getInputBuffer().setSwallowInput(false);
}
if (response.getStatus() < 200 || response.getStatus() > 299) {
if (expectation) {
// Client sent Expect: 100-continue but received a
// non-2xx response. Disable keep-alive (if enabled) to
// ensure the connection is closed. Some clients may
// still send the body, some may send the next request.
// No way to differentiate, so close the connection to
// force the client to send the next request.
getInputBuffer().setSwallowInput(false);
keepAlive = false;
}
}
endRequest();
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);
// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as
// and error, and update the statistics counter
if (error) {
response.setStatus(500);
}
request.updateCounters();
if (!isAsync() && !comet || error) {
getInputBuffer().nextRequest();
getOutputBuffer().nextRequest();
}
if (!disableUploadTimeout) {
if(endpoint.getSoTimeout() > 0) {
setSocketTimeout(endpoint.getSoTimeout());
} else {
setSocketTimeout(0);
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);
if (breakKeepAliveLoop(socketWrapper)) {
break;
}
}
rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);
}
}首先在Http11Processor的process方法里,会先从socket里读取http请求数据,并解析请求头,构造Request对象和Response对象,然后调用Adapter.service()方法。Adapter.service()完成请求行以及请求体的解析,并把解析出来的信息封装到Request和Response对象中,Adapter(确切说是org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter)是connector和container的桥梁,经过这一步,请求就从connector传递到container里了,Adapter.service()方法之后便将封装了Request以及Response对象的Socket传给Container容器了。
要注意的是:最先处理请求的Request是org.apache.coyote.Request类型,这是一个Tomcat中一个轻量级对象,完成基本的请求处理后很容易被JVM回收,那为什么不直接交给Connector.Request对象处理呢?由于后者是Servlet容器真正传递的对象其完成的职责比前者复杂,这里使用org.apache.coyote.Request主要减轻后者的任务负担,出于性能考虑才这么设计。
具体service方法清单如下:
@Override
public void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req,
org.apache.coyote.Response res)
throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);
if (request == null) {
// Create objects
request = connector.createRequest();
request.setCoyoteRequest(req);
response = connector.createResponse();
response.setCoyoteResponse(res);
// Link objects
request.setResponse(response);
response.setRequest(request);
// Set as notes
req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);
res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);
// Set query string encoding
req.getParameters().setQueryStringEncoding
(connector.getURIEncoding());
}
if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {
response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);
}
boolean comet = false;
boolean async = false;
try {
// Parse and set Catalina and configuration //specific
// request parameters
req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//postParseRequest方法把CoyoteRequest转换为Connector.Request对象
//后一类型的对象才是在Tomcat容器流转时真正传递的对象
boolean postParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);
if (postParseSuccess) {
//check valves if we support async
request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
// 调用Container容器的invoke方法,把请求交给Container容器
connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
if (request.isComet()) {
if (!response.isClosed() && !response.isError()) {
if (request.getAvailable() || (request.getContentLength() > 0 && (!request.isParametersParsed()))) {
// Invoke a read event right away if there are available bytes
if (event(req, res, SocketStatus.OPEN_READ)) {
comet = true;
res.action(ActionCode.COMET_BEGIN, null);
}
} else {
comet = true;
res.action(ActionCode.COMET_BEGIN, null);
}
} else {
// Clear the filter chain, as otherwise it will not be reset elsewhere
// since this is a Comet request
request.setFilterChain(null);
}
}
}
AsyncContextImpl asyncConImpl = (AsyncContextImpl)request.getAsyncContext();
if (asyncConImpl != null) {
async = true;
} else if (!comet) {
request.finishRequest();
response.finishResponse();
if (postParseSuccess &&
request.getMappingData().context != null) {
((Context) request.getMappingData().context).logAccess(
request, response,
System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(),
false);
}
req.action(ActionCode.POST_REQUEST , null);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// Ignore
} finally {
//ignore
}
}从connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);这句代码中可以知道下一步的处理需要交给Container容器了。
经过上面一系列复杂的操作流程,Tomcat的Connector已经完成了protocol.start()方法,返回Connector的startIntenal方法,还有一个步骤要完成就是mapperListener.start()的方法了,整个执行过程比较简单,有两步:
- 执行Connector的startIntenal方法
- 执行MapperListener的startIntenal方法
@Override
public void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
findDefaultHost();
Engine engine = (Engine) connector.getService().getContainer();
addListeners(engine);
Container[] conHosts = engine.findChildren();
for (Container conHost : conHosts) {
Host host = (Host) conHost;
if (!LifecycleState.NEW.equals(host.getState())) {
// Registering the host will register the context and wrappers
registerHost(host);
}
}
}首先注册已初始化的组件,然后为这些组件添加监听器,最后添加容器之间的映射关系。
原文博主地址:rhwayfunn