第5章:
主要介绍了文件I/O更深入的一些内容。
原子操作,将一个系统调用所要完成的所有动作作为一个不可中断的操作,一次性执行;这样可以避免竞争状态(两个或多个共享资源的进程或线程的运行结果是一个无法预期的顺序)。
以独占方式创建一个文件:对文件是否存在的检查和创建文件属于同一个原子操作。防止新建文件的时候因为检查文件是否存在和新建文件之间发生中断(而其他进程也在新建相同文件名的文件),导致两个进程都认为自己是文件的创建者。
向文件尾部追加数据:将文件的偏移量的移动与数据的写操作属于同一个原子操作。防止多个进程同时往同一个文件尾部添加数据导致数据混乱。
fcntl(),对一个打开的文件描述符执行一系列的操作。
1 #include <fcntl.h> 2 3 int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ...);
fd为文件描述符,cmd是决定具体操作,第三个参数(可选)用来设置为不同的类型。
cmd参数(部分),具体查看man手册:
| F_DUPFD | 复制文件描述符 |
| F_GETFD | 获取文件描述符 |
| F_SET_FD | 设置文件描述符 |
| F_GETFL | 获取文件访问模式和状态标志 |
| F_SETFL | 设置文件访问模式和状态标志 |
文件描述符与打开文件之间的关系:多个文件描述符可以指向同一个打开文件。他们的关系如下
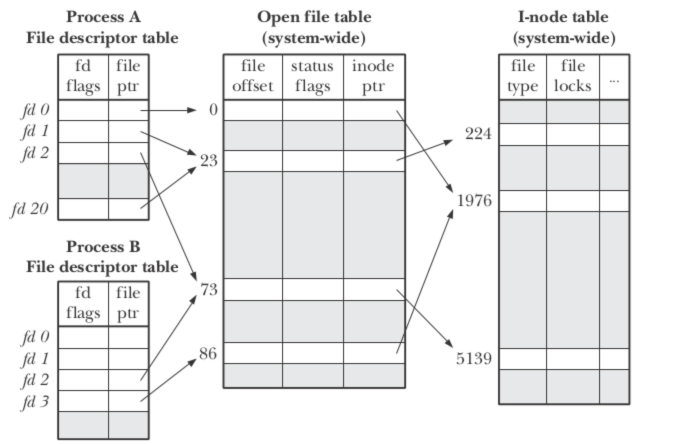
文件描述符表、打开文件表和i-node表。打开文件表的条目成为打开文件句柄(open file handle)。
PS:如果两个不同的文件描述符指向同一个打开文件句柄,这两个文件描述符将共享相同的文件偏移量。(打开文件句柄里包含文件偏移量file offset)。
dup(),复制一个打开的文件描述符oldfd,并返回新的描述符。
dup2(),复制oldfd指定的文件描述符,返回newfd参数指定的描述符。
dup3(),参数与dup2()相同,添加了flags,用于修改系统调用行为。
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 3 int dup(int oldfd); 4 5 int dup2(int oldfd, int newfd); 6 7 int dup3(int oldfd, int newfd, int flags);
成功调用返回新的文件描述符,失败返回-1。
pread()和pwrite(),在指定参数所指定的位置进行文件I/O操作,但不改变文件的偏移量。
1 #include <unistd.h> 2 3 ssize_t pread(int fd, void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset); 4 5 ssize_t pwrite(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset);
fd为文件描述符,buf为缓冲区, count为缓冲区字节数, offset为偏移量。
pread()成功调用返回读取的字节数,失败返回-1
pwrite()成功调用返回写入的字节数,失败返回-1
------------------------省略分散输入和集中输出,截断文件,非阻塞I/O和大文件I/O等一些知识点---------------
练习:
5-1,请使用标准文件I/O系统调用(open()和lseek())和off_t数据类型修改程序清单5-3中的程序。将宏_FILE_OFFSET_BITS的值设置为64进行编译,并测试该程序是否能够成功创建一个大文件。

1 /* 2 * ===================================================================================== 3 * 4 * Filename: large_file.c 5 * 6 * Description: 7 * 8 * Version: 1.0 9 * Created: 2014年03月17日 22时05分50秒 10 * Revision: none 11 * Compiler: gcc 12 * 13 * Author: alan (), alan19920626@gmail.com 14 * Organization: 15 * 16 * ===================================================================================== 17 */ 18 19 #define _FILE_OFFSET_BITS 64 20 #include <sys/stat.h> 21 #include <fcntl.h> 22 #include "tlpi_hdr.h" 23 24 int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ 25 int fd; 26 off_t off; 27 if(argc != 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0) 28 usageErr("%s pathname offset ", argv[0]); 29 30 fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_CREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR); 31 32 if(fd == -1) 33 errExit("open"); 34 35 off = atoll(argv[2]); 36 if(lseek(fd, off, SEEK_SET) == -1) 37 errExit("lseek"); 38 39 if(write(fd, "test", 4) == -1) 40 errExit("write"); 41 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 42 43 }
测试结果:
1 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ ./large_file largefile 10111222333 2 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ ls -l largefile 3 -rw------- 1 lancelot lancelot 10111222337 4月 9 23:22 largefile
5-2,编写一个程序,使用O_APPEND标志并以写方式打开一个已存在的文件,且将文件偏移量置于起始位置,再写入数据。数据会显示在文件中的哪个位置?为什么?

1 /* 2 * ===================================================================================== 3 * 4 * Filename: 5-2.c 5 * 6 * Description: 7 * 8 * Version: 1.0 9 * Created: 2014年03月17日 22时26分51秒 10 * Revision: none 11 * Compiler: gcc 12 * 13 * Author: alan (), alan19920626@gmail.com 14 * Organization: 15 * 16 * ===================================================================================== 17 */ 18 19 #include <sys/stat.h> 20 #include <ctype.h> 21 #include <fcntl.h> 22 #include "tlpi_hdr.h" 23 24 int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ 25 int fd; 26 off_t off; 27 ssize_t numWritten; 28 29 if(argc != 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0) 30 usageErr("%s file", argv[0]); 31 32 fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_APPEND, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR); 33 if(fd == -1) 34 errExit("open"); 35 36 off = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET); 37 if(off == -1) 38 errExit("lseek"); 39 40 numWritten = write(fd, "Kevin Durant ", 13); 41 if(numWritten == -1) 42 errExit("write"); 43 44 close(fd); 45 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 46 }
测试结果:
1 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ cat t1 2 This is the second line. 3 This is the third line. 4 This is the append line. 5 6 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ ./write_append t1 7 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ cat t1 8 This is the second line. 9 This is the third line. 10 This is the append line. 11 12 Kevin Durant
5-3,本习题的设计目标在于展示为何以O_APPEND标志打开文件来保障操作的原子性是必要的。请编写一程序,可接收多达3个命令行参数:
$ automic_append filename num-bytes [x]
该程序应打开制定的文件,然后以每次调用write()写入一个字节的方式,向文件尾部追加num-bytes个字节。缺省情况下,程序使用O_APPEND标志打开文件,但若存在第三个命令行参数(x),那么打开文件时将不再使用O_APPEND标志,代之以调用write()前调用lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END)。同时运行该程序的两个实例,不带x参数,将100万字节写入同一个文件:
$ automic_append f1 1000000 & automic_append f1 1000000
重复上述操作,将数据写入另一个文件,但运行时加入x参数
$ automic_append f2 1000000 x & automic_append f2 1000000 x
使用ls -l命令检查文件f1和f2的大小, 并解释两文件大小不同的原因。

1 /* 2 * ===================================================================================== 3 * 4 * Filename: atomic_append.c 5 * 6 * Description: 7 * 8 * Version: 1.0 9 * Created: 2014年03月17日 22时46分49秒 10 * Revision: none 11 * Compiler: gcc 12 * 13 * Author: alan (), alan19920626@gmail.com 14 * Organization: 15 * 16 * ===================================================================================== 17 */ 18 19 #include <sys/stat.h> 20 #include <fcntl.h> 21 #include "tlpi_hdr.h" 22 23 int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ 24 int i, fd, flags, numBytes; 25 off_t off; 26 ssize_t numWritten; 27 28 29 flags = O_RDWR | O_CREAT; 30 if(argc < 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0 ) 31 usageErr("%s filename num-bytes [x]"); 32 33 if(argc != 4) 34 flags = flags | O_APPEND; 35 36 numBytes = getInt(argv[2], 0, "num-bytes"); 37 38 fd = open(argv[1], flags, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR); 39 if(fd == -1) 40 errExit("open"); 41 42 /*if(argc == 4) 43 if(lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END) == -1) 44 errExit("lseek"); 45 46 */ 47 48 for(i = 0; i < numBytes; ++i){ 49 if(argc > 3 && argv[3] == "x") 50 if(lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END) == -1) 51 errExit("lseek"); 52 53 if(write(fd, "A", 1) != 1) 54 fatal("write() failed"); 55 } 56 57 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 58 }
测试结果:
1 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ ls -l f1 f2 2 -rw------- 1 lancelot lancelot 2000000 4月 9 23:45 f1 3 -rw------- 1 lancelot lancelot 1000000 4月 9 23:45 f2
5-4,使用fcntl()和close()来实现dup()和dup2()。务必牢记dup2()需要处理的一种特殊情况,即oldfd与newfd相等。这时,应检查oldfd是否有效,测试fcntl(oldfd, F_GETFL)是否成功就能达到这一目标。若oldfd无效,则dup2()将返回-1,并将errno置为EBADF。

1 /* 2 * ===================================================================================== 3 * 4 * Filename: 5-4.c 5 * 6 * Description: 7 * 8 * Version: 1.0 9 * Created: 2014年03月19日 08时48分46秒 10 * Revision: none 11 * Compiler: gcc 12 * 13 * Author: alan (), alan19920626@gmail.com 14 * Organization: 15 * 16 * ===================================================================================== 17 */ 18 19 #include <sys/stat.h> 20 #include <fcntl.h> 21 #include "tlpi_hdr.h" 22 23 int Dup(int oldfd); 24 25 int Dup2(int oldfd, int newfd); 26 27 int main(){ 28 int fd; 29 int newfd; 30 if((fd = open("t1", O_RDONLY)) == -1) 31 errExit("open"); 32 33 //newfd = fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, fd+1); 34 newfd = Dup(fd); 35 if(newfd == -1) 36 errExit("Dup"); 37 38 printf("old fd is %d, new fd is %d ", fd, newfd); 39 40 printf("Input the new fd:"); 41 scanf("%d", &newfd); 42 43 /*if(fcntl(oldfd, F_GETFL) == -1) 44 errExit("fd is ") 45 */ 46 47 newfd = Dup2(fd, newfd); 48 if(newfd == -1) 49 errExit("Dup2"); 50 printf("old fd is %d, new fd is %d ", fd, newfd); 51 52 exit(EXIT_SUCCESS); 53 } 54 55 int Dup(int oldfd){ 56 int newfd = fcntl(oldfd, F_DUPFD, oldfd+1); 57 return newfd; 58 } 59 60 int Dup2(int oldfd, int newfd){ 61 int fd = newfd; 62 if(fcntl(oldfd, F_GETFL) == -1){ 63 errno = EBADF; 64 return -1; 65 } 66 if(oldfd == newfd) 67 return newfd; 68 else{ 69 if(fcntl(newfd, F_GETFL) != -1) 70 close(newfd); 71 newfd = fcntl(oldfd, F_DUPFD, fd); 72 if(newfd != fd) 73 newfd = fcntl(newfd, F_SETFD, fd); 74 75 return newfd; 76 } 77 }
测试结果:
1 lancelot@debian:~/Code/tlpi$ ./my_dup 2 old fd is 3, new fd is 4 3 Input the new fd:13 4 old fd is 3, new fd is 13
