React Learning(Day2)(2019.7.6)
日常挤牙膏
一、拆分组件与组件之间的传值
- 1.父组件中加入子组件
import Child from './Child'
return(
<Child/>
)
-
2.父组件向子组件传数据
- 父组件给子组件传递数据,通过标签属性传递,既可以传递数据,又可以传递方法,eg:
<Child content={item} //data index={index} //data deleteItem={this.handleItemDlete.bind(this)} //function />- 子组件接受父组件传递的数据,通过
this.props.content使用 - 子组件接受父组件传递的函数,传值时要绑定父组件this,子组件再通过
this.props.deleteItem(this.props.index);调用
-
3.到达此步的源代码
- Todolist.js
import React, {Component,Fragment} from 'react'
import './style.css'
import TodoItem from './TodoItem'
class Todolist extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
inputValue: '',
list: []
};
}
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<div>
{/* 注释写法1 */}
{
// 注释写法2
}
<label htmlFor='insertArea'>输入内容:</label>
{/* 注意for用htmlFor代替 */}
<input
id='insertArea'
className='input' // 注意class用className代替
value={this.state.inputValue}
onChange={this.handleInputChange.bind(this)} //函数的this绑定组件对象的this
/>
<button onClick={this.handleBtnClick.bind(this)}>提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
{
this.state.list.map((item,index) => {
return (
<div>
<TodoItem
content={item}
index={index}
deleteItem={this.handleItemDlete.bind(this)} // this绑定到父组件
/>
{/* <li
key={index}
onClick={this.handleItemDlete.bind(this,index)}
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{__html: item}}
>
</li> */}
</div>
)
})
}
</ul>
</Fragment>
);
}
handleInputChange(e){
// console.log(this);
this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value
});
}
handleBtnClick(){
this.setState({
list: [...this.state.list,this.state.inputValue],
inputValue: ''
});
}
handleItemDlete(index){
// immutable
// state 不允许我们做任何更改,可以修改副本
const list = [...this.state.list];
list.splice(index,1);
this.setState({
list:list
})
}
}
export default Todolist;
- TodoItem.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class TodoItem extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleClick=this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
render() {
return (
<li
onClick={this.handleClick}
//key={this.props.index}
>
{this.props.content}
</li>
)
}
handleClick() {
this.props.deleteItem(this.props.index);
//alert(this.props.index);
}
}
export default TodoItem
二、代码优化
优化后代码如下:
- Todolist.js
import React, {Component,Fragment} from 'react'
import TodoItem from './TodoItem'
import './style.css'
class Todolist extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
inputValue: '',
list: []
};
this.handleInputChange=this.handleInputChange.bind(this);
this.handleBtnClick=this.handleBtnClick.bind(this);
this.handleItemDlete=this.handleItemDlete.bind(this);
}
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<div>
<label htmlFor='insertArea'>输入内容:</label> {/* 注意for用htmlFor代替 */}
<input
id='insertArea'
className='input' // 注意class用className代替
value={this.state.inputValue}
onChange={this.handleInputChange} //函数的this绑定组件对象的this
/>
<button onClick={this.handleBtnClick}>提交</button>
</div>
<ul>
{this.getTodoItem()}
</ul>
</Fragment>
);
}
getTodoItem(){
return this.state.list.map((item,index) => {
return (
<TodoItem
key={index}
content={item}
index={index}
deleteItem={this.handleItemDlete} // this绑定到父组件
/>
)
})
}
handleInputChange(e){
// console.log(this);
// 旧版
/* this.setState({
inputValue: e.target.value
}); */
//新版,对象变函数,异步,将e.target.value存在外层
const value = e.target.value;
this.setState(() => ({
inputValue: value
}))
}
handleBtnClick(){
/*this.setState({
list: [...this.state.list,this.state.inputValue],
inputValue: ''
});*/
this.setState((prevState) => ({
list: [...prevState.list,prevState.inputValue],
inputValue: ''
}))
}
handleItemDlete(index){
/*
const list = [...this.state.list];
list.splice(index,1);
this.setState({
list:list
})
*/
this.setState((prevState)=>{
const list = [...prevState.list];
list.splice(index,1);
return{list}
})
}
}
export default Todolist;
- TodoItem.js
import React, { Component } from 'react'
class TodoItem extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleClick=this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
render() {
const {content} = this.props;
return (
<div
onClick={this.handleClick}
//key={this.props.index}
>
{content}
</div>
)
}
handleClick() {
const {deleteItem,index} = this.props;
deleteItem(index);
//alert(this.props.index);
}
}
export default TodoItem
三、React开发一些概念
1、声明式开发
(与其对应的是命令式开发,直接操作dom)
我们只是操作数据,React自己操作dom。React是数据驱动的框架,数据变化,页面自动变化。可以减少DOM操作量
2、可以与其他框架并存
只负责自己组件挂载的节点
3、组件化
页面由一个个小组件构成
4、单向数据流
父组件可以向子组件传递数据,但子组件只读不能修改;
子组件可以使用父组件方法改数据。
5、视图层框架
React修改数据可能会很复杂,所以只负责页面,其他工作由其他框架flux,redux等完成
6、函数式编程
使其容易实现前端函数化测试
四、React开发插件安装
1.scientific上网,用Chrome浏览器安装React Developer Tools插件
2.打开页面,该插件灰色表示没用react开发,红色表示处于react开发阶段,黑色表示react编写已在线上状态。
五、传递参数的校验和默认值
propTypes
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
TodoItem.propTypes = {
test: PropTypes.string.isRequired, //要求一定检验
comtent: PropTypes.string,
deleteItem: PropTypes.func,
index: PropTypes.number
}
defaultProps
TodoItem.defaultProps = {
test: 'hello world'
}
参考官网地址:https://reactjs.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html
六、Props,State 与 render 函数
当组件的state或者props发生改变时,render函数就会重新执行
父组件的render函数被运行时,他的子组件的render都会被重新运行一次
七、什么是虚拟DOM
第一种:
- 1.state 数据
- 2.jsx 模板
- 3.数据 + 模板 结合,生成真实的DOM,来显示
- 4.state 发生改变
- 5.数据 + 模板 结合,生成真实的DOM,替换原始的DOM
缺陷:
第一次生成了一个完整的DOM片段
第二次生成了一个完整的DOM片段
第二次的DOM替换第一次的DOM,非常耗性能
改良:
- 1.state 数据
- 2.jsx 模板
- 3.数据 + 模板 结合,生成真实的DOM,来显示
- 4.state 发生改变
- 5.数据 + 模板 结合,生成真实的DOM,并不直接替换原始的DOM
- 6.对比新(DocumentFragment)旧DOM,找差异
- 7.找出input框发生变化
- 8.只用新的DOM中的input元素,替换老的DOM中的input元素
缺陷:
性能提升不明显
再改良:
- 1.state 数据
- 2.JSX模版
- 3.数据+模版结合,生成虚拟DOM (虚拟DOM就是一个JS对象,用它来描述真实DOM) (损耗了性能)
['div', {id: 'abc'}, ['span', {}, 'hello world']] - 4.用虚拟DOM的结构,生成真实的DOM,来显示
<div id='abc'><span>hello world</span></div> - 5.state 发生变化
- 6.数据 + 模板 生成新的虚拟DOM (极大地提升性能)
['div', {id: 'abc'}, ['span', {}, 'bye bye']] - 7.比较原始虚拟DOM和新的虚拟DOM的区别,找到区别是span中内容 (极大地提升性能)
- 8.直接操作DOM, 改变span中的内容
优点:
- 1.性能提升了
- 2.它使得跨端应用得以实现。React Native
- 虚拟DOM -> 真实DOM -> 网页
- 虚拟DOM -> 原生应用组件 -> 原生应用
八、深入理解虚拟DOM
JSX -> JS对象 -> 真实的DOM
JSX -> JS对象实现原理
return <div>item</div>
<=>
return React.createElement('div',{},item)
即:JSX -> createElement -> JS对象
九、虚拟DOM中的Diff算法
-
1.同层虚拟DOM比对,由上到下,一层变化,该层下面不再比对,该层及以下全部重新渲染
-
2.给节点绑定key值的原因:建立正确关系,方便对比。
-
3.给节点绑定key值不用index的原因:index会变化,失去key的价值,但可以用value作为key值。注意用稳定的参数作为key值才是正确的做法。eg:
<TodoItem
key={item}
/>
十、React中ref的使用
- 1.ref帮助我们在react中直接获取DOM元素,最好少用
- 2.eg:
<ul ref={(ul)=>{this.ul = ul}}>
{this.getTodoItem()}
</ul>
handleBtnClick(){
this.setState((prevState) => ({
list: [...prevState.list,prevState.inputValue],
inputValue: ''
}),()=>{
console.log(this.ul.querySelectorAll('div').length);
})
}
十一、React中的生命周期函数
1. 生命周期函数指在某一时刻组件会自动调用执行的函数。
2. eg:
- render() // state、props变化时自动调用
- constructor() // 组件创建时调用
3. 一些说明
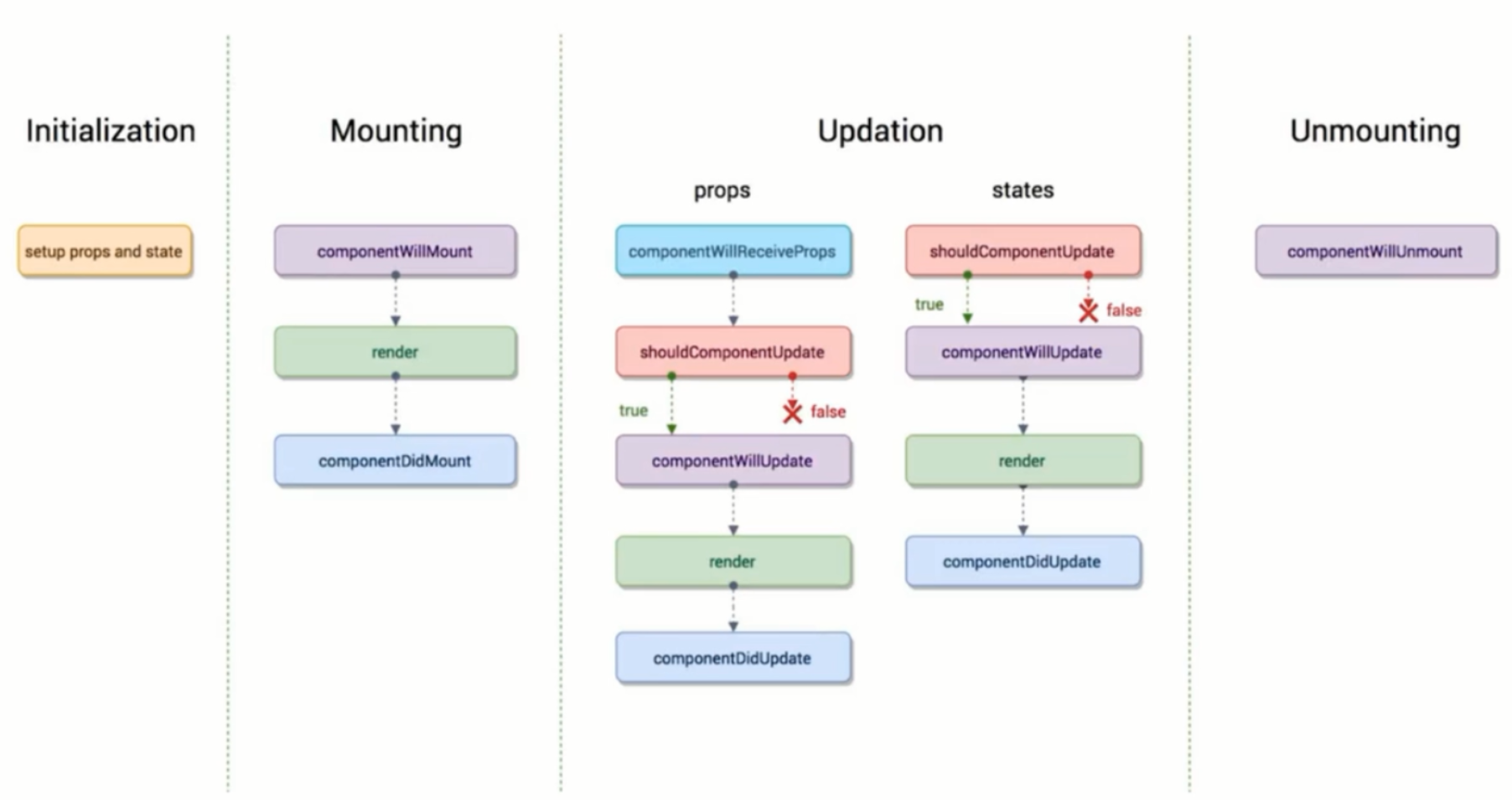
(react生命周期.png)
//1.初始化阶段
constructor(){}
//2.挂载阶段
componentWillMount(){} //①在组件即将被挂载到页面的时刻自动执行
render(){} //②挂载页面时执行
componentDidMount(){} //③组件被挂载到页面之后,自动被执行
//3.更新流程
//(1)props发生变化
//一个组件要从父组件接受参娄文
//只要父组件的render函数被重新执行了,子组件的这个生命周期函数就会被执行
componentWillReceiveProps(){}
shouldComponentUpdate(){return true;//false不更新组件,结束} //组件更新前自动执行
componentWillUpdate(){} //组件更新前shouldComponentUpdate返回true自动执行,返回false不执行
render(){}
componentDidUpdate(){} //组件更新后自动执行
//(2)states发生变化
shouldComponentUpdate(){return true;//false不更新组件,结束} //组件更新前自动执行
componentWillUpdate(){} //组件更新前shouldComponentUpdate返回true自动执行,返回false不执行
render(){}
componentDidUpdate(){} //组件更新后自动执行
//4.卸载阶段
//当这个组件即将被从页面中剔除的时候,会被执行
componentWillUnmount(){}
十二、生命周期函数应用场景
1. shouldComponentUpdate可以避免子组件在父组件更新时重复渲染,实现性能优化,子组件添加如下代码
shouldComponentUpdate (nextProps, nextState) {
if ( nextProps . content !== this. props. content) {
return true ;
}else {
return false;
}
}
2. ajax请求放在componentDidMount函数里
- 安装
axios
yarn add axios #或者 npm install axios -S
- 引入
axios和发送请求
import axios from 'axios'
componentDidMount() {
axios.get('/api/todolist')
.then(()=>{alert('succ')})
.catch(()=>{alert('error')})
}
十三、使用Charles进行接口数据模拟
1.install Charles Software
- 官网下载安装包安装:https://www.charlesproxy.com
- 破解教程:https://www.cnblogs.com/rrl92/p/7928770.html
- 破解工具:https://www.zzzmode.com/mytools/charles/
2.use Charles
Tools>Map local>
Map From
Protocol:http
Host:localhost
Port:3000
Path:api/todolist
Map to
Local path:C:UsersAdministratorDesktop odolist.json
todolist.json如下
["Dell","Lee","IMOOC"]
十四、引入css样式
部分css代码
.show{
opacity: 1;
transition: all 1s ease-in;
}
.hide{
opacity: 0;
transition: all 1s ease-in;
}
部分js代码
import './style.css'
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
show:true
};
this.handleToggle=this.handleToggle.bind(this);
}
render() {
return (
<div className={this.state.show?'show':'hide'}>hello</div>
<button onClick={this.handleToggle}>CSStoggle</button><br/>
)
}
handleToggle(){
this.setState({
show: this.state.show?false:true
})
}