目标:
1,掌握Resource接口的使用。
2,掌握ResourceLoader接口的使用。
3,掌握各种资源数据的读取操作。
具体内容:
要想进行资源读取操作,首先想到IO包中提供的操作类。
但是,有如下问题:
1,这些类的互相操作,难道太高,很多人对IO领悟并不是很彻底。
2,IO支持的读取有限且复杂。
-读取jar包里面的文件呢?
-读取不同资源文件的时候,操作不统一,例如:读取文件,网络读取;
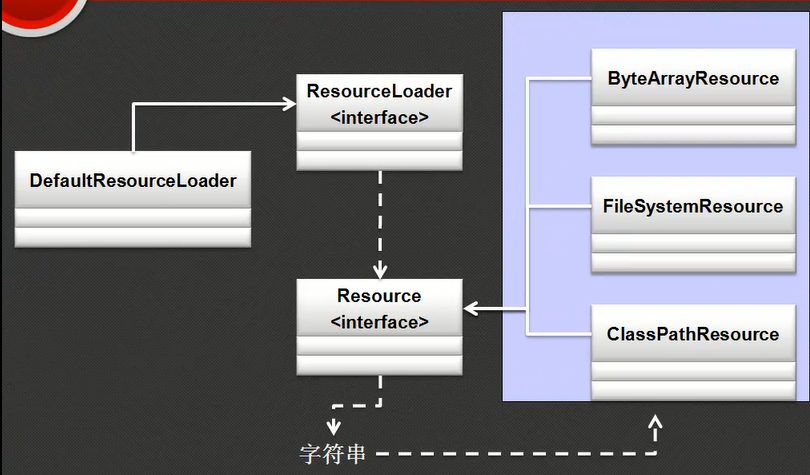
所以在整个spring设计过程中充分考虑了IO操作中的种种操作问题,提供了新的资源访问处理支持。而整个操作的关键在于:Resource接口。这个接口表示所有的可用资源读取,
而这个接口定义了如下几个常用方法:
1,取得资源的数据长度:public long contentLength()。
2,判断资源是否存在:public boolean exists()
3,取得资源对应的文件信息:public File getFile();
4,取得资源完整网络路径:getUrl()
5,判断资源是否打开:public boolean isOpen()
6,最后一次修改日期:public long lastModifid()
7,创建一个操作的资源:public Resource createRelative()
Resource本身是一个接口,要想使用这个接口,需要使用他的子类:
ByteArrayResource (内存读取),ClassPathResource(ClassPath读取),FileSystemResource(文件读取)
读取不同资源
首先按照基本开发进行基本资源的读取。
1,读取内存资源:ByteArrayResource
构造方法:public ByteArrayResource(byte [] byteArray);
范例:实现内存读取:
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.ByteArrayResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public class ByteResource { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //此处的内存处理流与之前IO里面的byteArrayInputStream使用形式类似 Resource resource=new ByteArrayResource("helloworld".getBytes()); //就取得更多资源信息来说,比InputStream强 System.out.println("数据长度"+resource.contentLength()); //如果给出的是InputStream,那么可以利用Scannner简化读取。 //getInputStream是通过InputStreamSource父接口继承而来的方法 Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
输出结果:
数据长度10
helloworld
文件读取:FileSystemResource
构造方法:public FileSystemResource(File file);--直接传入File
构造方法:public FileSystemResource(String path);--直接写文件路径
范例:进行文件读取:
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.ByteArrayResource; import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; public class FileResource { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //此处的内存处理流与之前IO里面的byteArrayInputStream使用形式类似 Resource resource=new FileSystemResource("D:"+File.separator+"test.txt"); //就取得更多资源信息来说,比InputStream强 System.out.println("数据长度:"+resource.contentLength()); //如果给出的是InputStream,那么可以利用Scannner简化读取。 //getInputStream是通过InputStreamSource父接口继承而来的方法 Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); //表示/n是换行符,而不是结束符 scan.useDelimiter(" "); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
3,CLASSPATH读取:CLASSPATHRESOURCE
构造方法:public ClassPathResource(String path):
只要保存在了CLASSPATH环境下的路径信息都可以通过此类读取进来。
范例:读取applicationContext.XML文件
如果要进行文件的读取,必须要有完整的路径,也就是说,默认情况下,要想读取指定的资源,那么必须想办法拼凑出路径,
(还需要取得一系列的系统属性,等一系列操作)。
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;; public class ClassResource { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //此处的内存处理流与之前IO里面的byteArrayInputStream使用形式类似 Resource resource=new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml"); //就取得更多资源信息来说,比InputStream强 System.out.println("数据长度:"+resource.contentLength()); //如果给出的是InputStream,那么可以利用Scannner简化读取。 //getInputStream是通过InputStreamSource父接口继承而来的方法 Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); //表示/n是换行符,而不是结束符 scan.useDelimiter(" "); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
输出结果:
ResourceLoader接口
ResourceLoader接口主要作用是进行ResourceLoader接口对象实例化使用的。这个接口的定义如下:
1,读取指定的资源信息,:public Resource getResource(String location);
2,取得类加载器:public ClassLoader getClassLoader();
ResourceLoader是一个接口,于是要使用这个接口,必须知道它的子类:
DefaultResourceLoader,利用这个子类就可以实现ResourceLoader接口实例化。
但是资源操作的问题并不在于Resource或者ResourceLoader接口,以及其一堆子类,而关键在于这个定位的字符串:
文件读取资源:“file:路径”;
CLASSPATH读取:“classpath:路径”;
网络读取:“http://路径”;
范例:进行文件读取:
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; public class FileResourceLoader { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ResourceLoader loader=new DefaultResourceLoader(); Resource resource=loader.getResource("file:D:"+File.separator+"test.txt"); System.out.println("数据长度:"+resource.contentLength()); Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); scan.useDelimiter(" "); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
路径只写了一个字符串,就可以读取了。
范例:读取ClassPath路径
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; public class ClassPathResourceLoader { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ResourceLoader loader=new DefaultResourceLoader(); Resource resource=loader.getResource("classpath:applicationContext.xml"); System.out.println("数据长度:"+resource.contentLength()); Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); scan.useDelimiter(" "); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
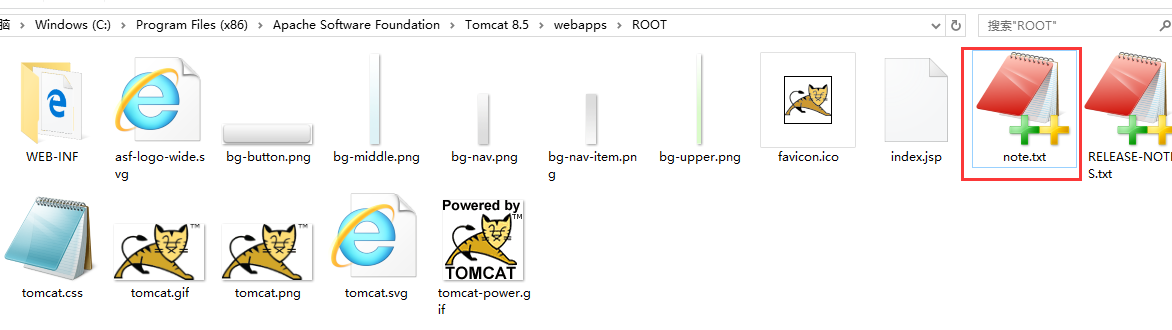
范例:读取网络资源
在tomcat这个目录下新建一个note.txt文件。
读取代码:
package com.Resource.Demo; import java.util.Scanner; import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader; import org.springframework.core.io.Resource; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; public class HttpResourceLoader { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ResourceLoader loader=new DefaultResourceLoader(); Resource resource=loader.getResource("http://localhost/note.txt"); System.out.println("数据长度:"+resource.contentLength()); Scanner scan=new Scanner(resource.getInputStream()); scan.useDelimiter(" "); while(scan.hasNext()) { System.out.println(scan.next()); } } }
所有的读取的操作过程之中,可以清楚的看到,都是利用字符串来进行资源定位,
核心的设计思想就是:利用合理的字符串格式,来进行更加复杂的操作。