一、简介
装饰(Decorator)模式被称为包装(Wrapper)模式。 装饰模式以对客户端透明的方式扩展对象的功能,是继承关系的一个替代方案。并可以在不创造更多子类的情况下,将对象的功能加以扩展。
装饰模式有如下特点:
- 装饰对象和真实对象有相同的接口。这样客户端对象就可以 以和真实对象相同的方式与装饰对象进行交互。
- 装饰对象包含一个真实对象的引用,当装饰对象接收所有来自客户端的请求。它把这些请求转发给真实的对象。
- 装饰对象可以在转发这些请求以前或以后增加一些附加功能。这样就确保了在运行时,不用修改给定对象的结构就可以在外部增加附加的功能。在面向对象的设计中,通常是通过继承来实现对给定类的功能扩展。
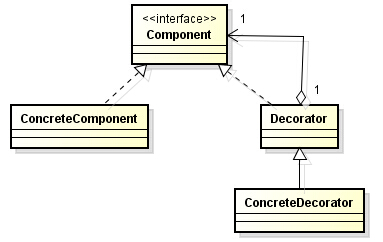
装饰模式的角色:
- 抽象构件角色(Component):给出一个抽象接口,以规范准备接收附加责任的对象。
- 具体构件角色(Concrete Component):定义一个将要接收附加责任的类。
- 装饰角色(Decorator):持有一个构件(Component)对象的引用,并定义一个与抽象构件接口一致的接口
- 具体装饰角色(Concrete Decorator):负责给构件对象“贴上”附加的责任。
装饰模式类图如下:
二、java JDK 中的装饰模式
java JDK中的IO流就是用到了装饰模式。其中InputStream,OutputStream,Reader,Writer就已经使用了装饰模式。以下分析以InputStream为例:
InputStream相关继承结构如下:

InputStream 是一个抽象类。
FileInputStream 继承了InputStream类。
FilterInputStream 也继承了InputStream类,并且持有一个InputStream类型的引用。
BufferedInputStream 等类继承了FilterInputStream类。
这里是使用到的就是一个装饰模式。InputStream就是抽象构件角色,FileInputStream、DataInputStream就是具体构件角色;而FilterInputStream就是装饰角色;BufferedInputStream、ByteArrayInputStream等类就是具体构件角色。
我们一般这样使用FileInputStream:
InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(ClassLoader.getSystemResource("").getPath() + "test.txt"))); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while((len = is.read(bytes)) != -1){ System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len)); }
调用read(byte b[])方法的时候过程如下:
1、首先会调用父类FilterInputStream的read(byte b[])方法,因为BufferedInputStream没有重写该方法。
FilterInputStream类中read(byte b[]) 方法代码如下:
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException { return read(b, 0, b.length); }
2、根据FilterInputStream类中read(byte b[]) 方法的处理,接着就会调用BufferedInputStream类中的read(byte b[], int off, int len)方法。
BufferedInputStream类中的read(byte b[], int off, int len)方法代码如下:
1 public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len)throws IOException{ 2 getBufIfOpen(); // Check for closed stream 3 if ((off | len | (off + len) | (b.length - (off + len))) < 0) { 4 throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(); 5 } else if (len == 0) { 6 return 0; 7 } 8 9 int n = 0; 10 for (;;) { 11 int nread = read1(b, off + n, len - n);//此处进行读操作 12 if (nread <= 0) 13 return (n == 0) ? nread : n; 14 n += nread; 15 if (n >= len) 16 return n; 17 // if not closed but no bytes available, return 18 InputStream input = in; 19 if (input != null && input.available() <= 0) 20 return n; 21 } 22 } 23 24 /** 25 * 进行读取 26 */ 27 private int read1(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException { 28 int avail = count - pos; 29 if (avail <= 0) { 30 /* If the requested length is at least as large as the buffer, and 31 if there is no mark/reset activity, do not bother to copy the 32 bytes into the local buffer. In this way buffered streams will 33 cascade harmlessly. */ 34 if (len >= getBufIfOpen().length && markpos < 0) { 35 return getInIfOpen().read(b, off, len);//调用FileInputStream对象的read方法。真正完成读操作 36 } 37 fill(); 38 avail = count - pos; 39 if (avail <= 0) return -1; 40 } 41 int cnt = (avail < len) ? avail : len; 42 System.arraycopy(getBufIfOpen(), pos, b, off, cnt); 43 pos += cnt; 44 return cnt; 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * 返回创建BufferedInputStream对象时候传递进来的FileInputStream对象 49 */ 50 private InputStream getInIfOpen() throws IOException { 51 InputStream input = in; 52 if (input == null) 53 throw new IOException("Stream closed"); 54 return input; 55 }
3、在read(byte b[], int off, int len)方法中进行额外缓存处理,并FileInputStream中的read(byte b[], int off, int len)方法,从而完成对具体构件角色的调用。
这里就是BufferedInputStream对FileInputStream进行装饰(提供了缓冲功能),其他OutputStream,Reader,Writer也是类似的。
三、装饰模式实现
1、抽象构件角色
package com.decorator; /** * 抽象构件角色(类似InputStream) */ public interface Component { public void doSomething(); }
2、具体构件角色
package com.decorator; /** * 具体构件角色(类似FileInputStream) */ public class ConcreteComponent implements Component { @Override public void doSomething() { System.out.println("dosomething"); } }
3、装饰角色
package com.decorator; /** * 装饰角色(类似FilterInputStream) * */ public class Decorator implements Component { private Component component;//构件角色或装饰角色的引用 public Decorator(Component component) { this.component = component; } /** * 如果需要添加功能,则子类应该重写该方法 */ public void doSomething() { this.component.doSomething();//构件角色或装饰角色的方法 } }
4.1、具体装饰角色1
package com.decorator; /** * 具体装饰角色(类似BufferedInputStream) * */ public class ConcreteDecorator1 extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecorator1(Component component) { super(component);// 调用父类的构造方法,并将对象设置进去 } @Override public void doSomething() { super.doSomething();// 调用父类方法 this.addFunction();// 添加新的功能 } private void addFunction() { System.out.println("add new function from ConcreteDecorator1"); } }
4.2、具体装饰角色2
package com.decorator; /** * 具体装饰角色(类似BufferedInputStream) * */ public class ConcreteDecorator2 extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecorator2(Component component) { super(component);// 调用父类的构造方法,并将对象设置进去 } @Override public void doSomething() { super.doSomething();// 调用父类方法 this.addFunction();// 添加新的功能 } private void addFunction() { System.out.println("add new function from ConcreteDecorator2"); } }
5、调用程序
import java.io.IOException; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Component component = new ConcreteComponent();//具体构件角色 Component decorator1 = new ConcreteDecorator1(component);//具体装饰角色1 Component decorator2 = new ConcreteDecorator2(decorator1);//具体装饰角色2 decorator2.doSomething();//该方法会完成对具体构建角色方法的调用 } }
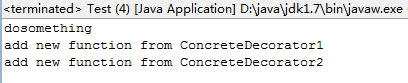
调用结果如下: