判断js中的数据类型有一下几种方法:typeof、instanceof、 constructor、 prototype、 $.type()/jquery.type(),接下来主要比较一下这几种方法的异同。
先举几个例子:
var a = "iamstring."; var b = 222; var c= [1,2,3]; var d = new Date(); var e = function(){alert(111);}; var f = function(){this.name="22";};
1、最常见的判断方法:typeof
alert(typeof a) ------------> string alert(typeof b) ------------> number alert(typeof c) ------------> object alert(typeof d) ------------> object alert(typeof e) ------------> function alert(typeof f) ------------> function 其中typeof返回的类型都是字符串形式,需注意,例如: alert(typeof a == "string") -------------> true alert(typeof a == String) ---------------> false 另外typeof 可以判断function的类型;在判断除Object类型的对象时比较方便。
2、判断已知对象类型的方法: instanceof
alert(c instanceof Array) ---------------> true alert(d instanceof Date) alert(f instanceof Function) ------------> true alert(f instanceof function) ------------> false 注意:instanceof 后面一定要是对象类型,并且大小写不能错,该方法适合一些条件选择或分支。
3、根据对象的constructor判断: constructor
alert(c.constructor === Array) ----------> true alert(d.constructor === Date) -----------> true alert(e.constructor === Function) -------> true 注意: constructor 在类继承时会出错 eg: function A(){}; function B(){}; A.prototype = new B(); //A继承自B var aObj = new A(); alert(aobj.constructor === B) -----------> true; alert(aobj.constructor === A) -----------> false; 而instanceof方法不会出现该问题,对象直接继承和间接继承的都会报true: alert(aobj instanceof B) ----------------> true; alert(aobj instanceof B) ----------------> true; 言归正传,解决construtor的问题通常是让对象的constructor手动指向自己: aobj.constructor = A; //将自己的类赋值给对象的constructor属性 alert(aobj.constructor === A) -----------> true; alert(aobj.constructor === B) -----------> false; //基类不会报true了;
4、通用但很繁琐的方法: prototype
alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(a) === ‘[object String]’) -------> true; alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(b) === ‘[object Number]’) -------> true; alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(c) === ‘[object Array]’) -------> true; alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(d) === ‘[object Date]’) -------> true; alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(e) === ‘[object Function]’) -------> true; alert(Object.prototype.toString.call(f) === ‘[object Function]’) -------> true; 大小写不能写错,比较麻烦,但胜在通用。
5、无敌万能的方法:jquery.type()
如果对象是undefined或null,则返回相应的“undefined”或“null”。 jQuery.type( undefined ) === "undefined" jQuery.type() === "undefined" jQuery.type( window.notDefined ) === "undefined" jQuery.type( null ) === "null" 如果对象有一个内部的[[Class]]和一个浏览器的内置对象的 [[Class]] 相同,我们返回相应的 [[Class]] 名字。 (有关此技术的更多细节。 ) jQuery.type( true ) === "boolean" jQuery.type( 3 ) === "number" jQuery.type( "test" ) === "string" jQuery.type( function(){} ) === "function" jQuery.type( [] ) === "array" jQuery.type( new Date() ) === "date" jQuery.type( new Error() ) === "error" // as of jQuery 1.9 jQuery.type( /test/ ) === "regexp" 其他一切都将返回它的类型“object”。
通常情况下用typeof 判断就可以了,遇到预知Object类型的情况可以选用instanceof或constructor方法,实在没辙就使用$.type()方法。
=====================================================================================================
1.typeof
1 console.log(typeof "");
2 console.log(typeof 1);
3 console.log(typeof true);
4 console.log(typeof null);
5 console.log(typeof undefined);
6 console.log(typeof []);
7 console.log(typeof function(){});
8 console.log(typeof {});
看看控制台输出什么
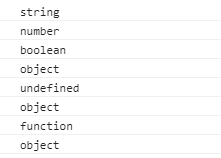
可以看到,typeof对于基本数据类型判断是没有问题的,但是遇到引用数据类型(如:Array)是不起作用的。
2.instanceof
1 console.log("1" instanceof String);
2 console.log(1 instanceof Number);
3 console.log(true instanceof Boolean);
4 // console.log(null instanceof Null);
5 // console.log(undefined instanceof Undefined);
6 console.log([] instanceof Array);
7 console.log(function(){} instanceof Function);
8 console.log({} instanceof Object);
暂且不考虑null和undefined(这两个比较特殊),看看控制台输出什么
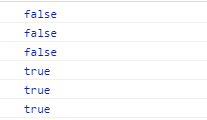
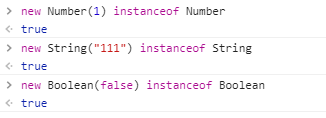
可以看到前三个都是以对象字面量创建的基本数据类型,但是却不是所属类的实例,这个就有点怪了。后面三个是引用数据类型,可以得到正确的结果。如果我们通过new关键字去创建基本数据类型,你会发现,这时就会输出true,如下:
接下再来说说为什么null和undefined为什么比较特殊,实际上按理来说,null的所属类就是Null,undefined就是Undefined,但事实并非如此:控制台输出如下结果:
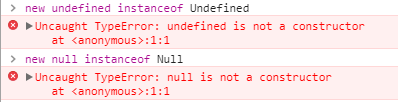
l浏览器压根不认识这两货,直接报错。在第一个例子你可能已经发现了,typeof null的结果是object,typeof undefined的结果是undefined
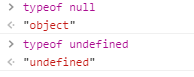
尤其是null,其实这是js设计的一个败笔,早期准备更改null的类型为null,由于当时已经有大量网站使用了null,如果更改,将导致很多网站的逻辑出现漏洞问题,就没有更改过来,于是一直遗留到现在。作为学习者,我们只需要记住就好。
3.constructor
1 console.log(("1").constructor === String);
2 console.log((1).constructor === Number);
3 console.log((true).constructor === Boolean);
4 //console.log((null).constructor === Null);
5 //console.log((undefined).constructor === Undefined);
6 console.log(([]).constructor === Array);
7 console.log((function() {}).constructor === Function);
8 console.log(({}).constructor === Object);

(这里依然抛开null和undefined)乍一看,constructor似乎完全可以应对基本数据类型和引用数据类型,都能检测出数据类型,事实上并不是如此,来看看为什么:
1 function Fn(){};
2
3 Fn.prototype=new Array();
4
5 var f=new Fn();
6
7 console.log(f.constructor===Fn);
8 console.log(f.constructor===Array);

我声明了一个构造函数,并且把他的原型指向了Array的原型,所以这种情况下,constructor也显得力不从心了。
看到这里,是不是觉得绝望了。没关系,终极解决办法就是第四种办法,看过jQuery源码的人都知道,jQuery实际上就是采用这个方法进行数据类型检测的。
4.Object.prototype.toString.call()
1 var a = Object.prototype.toString;
2
3 console.log(a.call("aaa"));
4 console.log(a.call(1));
5 console.log(a.call(true));
6 console.log(a.call(null));
7 console.log(a.call(undefined));
8 console.log(a.call([]));
9 console.log(a.call(function() {}));
10 console.log(a.call({}));
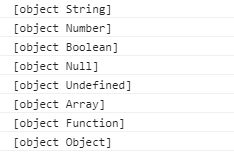
可以看到,所有的数据类型,这个办法都可以判断出来。那就有人质疑了,假如我把他的原型改动一下呢?如你所愿,我们看一下:
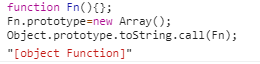
可以看到,依然可以得到正确的结果。好了,今天就说到这里,欢迎关注我的博客,一起交流学习前端知识。
