System.IO.Pipelines 是一个新库,旨在使在 .NET 中执行高性能 I/O 更加容易。 该库的目标为适用于所有 .NET 实现的 .NET Standard。
System.IO.Pipelines 解决什么问题
System.IO.Pipelines 已构建为:
- 具有高性能的流数据分析功能。
- 减少代码复杂性。
下面的代码是典型的 TCP 服务器,它从客户机接收行分隔的消息(由 '
' 分隔):
async Task ProcessLinesAsync(NetworkStream stream)
{
var buffer = new byte[1024];
await stream.ReadAsync(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
// Process a single line from the buffer
ProcessLine(buffer);
}
前面的代码有几个问题:
- 单次调用
ReadAsync可能无法接收整条消息(行尾)。 - 忽略了
stream.ReadAsync的结果。stream.ReadAsync返回读取的数据量。 - 它不能处理在单个
ReadAsync调用中读取多行的情况。 - 它为每次读取分配一个
byte数组。
要解决上述问题,需要进行以下更改:
-
缓冲传入的数据,直到找到新行。
-
分析缓冲区中返回的所有行。
-
该行可能大于 1KB(1024 字节)。 找到需要调整输入缓冲区大小的代码(一行完整的代码)。
- 如果调整缓冲区的大小,当输入中出现较长的行时,将生成更多缓冲区副本。
- 压缩用于读取行的缓冲区,以减少空余。
-
请考虑使用缓冲池来避免重复分配内存。
下面的代码解决了其中一些问题:

1 async Task ProcessLinesAsync(NetworkStream stream) 2 { 3 byte[] buffer = ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Rent(1024); 4 var bytesBuffered = 0; 5 var bytesConsumed = 0; 6 7 while (true) 8 { 9 // Calculate the amount of bytes remaining in the buffer. 10 var bytesRemaining = buffer.Length - bytesBuffered; 11 12 if (bytesRemaining == 0) 13 { 14 // Double the buffer size and copy the previously buffered data into the new buffer. 15 var newBuffer = ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Rent(buffer.Length * 2); 16 Buffer.BlockCopy(buffer, 0, newBuffer, 0, buffer.Length); 17 // Return the old buffer to the pool. 18 ArrayPool<byte>.Shared.Return(buffer); 19 buffer = newBuffer; 20 bytesRemaining = buffer.Length - bytesBuffered; 21 } 22 23 var bytesRead = await stream.ReadAsync(buffer, bytesBuffered, bytesRemaining); 24 if (bytesRead == 0) 25 { 26 // EOF 27 break; 28 } 29 30 // Keep track of the amount of buffered bytes. 31 bytesBuffered += bytesRead; 32 var linePosition = -1; 33 34 do 35 { 36 // Look for a EOL in the buffered data. 37 linePosition = Array.IndexOf(buffer, (byte)' ', bytesConsumed, 38 bytesBuffered - bytesConsumed); 39 40 if (linePosition >= 0) 41 { 42 // Calculate the length of the line based on the offset. 43 var lineLength = linePosition - bytesConsumed; 44 45 // Process the line. 46 ProcessLine(buffer, bytesConsumed, lineLength); 47 48 // Move the bytesConsumed to skip past the line consumed (including ). 49 bytesConsumed += lineLength + 1; 50 } 51 } 52 while (linePosition >= 0); 53 } 54 }
Pipe
Pipe 类可用于创建 PipeWriter/PipeReader 对。 写入 PipeWriter 的所有数据都可用于 PipeReader:
var pipe = new Pipe(); PipeReader reader = pipe.Reader; PipeWriter writer = pipe.Writer;
Pipe基本用法

1 async Task ProcessLinesAsync(Socket socket) 2 { 3 var pipe = new Pipe(); 4 Task writing = FillPipeAsync(socket, pipe.Writer); 5 Task reading = ReadPipeAsync(pipe.Reader); 6 7 await Task.WhenAll(reading, writing); 8 } 9 10 async Task FillPipeAsync(Socket socket, PipeWriter writer) 11 { 12 const int minimumBufferSize = 512; 13 14 while (true) 15 { 16 // Allocate at least 512 bytes from the PipeWriter. 17 Memory<byte> memory = writer.GetMemory(minimumBufferSize); 18 try 19 { 20 int bytesRead = await socket.ReceiveAsync(memory, SocketFlags.None); 21 if (bytesRead == 0) 22 { 23 break; 24 } 25 // Tell the PipeWriter how much was read from the Socket. 26 writer.Advance(bytesRead); 27 } 28 catch (Exception ex) 29 { 30 LogError(ex); 31 break; 32 } 33 34 // Make the data available to the PipeReader. 35 FlushResult result = await writer.FlushAsync(); 36 37 if (result.IsCompleted) 38 { 39 break; 40 } 41 } 42 43 // By completing PipeWriter, tell the PipeReader that there's no more data coming. 44 await writer.CompleteAsync(); 45 } 46 47 async Task ReadPipeAsync(PipeReader reader) 48 { 49 while (true) 50 { 51 ReadResult result = await reader.ReadAsync(); 52 ReadOnlySequence<byte> buffer = result.Buffer; 53 54 while (TryReadLine(ref buffer, out ReadOnlySequence<byte> line)) 55 { 56 // Process the line. 57 ProcessLine(line); 58 } 59 60 // Tell the PipeReader how much of the buffer has been consumed. 61 reader.AdvanceTo(buffer.Start, buffer.End); 62 63 // Stop reading if there's no more data coming. 64 if (result.IsCompleted) 65 { 66 break; 67 } 68 } 69 70 // Mark the PipeReader as complete. 71 await reader.CompleteAsync(); 72 } 73 74 bool TryReadLine(ref ReadOnlySequence<byte> buffer, out ReadOnlySequence<byte> line) 75 { 76 // Look for a EOL in the buffer. 77 SequencePosition? position = buffer.PositionOf((byte)' '); 78 79 if (position == null) 80 { 81 line = default; 82 return false; 83 } 84 85 // Skip the line + the . 86 line = buffer.Slice(0, position.Value); 87 buffer = buffer.Slice(buffer.GetPosition(1, position.Value)); 88 return true; 89 }
有两个循环:
FillPipeAsync从Socket读取并写入PipeWriter。ReadPipeAsync从PipeReader读取并分析传入的行。
没有分配显式缓冲区。 所有缓冲区管理都委托给 PipeReader 和 PipeWriter 实现。 委派缓冲区管理使使用代码更容易集中关注业务逻辑。
在第一个循环中:
- 调用 PipeWriter.GetMemory(Int32) 从基础编写器获取内存。
- 调用 PipeWriter.Advance(Int32) 以告知
PipeWriter有多少数据已写入缓冲区。 - 调用 PipeWriter.FlushAsync 以使数据可用于
PipeReader。
在第二个循环中,PipeReader 使用由 PipeWriter 写入的缓冲区。 缓冲区来自套接字。 对 PipeReader.ReadAsync 的调用:
-
返回包含两条重要信息的 ReadResult:
- 以
ReadOnlySequence<byte>形式读取的数据。 - 布尔值
IsCompleted,指示是否已到达数据结尾 (EOF)。
- 以
找到行尾 (EOL) 分隔符并分析该行后:
- 该逻辑处理缓冲区以跳过已处理的内容。
- 调用
PipeReader.AdvanceTo以告知PipeReader已消耗和检查了多少数据。
读取器和编写器循环通过调用 Complete 结束。 Complete 使基础管道释放其分配的内存。
反压和流量控制
理想情况下,读取和分析可协同工作:
- 写入线程使用来自网络的数据并将其放入缓冲区。
- 分析线程负责构造适当的数据结构。
通常,分析所花费的时间比仅从网络复制数据块所用时间更长:
- 读取线程领先于分析线程。
- 读取线程必须减缓或分配更多内存来存储用于分析线程的数据。
为了获得最佳性能,需要在频繁暂停和分配更多内存之间取得平衡。
为解决上述问题,Pipe 提供了两个设置来控制数据流:
- PauseWriterThreshold:确定在调用 FlushAsync 暂停之前应缓冲多少数据。
- ResumeWriterThreshold:确定在恢复对
PipeWriter.FlushAsync的调用之前,读取器必须观察多少数据。
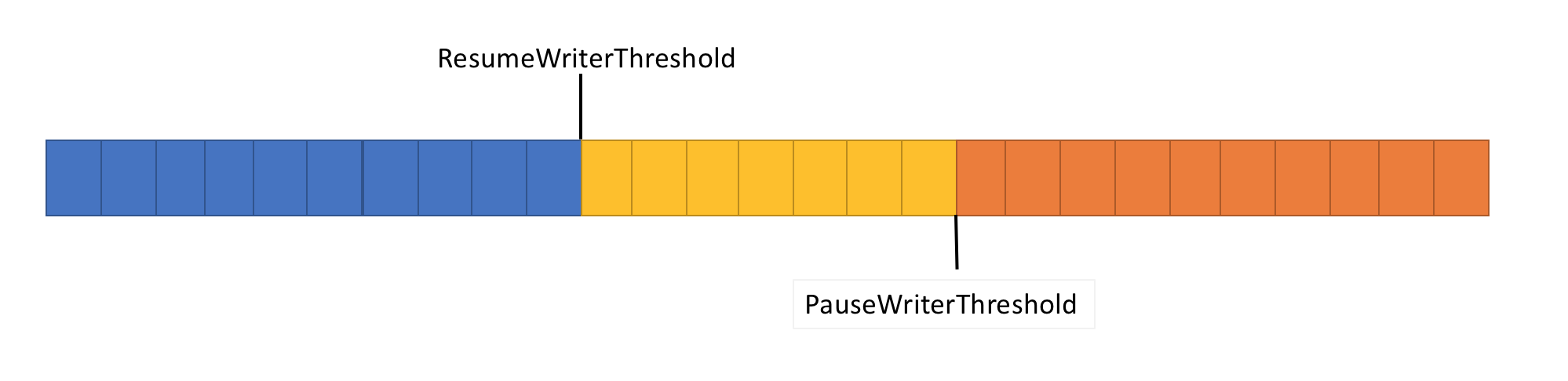
- 当
Pipe中的数据量超过PauseWriterThreshold时,返回不完整的ValueTask<FlushResult>。 - 低于
ResumeWriterThreshold时,返回完整的ValueTask<FlushResult>。
使用两个值可防止快速循环,如果只使用一个值,则可能发生这种循环。
