意义:简单实现摩斯码的破译和生成
代码:
#-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- __author__ = '007' __date__ = '2016/2/2' import pprint import re chars = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890" codes = """.- -... -.-. -.. . ..-. --. .... .. .--- -.- .-.. -- -. --- .--. --.- .-. ... - ..- ...- .-- -..- -.-- --.. .---- ..--- ...-- ....- ..... -.... --... ---.. ----. -----""" dd = dict(zip(chars.lower(),codes.split())) DD = dict(zip(codes.split(),chars.lower())) #pprint.pprint(DD) def chars2morse(char): return dd.get(char.lower(),' ') def morse2chars(morse): return DD.get(morse,' ') while True: str = raw_input() x = str.split(' ') ccc = ''.join(x) if re.match('^[0-9a-zA-Z]+$',ccc): print ' '.join(chars2morse(c) for c in ccc) else: cc = str.split() print ' '.join(morse2chars(c) for c in cc)
运行结果:
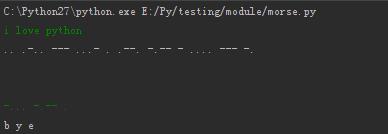
知识点:
split()
意义:通过指定分割符对字符串进行切片
语法:
str.split(str="", num=string.count(str))
- 参数str:分隔符,默认为空格
- 参数num:分割次数
返回值:返回分割后的字符串列表
实例:
1 In[2]: str = "I Love Python!" 2 In[3]: str.split() 3 Out[3]: ['I', 'Love', 'Python!'] 4 In[4]: str.split(' ',1) 5 Out[4]: ['I', 'Love Python!']
lower()
意义:转换字符串中所有大写字符为小写
语法:
str.lower()
返回值:返回将字符串中所有大写字符转换为小写后生成的字符串
实例:
1 In[2]: str = "I Love Python!" 2 In[5]: str.lower() 3 Out[5]: 'i love python!'
zip()
意义:Python内建函数,它接受一系列可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个tuple(元组),然后返回由这些tuples组成的 list(列表)。若传入参数的长度不等,则返回list的长度和参数中长度最短的对象相同
语法:
zip([iterable, ...])
- 参数:任意多个列表
返回值:有元祖组成的列表
实例:
1 In[6]: a = [1,2,3] 2 In[7]: b = [4,5,6] 3 In[8]: c = [7,8,9,0] 4 In[9]: zip(a,b,c) 5 Out[9]: [(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)]
利用*号操作符,可以将list unzip(解压)
1 In[11]: d = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 2 In[12]: zip(*d) 3 Out[12]: [(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)] 4 In[13]: e = [(1, 4, 7), (2, 5, 8), (3, 6, 9)] 5 In[14]: zip(*e) 6 Out[14]: [(1, 2, 3), (4, 5, 6), (7, 8, 9)]
dict()
意义:创建新字典
语法:
dict(iterable, **kwarg)
返回值:返回一个新字典
实例:
1 #键值对方式构造字典 2 In[17]: dict(a=1,b=2,c=3) 3 Out[17]: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} 4 #映射函数方式构造字典 5 In[18]: dict(zip(['a','b','c'],[1,2,3])) 6 Out[18]: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} 7 #可迭代对象方式构造字典 8 In[19]: dict([('a',1),('b',2),('c',3)]) 9 Out[19]: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
get()
意义:返回字典中指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值
语法:
dict.get(key, default=None)
- 参数key:字典中要查找的键
- default:如果指定键的值不存在时,返回该默认值值
返回值:字典中指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值None
实例:
1 In[23]: d = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3} 2 In[24]: d.get('a') 3 Out[24]: 1 4 In[25]: d.get('d','Not Found!') 5 Out[25]: 'Not Found!'