AOP:(Aspect Oriented Programing):面向切面编程
定义:指在程序运行期间,动态的将某段代码插入到指定方法的指定位置进行运行的一种编程方式;
AOP功能使用步骤:
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
2、AOP功能包;
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar 增强版的面向切面功能: com.springsource.net.sf.cglib-2.2.0.jar com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.soyoungboy"></context:component-scan> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> </beans>
public interface Calculator { public int add(int i,int j); public int sub(int i,int j); public int mul(int i,int j); public int div(int i,int j); }
实现类:
package com.soyoungboy.inter; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /** * 业务逻辑 * @author soyoungboy * */ @Service public class MathCalculator implements Calculator { public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i + j; System.out.println("======加法内部"); return result; } public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i - j; return result; } public int mul(int i, int j) { int result = i * j; return result; } public int div(int i, int j) { int result = i / j; return result; } }
切面类:
package com.soyoungboy.util; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 切面类 * @author soyoungboy * */ @Component @Aspect public class LogUtils { /** * try{ * @Before: * method.invoke(.....); * @AfterReturning * }catch(e){ * @AfterThrowing * }finally{ * @After * } * * * 提供了几个注解: * @Before:意思在目标方法运行之前运行: 前置通知 * @After:目标方法结束之后 后置通知 * @AfterReturning:方法正常执行并返回 返回通知 * @AfterThrowing:方法出现异常以后调用 异常通知 * @Around:最强大的通知(这就是动态代理) 环绕通知 * * 使用切入点表达式,指定到底是来拦截哪些方法的; * execution(访问权限控制符 返回值类型 方法的全描述(参数表)) */ //日志开始 @Before(value="execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(int, int))") public static void logStart(){ System.out.println("xxx方法开始,参数列表【xxx】"); } //日志方法正常返回 @AfterReturning(value="execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(int, int))") public static void logReturn() { System.out.println("xxx方法正常返回,返回值是:xxx"); } //日志记录异常 @AfterThrowing(value="execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(int, int))") public static void logException() { System.out.println("xxx方法出现异常,异常信息是:xxx"); } //方法结束 @After(value="execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(int, int))") public static void logEnd() { System.out.println("xxx方法结束"); } }
junit测试代码:
package com.soyoungboy.test; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.soyoungboy.inter.Calculator; import com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator; public class AOPTest { ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); /** * 1、如果没有接口,我们的cglib会根据当前类作为父模板;创建出一个内置的代理对象; */ @Test public void test02(){ MathCalculator bean = (MathCalculator) ioc.getBean("mathCalculator"); System.out.println(bean.getClass()); bean.add(2, 3); } /** * 如果有接口一定要用接口类型,因为获取到的组件是一个代理对象。 * 和被代理对象的共同特点就是实现了同一个接口 */ @Test public void test01(){ //MathCalculator calculator = new MathCalculator(); //calculator.add(1, 2); //1、有接口必须写接口类型 //Calculator calculator = ioc.getBean(Calculator.class); Calculator calculator = (Calculator) ioc.getBean("mathCalculator"); calculator.add(1, 3); //容器中保存的是这个组件的代理对象;如果是切面进行动态切入的组件。 //com.sun.proxy.$Proxy12 System.out.println(calculator.getClass()); Class<?>[] classes = calculator.getClass().getInterfaces(); System.out.println(classes[0]); } }
test2方法在MathCalculator没实现Calculator的时候可以执行:
结果为:
class com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$97f6d938 xxx方法开始,参数列表【xxx】 ======加法内部 xxx方法结束 xxx方法正常返回,返回值是:xxx
test01在MathCalculator实现Calculator的情况下执行:
结果为:
xxx方法开始,参数列表【xxx】 ======加法内部 xxx方法结束 xxx方法正常返回,返回值是:xxx class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy13 interface com.soyoungboy.inter.Calculator
评论区说到了方法信息的获取,那就再说说aop的细节:
aop的细节
当前连接点所在方法的方法名、当前传入的参数值等等。这些信息都封装在JoinPoint接口的实例对象中。
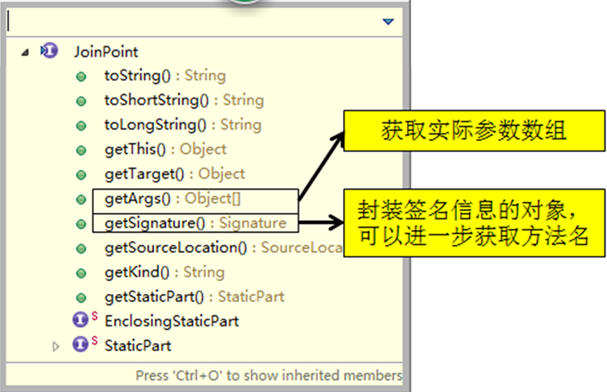
通知
概述
在具体的连接点上要执行的操作。
一个切面可以包括一个或者多个通知。
通知所使用的注解的值往往是切入点表达式。
前置通知
前置通知:在方法执行之前执行的通知
使用@Before注解
后置通知
后置通知:后置通知是在连接点完成之后执行的,即连接点返回结果或者抛出异常的时候
使用@After注解
返回通知
返回通知:无论连接点是正常返回还是抛出异常,后置通知都会执行。如果只想在连接点返回的时候记录日志,应使用返回通知代替后置通知。
使用@AfterReturning注解
在返回通知中访问连接点的返回值
在返回通知中,只要将returning属性添加到@AfterReturning注解中,就可以访问连接点的返回值。该属性的值即为用来传入返回值的参数名称
必须在通知方法的签名中添加一个同名参数。在运行时Spring AOP会通过这个参数传递返回值
原始的切点表达式需要出现在pointcut属性中
异常通知
异常通知:只在连接点抛出异常时才执行异常通知
将throwing属性添加到@AfterThrowing注解中,也可以访问连接点抛出的异常。Throwable是所有错误和异常类的顶级父类,所以在异常通知方法可以捕获到任何错误和异常。
如果只对某种特殊的异常类型感兴趣,可以将参数声明为其他异常的参数类型。然后通知就只在抛出这个类型及其子类的异常时才被执行
环绕通知
环绕通知是所有通知类型中功能最为强大的,能够全面地控制连接点,甚至可以控制是否执行连接点。
对于环绕通知来说,连接点的参数类型必须是ProceedingJoinPoint。它是 JoinPoint的子接口,允许控制何时执行,是否执行连接点。
在环绕通知中需要明确调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed()方法来执行被代理的方法。如果忘记这样做就会导致通知被执行了,但目标方法没有被执行。
注意:环绕通知的方法需要返回目标方法执行之后的结果,即调用 joinPoint.proceed();的返回值,否则会出现空指针异常。
重用切入点定义
在编写AspectJ切面时,可以直接在通知注解中书写切入点表达式。但同一个切点表达式可能会在多个通知中重复出现。
在AspectJ切面中,可以通过@Pointcut注解将一个切入点声明成简单的方法。切入点的方法体通常是空的,因为将切入点定义与应用程序逻辑混在一起是不合理的。
切入点方法的访问控制符同时也控制着这个切入点的可见性。如果切入点要在多个切面中共用,最好将它们集中在一个公共的类中。在这种情况下,它们必须被声明为public。在引入这个切入点时,必须将类名也包括在内。如果类没有与这个切面放在同一个包中,还必须包含包名。
其他通知可以通过方法名称引入该切入点
指定切面的优先级
在同一个连接点上应用不止一个切面时,除非明确指定,否则它们的优先级是不确定的。
切面的优先级可以通过实现Ordered接口或利用@Order注解指定。
实现Ordered接口,getOrder()方法的返回值越小,优先级越高。
若使用@Order注解,序号出现在注解中
废话少说,上代码:
package com.soyoungboy.util; import java.util.Arrays; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.Signature; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * @author soyoungboy * 1、在切面类里面配置每一个方法都是何时何地运行 * order指定优先级 */ @Order(2) @Component @Aspect public class LogUtils { /** * 抽取可重用的切入点表达式 * 定义一个可重用的切入点表达式,以后的表达式直接引用; */ @Pointcut("execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(..))") public void myPoint(){} /** * 前置通知 * Object result = null; try { LogUtils.logStart(method, args);//@Before //目标方法执行 result = method.invoke(cal, args); LogUtils.logReturn(method, result);//@AfterReturning } catch (Exception e) { LogUtils.logException(method,e); //@AfterThrowing //动态代理的时候,我们一般建议都需要将异常继续抛出去,这样外界才能知道; throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ //记录方法最终结束 LogUtils.logEnd(method);//@After } return result; * * * * 将日志代码切入到业务逻辑方法; * Spring提供了几个简单的注解; * 可以标注在某些方法上,意思就是这个方法在指定位置会运行 * @Before:前置通知;在目标方法运行之前运行; * * @After:后置通知:在目标方法最终结束的时候运行; * * @AfterReturning:返回通知:在目标方法正常返回之后运行; * @AfterThrowing:异常通知:在目标方法出现异常之后运行 * * * * @Around(后来再说) * * @param method * @param args */ //方法开始要记录使用的参数 //切入点表达式:指定是在哪些方法执行的时候进行动态切入 //execution(访问权限控制符 返回值类型 全类名.方法名(参数类型列表)) @Before("myPoint()") public static void logStart(JoinPoint joinPoint){ //1、获取方法的目标方法运行时的参数列表;result = method.invoke(cal, 【args】); Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); //2、获取方法签名;当前方法的所有详细信息都在 Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); //3、获取方法名 String name = signature.getName(); System.out.println("【日志】前置通知logStart:方法名:【"+name+"】方法运行开始了;使用的参数列表:【"+Arrays.asList(args)+"】"); } /** * 切入点表达式: * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(int, int)) * execution(访问权限控制符 返回值类型 全类名.方法名(参数类型列表)); * * 提供了两种通配符: * *:匹配任意多字符; * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.*.a*(*, int)) * 参数位置: * *:任意类型的参数,匹配一个参数位置 * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.inter.*.*(int,*)) * 只能匹配两个参数的,但是最后一个参数任意 * * ..:匹配任意多字符,任意多个参数; * 1)、..写在方法的参数位置 * 方法重载:execution(public int com.soyoungboy.impl.*.*(..)) * 表示任意类的任意方法的任意参数(个数类型都不限); * * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.impl.*.*(int,..)) * 能匹配任意参数的,但是第一个参数必须是int * 2)、..写在包的层级位置:匹配多层路径 * * * 特别:访问权限控制符(要么不写,要写也只能写public) * * * 最模糊的: * execution(* *(..)) * 最详细的: * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.impl.MathCalculator.add(int,int)) * * 高级应用: * &&:并且 * eg:切入的位置,比须满足前面的表达式还必须满足后面的表达式。交集 * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.impl.MathCalculator.add(..))&&execution(* *(int,int)) * div(int,int)不会切入,add(int,int)会切入 * ||: * eg:切入的位置满足前面的表达式或者后面的都行;只要满足任意一个表达式的条件即可 * execution(public int com.soyoungboy.impl.MathCalculator.add(..))||execution(* *(int,int)) * div(int,int)会切入,add(int,int)会切入 */ @AfterReturning(value="myPoint()",returning="data") public static void logReturn(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object data){ System.out.println("【日志】返回通知【"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"】" + "正常返回,返回值:【"+data+"】"); } /** * 方法的细节信息,如返回值,异常,【方法名】,【参数列表】...如何获取; * 1)、在返回通知的时候可以用returning:指定哪个参数用来接受返回值 * 指定的类型,表示的就是当前通知只是用来接受指定类型返回值的,如果返回值类型不一样,返回通知不会被调用 * 2)、在异常通知的时候可以用throwing:指定哪个参数用来接受异常 * NullPointerException:当前通知方法只是用来接受空指针异常的;如果目标方法出现其他异常,通知方法都不会被调用 * JoinPoint joinPoint(封装了当前连接点的详细信息); * AJAX:类似的; * $.ajax({ * url:"xxx", * success:function(data){ * alert(data) * } * }) * */ @AfterThrowing(value="myPoint()",throwing="e") public static void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception e) { System.out.println("【日志】异常通知【"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"】方法出现异常:【"+e+"】"); } /** * 后置通知 * 1、通知方法的约束; * 只有一个约束;参数列表Spring必须清楚,每个参数代表什么; * * AOP细节五: * 通知方法的调用顺序; @Before @After @AfterReturning @AfterThrowing * try{ * @Before * method.invoke(obj,args); * @AfterReturning * }catch(Exception e){ * @AfterThrowing * }finally{ * @After * } * 正常顺序:@Before==目标方法执行=>@After===>@AfterReturning * 异常顺序:@Before==目标方法执行=>@After===>@AfterThrowing * * @param joinPoint */ @After("myPoint()") public int logEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("【日志】后置通知【"+joinPoint.getSignature().getName()+"】最终结束;"); return 1; } /** * @Before * @After * @AfterThrowing * @AfterReturing * * @Around:环绕通知;(四合一的);就是一个动态代理; * 参数: * 关注的几个点: * 1)、将目标方法执行后的返回返回出去; * return proceed = pjp.proceed(args); * 2)、将异常抛出去方便外界感知; * 3)、环绕的几个位置和其他通知在一起时:执行顺序; * 环绕通知在自己的切面里面拥有最高优先级,优先执行;环绕先进去先出来; 【环绕】前置通知 【日志】前置通知:【add】方法运行开始了;使用的参数列表【[10, 1, 1]】 方法内部打印:11 【环绕】返回通知,返回值:11 【环绕】后置通知 【日志】后置通知【add】最终结束; 【日志】返回通知【add】正常返回,返回值:【11】 * * * 多切面带环绕顺序: * 背景:BV order1 LOG(普通+环绕) order2 * BV===前置 * LOG===环绕前置 * LOG===前置 * 目标方法 * LOG===环绕返回 * LOG===环绕后置 * LOG===后置 * LOG===返回 * BV===后置 * BV===返回 * * * 环绕在单切面环境: * LOG===环绕前置 * LOG===前置 * 目标方法 * LOG===环绕返回 * LOG===环绕后置 * LOG===后置 * LOG===返回 * * 业务逻辑: * */ @Around("myPoint()") public Object logAround(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp){ Object[] args = pjp.getArgs(); Object proceed = null; try { //Object result = method.invoke(arg0); //推进目标方法的执行,传入目标方法执行时要用的参数,返回目标方法执行后的返回值 //@Before System.out.println("【环绕】前置通知"); //放行目标方法执行。。。 proceed = pjp.proceed(args); //@AfterReturing System.out.println("【环绕】返回通知,返回值:"+proceed); } catch (Throwable e) { //e.printStackTrace(); //@AfterThrowing //异常信息一般抛出去让外界感知 System.out.println("【环绕】异常通知"); throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally{ //@After System.out.println("【环绕】后置通知"); } return proceed; } }
通过xml配置AOP
<!-- 2、写配置;告诉Spring,切面类的这些日志方法,要何时何地运行即可 --> <!-- 2.1)、将切面类和业务逻辑类都加入到容器中 --> <bean id="mathCalculator" class="com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator"></bean> <bean id="BValidateApspect" class="com.soyoungboy.util.BValidateApspect"></bean> <bean id="logUtils" class="com.soyoungboy.util.LogUtils"></bean> <!-- 2.2)、告诉Spring,哪个组件是切面类:@Aspect;需要aop名称空间 --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(..))" id="globalPoint"/> <aop:aspect ref="BValidateApspect" order="1"> <aop:before method="vaStart" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"/> <aop:after method="vaEnd" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"/> <aop:after-returning method="vaReturn" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"/> <aop:after-throwing method="vaEnd" pointcut-ref="globalPoint"/> </aop:aspect> <!-- 配置aop切面 :一个aop:aspect配置一个切面--> <aop:aspect ref="logUtils" order="0"> <!-- 2.3)、配置切面类里面的每一个方法何时何地运行 配合通知注解和切入点表达式 --> <!-- aop:pointcut:抽取一个当前切面可重用的切入点表达式 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(..))" id="mypoint"/> <!--aop:before:指定前置通知 --> <aop:before method="logStart" pointcut="execution(* com.soyoungboy.inter.MathCalculator.*(..))"/> <aop:after method="logEnd" pointcut-ref="mypoint"/> <aop:after-returning method="logReturn" pointcut-ref="mypoint" returning="result"/> <aop:after-throwing method="logException" pointcut-ref="mypoint" throwing="exception"/> <aop:around method="logAround" pointcut-ref="mypoint"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> <!-- 2.4)、启动基于注解的aop模式;依赖aop名称空间 --> <!-- 推荐:重要的东西可以写配置,正常的我们都去写注解 -->