启用checkpoint机制
调用StreamExecutionEnvironment的enableCheckpointing方法,interval间隔需要大于等于10ms
public StreamExecutionEnvironment enableCheckpointing(long interval) {
checkpointCfg.setCheckpointInterval(interval);
return this;
}
作业checkpoint流程描述
JobGraphGenerator构建JobGraph的过程中会生成三个List<JobVertexID>类型的节点列表:
- triggerVertices:所有的source并行实例节点,会定时接收到
CheckpointCoordinator发送的triggerCheckpoint请求 - ackVertices:所有并行实例节点,用于接收并处理各自checkpoint完成
acknowledge确认消息 - commitVertices: 所有并行实例节点,当所有实例节点都确认完成checkpoint后,
CheckpointCoordinator会调用notifyCheckpointComplete通知这些实例节点该检查点已经全部完成
如果用户启用了checkpoint,则CheckpointCoordinator的定时任务会周期性的生成新的checkpoint id并调用与triggerVertices对应的CheckpointCoordinator.tasksToTrigger中各节点的triggerCheckpoint方法,该方法通过RPC方式触发TaskExecutor->triggerCheckpoint,然后TaskExecutor会找到对应的Task并调用其triggerCheckpointBarrier方法,在此方法中会异步调用StreamTask的triggerCheckpoint方法。然后各Task节点checkpoint执行完成后会远程调用acknowledgeCheckpoint通知CheckpointCoordinator,如果该checkpoint所有节点都已经确认完成则CheckpointCoordinator会调用tasksToCommitTo中各节点的notifyCheckpointComplete方法通知各节点该检查点已经成功完成。
组件之间的交互图
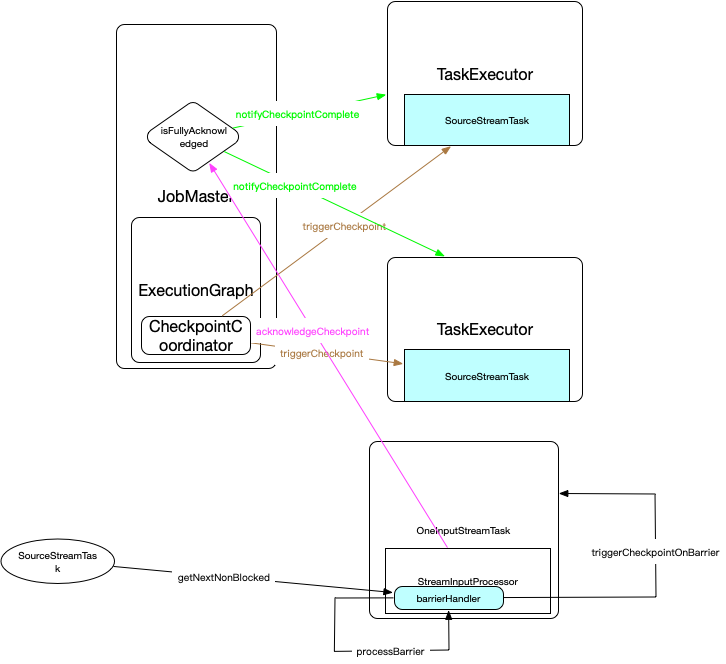
CheckpointCoordinator定时任务
triggerCheckpoint方法:
final CheckpointOptions checkpointOptions = new CheckpointOptions(
props.getCheckpointType(),
checkpointStorageLocation.getLocationReference());
// send the messages to the tasks that trigger their checkpoint
for (Execution execution: executions) {
execution.triggerCheckpoint(checkpointID, timestamp, checkpointOptions);
}
Execution
Execution.triggerCheckpoint方法会通过RPC方式调用TaskExecutor.triggerCheckpoint方法:
/**
* Trigger a new checkpoint on the task of this execution.
*
* @param checkpointId of th checkpoint to trigger
* @param timestamp of the checkpoint to trigger
* @param checkpointOptions of the checkpoint to trigger
*/
public void triggerCheckpoint(long checkpointId, long timestamp, CheckpointOptions checkpointOptions) {
final LogicalSlot slot = assignedResource;
if (slot != null) {
final TaskManagerGateway taskManagerGateway = slot.getTaskManagerGateway();
taskManagerGateway.triggerCheckpoint(attemptId, getVertex().getJobId(), checkpointId, timestamp, checkpointOptions);
} else {
LOG.debug("The execution has no slot assigned. This indicates that the execution is " +
"no longer running.");
}
}
TaskExecutor
triggerCheckpoint方法会调用Task.triggerCheckpointBarrier方法:
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Acknowledge> triggerCheckpoint(
ExecutionAttemptID executionAttemptID,
long checkpointId,
long checkpointTimestamp,
CheckpointOptions checkpointOptions) {
log.debug("Trigger checkpoint {}@{} for {}.", checkpointId, checkpointTimestamp, executionAttemptID);
final Task task = taskSlotTable.getTask(executionAttemptID);
if (task != null) {
task.triggerCheckpointBarrier(checkpointId, checkpointTimestamp, checkpointOptions);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(Acknowledge.get());
} else {
final String message = "TaskManager received a checkpoint request for unknown task " + executionAttemptID + '.';
log.debug(message);
return FutureUtils.completedExceptionally(new CheckpointException(message));
}
}
Task
triggerCheckpointBarrier方法异步调用StreamTask.triggerCheckpoint方法:
if (executionState == ExecutionState.RUNNING && invokable != null) {
// build a local closure
final String taskName = taskNameWithSubtask;
final SafetyNetCloseableRegistry safetyNetCloseableRegistry =
FileSystemSafetyNet.getSafetyNetCloseableRegistryForThread();
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// set safety net from the task's context for checkpointing thread
LOG.debug("Creating FileSystem stream leak safety net for {}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
FileSystemSafetyNet.setSafetyNetCloseableRegistryForThread(safetyNetCloseableRegistry);
try {
boolean success = invokable.triggerCheckpoint(checkpointMetaData, checkpointOptions);
if (!success) {
checkpointResponder.declineCheckpoint(
getJobID(), getExecutionId(), checkpointID,
new CheckpointDeclineTaskNotReadyException(taskName));
}
}
catch (Throwable t) {
if (getExecutionState() == ExecutionState.RUNNING) {
failExternally(new Exception(
"Error while triggering checkpoint " + checkpointID + " for " +
taskNameWithSubtask, t));
} else {
LOG.debug("Encountered error while triggering checkpoint {} for " +
"{} ({}) while being not in state running.", checkpointID,
taskNameWithSubtask, executionId, t);
}
} finally {
FileSystemSafetyNet.setSafetyNetCloseableRegistryForThread(null);
}
}
};
executeAsyncCallRunnable(runnable, String.format("Checkpoint Trigger for %s (%s).", taskNameWithSubtask, executionId));
}
StreamTask执行checkopint
private boolean performCheckpoint(
CheckpointMetaData checkpointMetaData,
CheckpointOptions checkpointOptions,
CheckpointMetrics checkpointMetrics) throws Exception {
LOG.debug("Starting checkpoint ({}) {} on task {}",
checkpointMetaData.getCheckpointId(), checkpointOptions.getCheckpointType(), getName());
synchronized (lock) {
if (isRunning) {
// we can do a checkpoint
// All of the following steps happen as an atomic step from the perspective of barriers and
// records/watermarks/timers/callbacks.
// We generally try to emit the checkpoint barrier as soon as possible to not affect downstream
// checkpoint alignments
// Step (1): Prepare the checkpoint, allow operators to do some pre-barrier work.
// The pre-barrier work should be nothing or minimal in the common case.
operatorChain.prepareSnapshotPreBarrier(checkpointMetaData.getCheckpointId());
// Step (2): Send the checkpoint barrier downstream
operatorChain.broadcastCheckpointBarrier(
checkpointMetaData.getCheckpointId(),
checkpointMetaData.getTimestamp(),
checkpointOptions);
// Step (3): Take the state snapshot. This should be largely asynchronous, to not
// impact progress of the streaming topology
checkpointState(checkpointMetaData, checkpointOptions, checkpointMetrics);
return true;
}
AbstractUdfStreamOperator的snapshotState方法:
@Override
public void snapshotState(StateSnapshotContext context) throws Exception {
super.snapshotState(context);
StreamingFunctionUtils.snapshotFunctionState(context, getOperatorStateBackend(), userFunction);
}
然后会根据userFunction实现的是CheckpointedFunction还是ListCheckpointed接口执行对应的方法:
private static boolean trySnapshotFunctionState(
StateSnapshotContext context,
OperatorStateBackend backend,
Function userFunction) throws Exception {
if (userFunction instanceof CheckpointedFunction) {
((CheckpointedFunction) userFunction).snapshotState(context);
return true;
}
if (userFunction instanceof ListCheckpointed) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Serializable> partitionableState = ((ListCheckpointed<Serializable>) userFunction).
snapshotState(context.getCheckpointId(), context.getCheckpointTimestamp());
ListState<Serializable> listState = backend.
getSerializableListState(DefaultOperatorStateBackend.DEFAULT_OPERATOR_STATE_NAME);
listState.clear();
if (null != partitionableState) {
try {
for (Serializable statePartition : partitionableState) {
listState.add(statePartition);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
listState.clear();
throw new Exception("Could not write partitionable state to operator " +
"state backend.", e);
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
调用时序图

锁的使用
StreamTask与StreamOperator交互使用StreamTask.lock对象进行同步,保证checkpoint的一致性调用。
SourceStreamTask
/**
* Gets the lock object on which all operations that involve data and state mutation have to lock.
* @return The checkpoint lock object.
*/
public Object getCheckpointLock() {
return lock;
}
@Override
protected void run() throws Exception {
headOperator.run(getCheckpointLock(), getStreamStatusMaintainer());
}
StreamSource.run方法:
this.ctx = StreamSourceContexts.getSourceContext(
timeCharacteristic,
getProcessingTimeService(),
lockingObject,
streamStatusMaintainer,
collector,
watermarkInterval,
-1);
try {
userFunction.run(ctx);
// if we get here, then the user function either exited after being done (finite source)
// or the function was canceled or stopped. For the finite source case, we should emit
// a final watermark that indicates that we reached the end of event-time
if (!isCanceledOrStopped()) {
ctx.emitWatermark(Watermark.MAX_WATERMARK);
}
因此如果SourceFunction需要checkpoint(实现了CheckpointedFunction或者ListCheckpointed)则必须在run方法中使用synchronized (ctx.getCheckpointLock())进行同步,类似下面这样:
public void run(SourceContext<T> ctx) {
while (isRunning && count < 1000) {
// this synchronized block ensures that state checkpointing,
// internal state updates and emission of elements are an atomic operation
synchronized (ctx.getCheckpointLock()) {
ctx.collect(count);
count++;
}
}
}
OneInputStreamTask
@Override
protected void run() throws Exception {
// cache processor reference on the stack, to make the code more JIT friendly
final StreamInputProcessor<IN> inputProcessor = this.inputProcessor;
while (running && inputProcessor.processInput()) {
// all the work happens in the "processInput" method
}
}
StreamInputProcessor.processInput方法保证了所有用户自定义方法的调用都在lock同步块内:
} else if (recordOrMark.isLatencyMarker()) {
// handle latency marker
synchronized (lock) {
streamOperator.processLatencyMarker(recordOrMark.asLatencyMarker());
}
continue;
} else {
// now we can do the actual processing
StreamRecord<IN> record = recordOrMark.asRecord();
synchronized (lock) {
numRecordsIn.inc();
streamOperator.setKeyContextElement1(record);
streamOperator.processElement(record);
}
return true;
}
StreamMap.processElement:
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
output.collect(element.replace(userFunction.map(element.getValue())));
}
非Source类型的Function自定义方法中不需要再进行额外的checkpoint锁同步。