以下是自己写的 记录日志的代码。(和logging不搭嘎,如果如要学loggging模块,本文末尾有他人的链接。)
# prtlog.py ############################################# # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Dec 12 10:46:06 2018 需求起源:1. 在spyder中写python脚本时,经常要写print来调试; 开发完执行时(python file.py),也需要运行log来找bug. 2. 如果用print, 运行时python file.py >> log 缺点:(1) file.py不结束无法查看log文件 (2)别人模块中的输出,会不断在输出到log. 3. 如果用logging模块 缺点:(1) spyder调试时,log文件一直处于打开状态 (2)在spyder中调试时不好用,logging好像主要为了记录运行时的日志。 功能: 1. 开发时输出print结果,运行时输出同目录下1.log文件 2. 保留最新log中前num行 3. 每次使用prtlog输出都会打开并关闭1.log文件 缺点:效率不高(不追求效率就无所谓了) """ import os,sys import time,datetime def checklog(logfile,num=1000): #保留文件中至少num行 try: if os.path.exists(logfile): lines = open(logfile,'r').readlines() if len(lines)>num+num*0.5: #当文件大于num+500时,只保留最近num行,避免删除重写文件频率太高。 os.remove(logfile) with open(logfile,'w') as f: for line in lines[-num:]: f.write(line) else: pass except: print('Wrong! : [fun]checklog.') def prtlog(logstr='123',linenum='',maxlines=1000): #linenum 指运行时所在行号 logstr= str(logstr);
dirname, filename = os.path.split(os.path.abspath(sys.argv[0])) logfile = os.path.join(dirname,'1.log') checklog(logfile,maxlines) with open(logfile,'a+') as f: lineheader='%s %s[%s]: '%(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"),filename,linenum) f.write(lineheader+logstr+' ') print(lineheader+logstr) f.close() if __name__ == '__main__': prtlog(logstr='123') # b.py ############################################# from prtlog import prtlog prtlog('haha',maxlines=10)
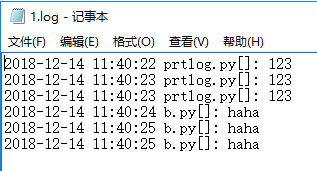
同目录下生成1.log

运行prtlog.py3次,运行b.py3次. 1.log内容:
如需了解logging:
python中logging模块的一些简单用法 ★★★★★★★,
python模块之logging ★★★★