Description
Prof. Tigris is the head of an archaeological team who is currently in charge of an excavation in a site of ancient relics. This site contains relics of a village where civilization once flourished. One night, examining a writing record, you find some text meaningful to you. It reads as follows. “Our village is of glory and harmony. Our relationships are constructed in such a way that everyone except the village headman has exactly one direct boss and nobody will be the boss of himself, the boss of boss of himself, etc. Everyone expect the headman is considered as his boss’s subordinate. We call it relationship configuration. The village headman is at level 0, his subordinates are at level 1, and his subordinates’ subordinates are at level 2, etc. Our relationship configuration is harmonious because all people at same level have the same number of subordinates. Therefore our relationship is …” The record ends here. Prof. Tigris now wonder how many different harmonious relationship configurations can exist. He only cares about the holistic shape of configuration, so two configurations are considered identical if and only if there’s a bijection of n people that transforms one configuration into another one. Please see the illustrations below for explanation when n = 2 and n = 4. 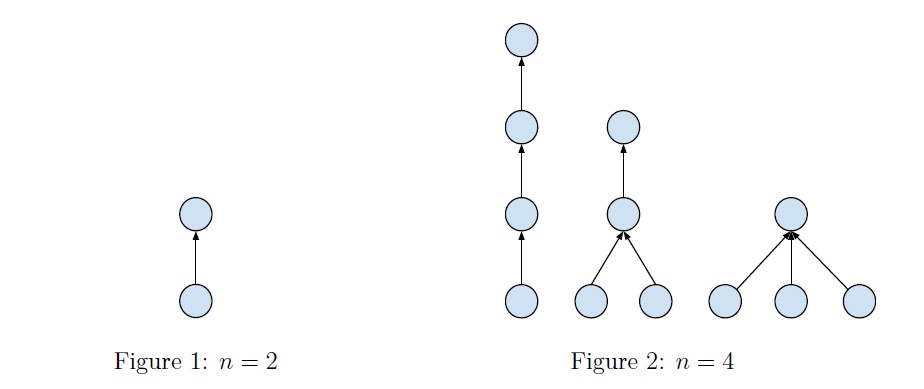

Input
There are several test cases. For each test case there is a single line containing only one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000). Input is terminated by EOF.
Output
For each test case, output one line “Case X: Y” where X is the test case number (starting from 1) and Y is the desired answer.
Sample Input
1 2 3 40 50 600 700
Sample Output
Case 1: 1
Case 2: 1
Case 3: 2
Case 4: 924
Case 5: 1998
Case 6: 315478277
Case 7: 825219749
这个题目可以这样考虑,对于k个节点的这种树,可以先去掉根节点,于是就是若干个这样的树组合而成。自然,这样就能想到,只要剩下的k-1个结点能构成若干个满足条件的树,k个节点便能构成一个满足条件的树。即,当k-1是某个i的倍数时,k的满足条件的树的个数就要加上i的满足条件的树的个数。当然,初始化所有个数全部是0;
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#define N 1000000007
using namespace std;
int ans[1005];
int n;
void qt ()
{
memset (ans, 0, sizeof (ans));
ans[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= 1000; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j < i; ++j)
{
if ((i-1) % j == 0)
ans[i] = (ans[i] + ans[j]) % N;
}
}
}
int main()
{
//freopen ("test.txt", "r", stdin);
qt ();
int times = 1;
while (scanf ("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
printf ("Case %d: %d
", times++, ans[n]);
}
return 0;
}