简介
先说Future, 它用来描述一个异步计算的结果。isDone方法可以用来检查计算是否完成,get方法可以用来获取结果,直到完成前一直阻塞当前线程,cancel方法可以取消任务。而对于结果的获取,只能通过阻塞(get())或者轮询的方式[while(!isDone)]. 阻塞的方式违背了异步编程的理念,轮询的方式耗费无谓的CPU资源(CPU空转)。于是,CompletableFuture应运而生。
样例
后面介绍的源码都会以下面的用例为切入点,循着调用轨迹理解源码。如果任务很耗时,记得传Executor, 或者方法末尾加上future.get(); 因为CompletableFuture默认使用ForkJoinPool, 而ForkJoinPool里面的线程都是daemon线程,主线程跑完了,虚拟机也就over了。
1 public void whenComplete() { 2 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 3 future.whenComplete((l, r) -> System.out.println(l)); 4 } 5 6 public void thenApply() { 7 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 8 future.thenApply(i -> -i); 9 } 10 11 public void thenAccept() { 12 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 13 future.thenAccept(System.out::println); 14 } 15 16 public void thenRun() { 17 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 18 future.thenRun(() -> System.out.println("Done")); 19 } 20 21 public void thenAcceptBoth() { 22 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 23 CompletableFuture<Integer> other = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 200); 24 future.thenAcceptBoth(other, (x, y) -> System.out.println(x + y)); 25 } 26 27 public void acceptEither() { 28 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 29 CompletableFuture<Integer> other = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 200); 30 future.acceptEither(other, System.out::println); 31 32 } 33 34 public void allOf() { 35 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 36 CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 200); 37 CompletableFuture<Integer> third = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 300); 38 CompletableFuture.allOf(future, second, third); 39 40 } 41 42 public void anyOf() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 43 CompletableFuture<Integer> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 100); 44 CompletableFuture<Integer> second = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 200); 45 CompletableFuture<Integer> third = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> 300); 46 CompletableFuture.anyOf(future, second, third); 47 }
源码分析
supplyAsync
supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
1 public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) { 2 return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier); // asyncPool, ForkJoinPool.commonPool()或者ThreadPerTaskExecutor(实现了Executor接口,里面的内容是{new Thread(r).start();}) 3 }
asyncSupplyStage(Executor e, Supplier<U> f)
1 static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e, Supplier<U> f) { 2 if (f == null) 3 throw new NullPointerException(); 4 CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>(); // 构建一个新的CompletableFuture, 以此构建AsyncSupply作为Executor的执行参数 5 e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f)); // AsyncSupply继承了ForkJoinTask, 实现了Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask接口 6 return d; // 返回d,立返 7 }
AsyncSupply
1 // CompletableFuture的静态内部类,作为一个ForkJoinTask 2 static final class AsyncSupply<T> extends ForkJoinTask<Void> implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask { 3 CompletableFuture<T> dep; // AsyncSupply作为一个依赖Task,dep作为这个Task的Future 4 Supplier<T> fn; // fn作为这个Task的具体执行逻辑,函数式编程 5 6 AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture<T> dep, Supplier<T> fn) { 7 this.dep = dep; 8 this.fn = fn; 9 } 10 11 public final Void getRawResult() { 12 return null; 13 } 14 15 public final void setRawResult(Void v) { 16 } 17 18 public final boolean exec() { 19 run(); 20 return true; 21 } 22 23 public void run() { 24 CompletableFuture<T> d; 25 Supplier<T> f; 26 if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) { // 非空判断 27 dep = null; 28 fn = null; 29 if (d.result == null) { // 查看任务是否结束,如果已经结束(result != null),直接调用postComplete()方法 30 try { 31 d.completeValue(f.get()); // 等待任务结束,并设置结果 32 } catch (Throwable ex) { 33 d.completeThrowable(ex); // 异常 34 } 35 } 36 d.postComplete(); // 任务结束后,会执行所有依赖此任务的其他任务,这些任务以一个无锁并发栈的形式存在 37 } 38 } 39 }
postComplete()
1 final void postComplete() { 2 CompletableFuture<?> f = this; // 当前CompletableFuture 3 Completion h; // 无锁并发栈,(Completion next), 保存的是依靠当前的CompletableFuture一串任务,完成即触发(回调) 4 while ((h = f.stack) != null || (f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) { // 当f的stack为空时,使f重新指向当前的CompletableFuture,继续后面的结点 5 CompletableFuture<?> d; 6 Completion t; 7 if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) { // 从头遍历stack,并更新头元素 8 if (t != null) { 9 if (f != this) { // 如果f不是当前CompletableFuture,则将它的头结点压入到当前CompletableFuture的stack中,使树形结构变成链表结构,避免递归层次过深 10 pushStack(h); 11 continue; // 继续下一个结点,批量压入到当前栈中 12 } 13 h.next = null; // 如果是当前CompletableFuture, 解除头节点与栈的联系 14 } 15 f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d; // 调用头节点的tryFire()方法,该方法可看作Completion的钩子方法,执行完逻辑后,会向后传播的 16 } 17 } 18 }
示意图
每个CompletableFuture持有一个Completion栈stack, 每个Completion持有一个CompletableFuture -> dep, 如此递归循环下去,是层次很深的树形结构,所以想办法将其变成链表结构。
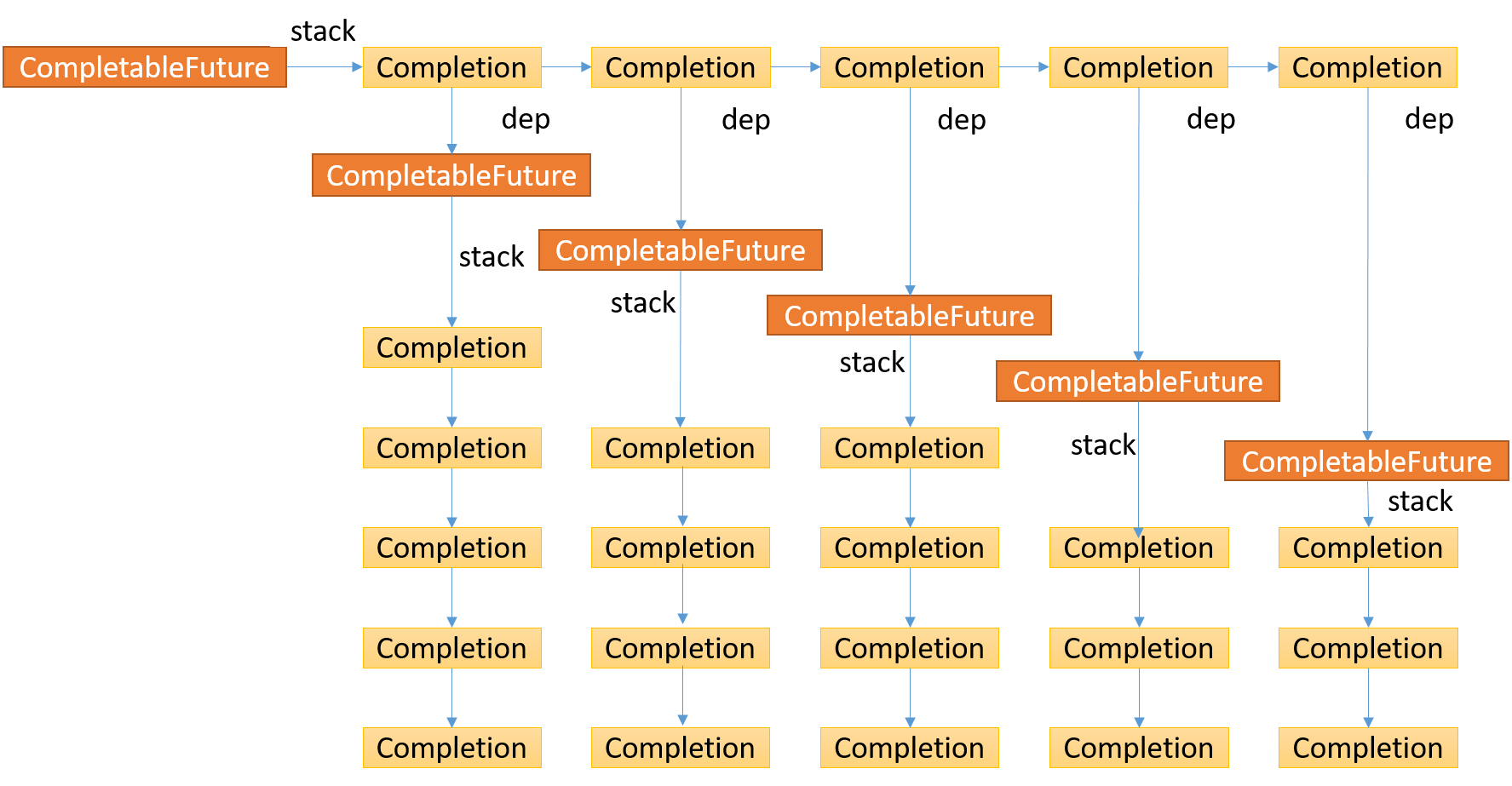
首先取出头结点,下图中灰色Completion结点,它会返回一个CompletableFuture, 同样也拥有一个stack,策略是遍历这个CompletableFuture的stack的每个结点,依次压入到当前CompletableFuture的stack中,关系如下箭头所示,灰色结点指的是处理过的结点。

第一个Completion结点返回的CompletableFuture, 将拥有的stack里面的所有结点都压入了当前CompletableFuture的stack里面
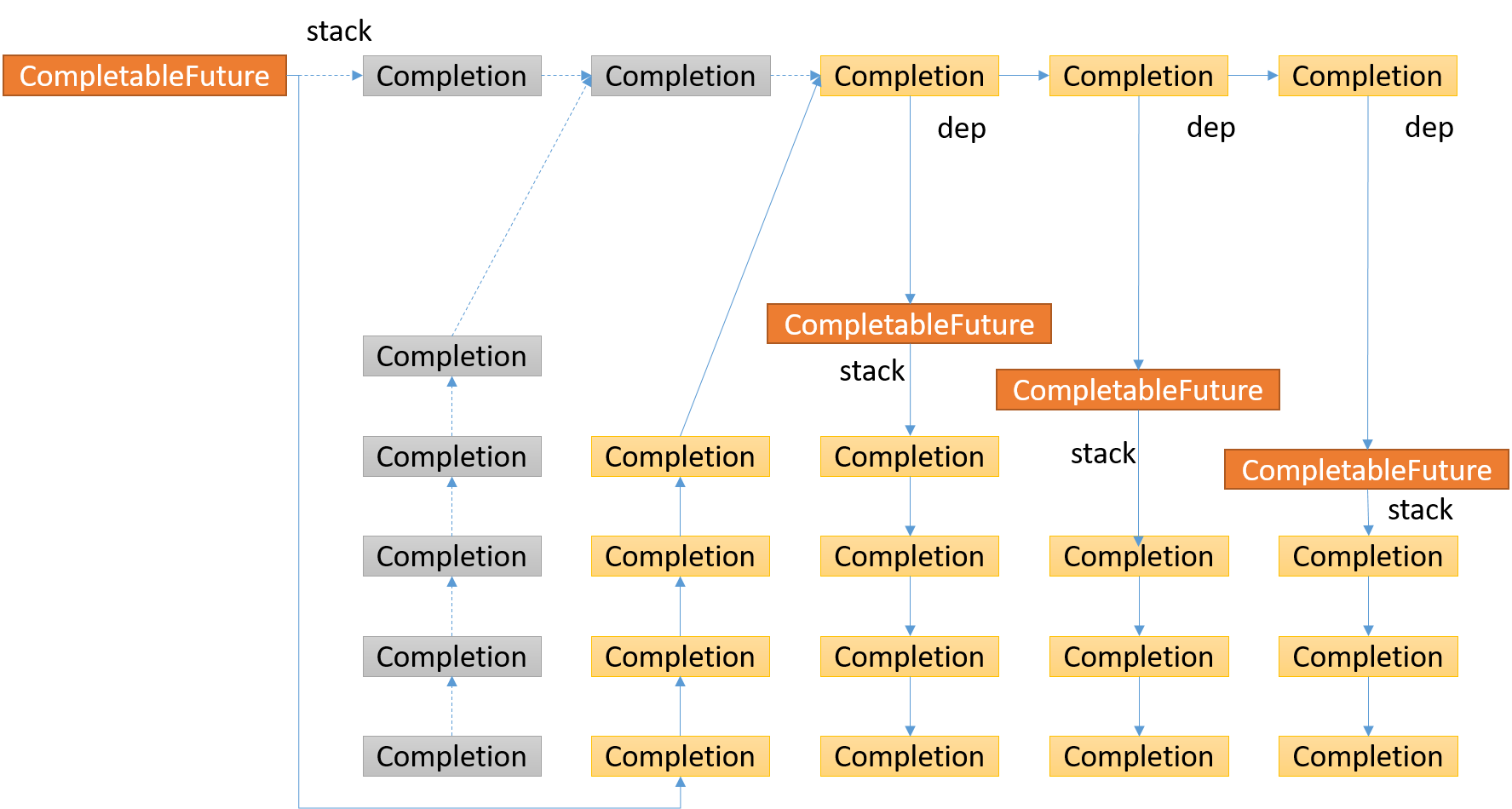
后续的Completion结点返回的CompletableFuture, 将拥有的stack里面的所有结点都压入了当前CompletableFuture的stack里面,重新构成了一个链表结构,后续也按照前面的逻辑操作,如此反复,便会遍历完所有的CompletableFuture, 这些CompletableFuture(叶子结点)的stack为空,也是结束条件。
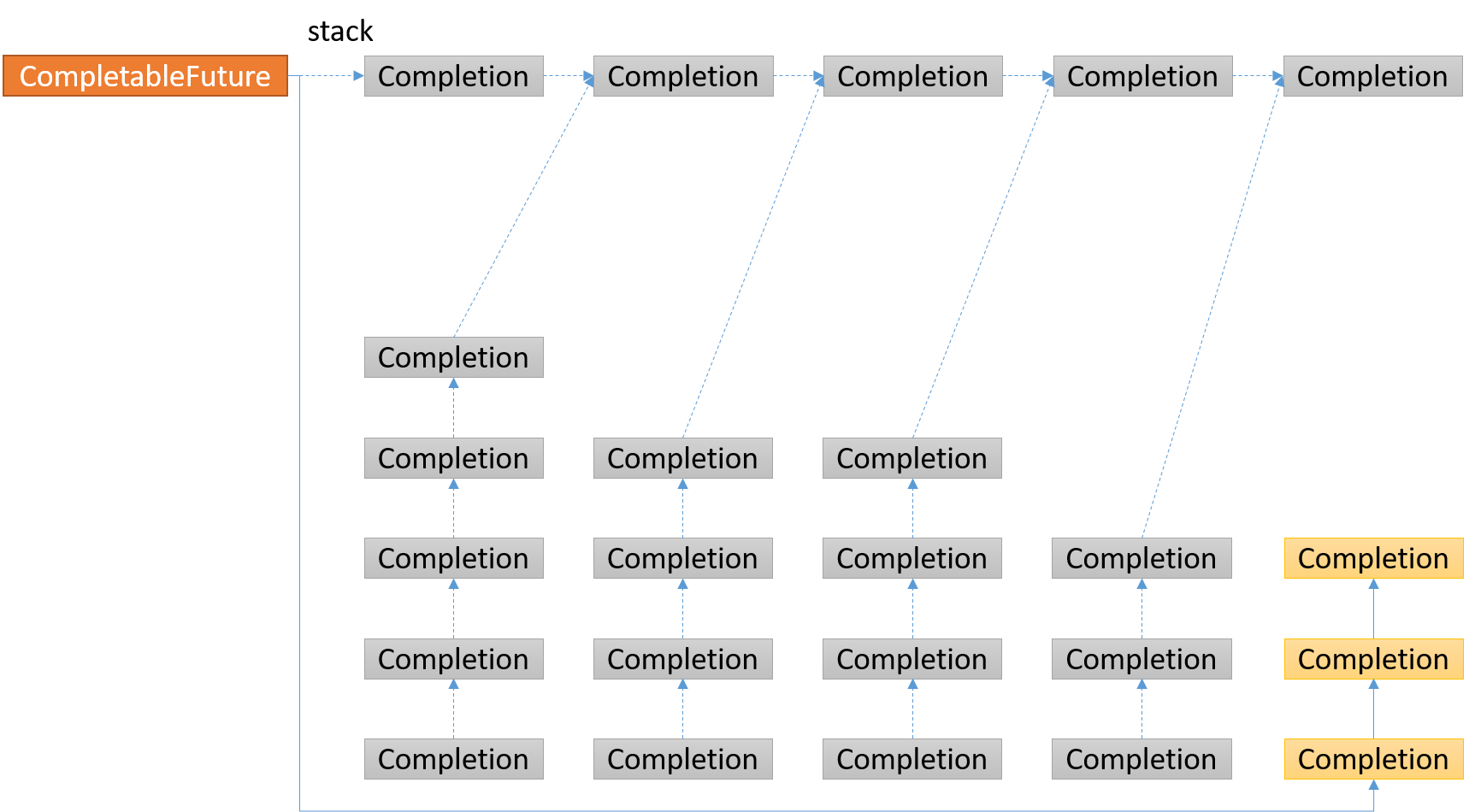
postComplete()最后调用的是Completion#tryFire()方法,先看下Completion的数据结构
Completion
1 abstract static class Completion extends ForkJoinTask<Void> implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask { 2 volatile Completion next; // 无锁并发栈 3 4 /** 5 * 钩子方法,有三种模式,postComplete()方法里面使用的是NESTED模式,避免过深的递归调用 SYNC, ASYNC, or NESTED 6 */ 7 abstract CompletableFuture<?> tryFire(int mode); // run()和exec()都调用了这个钩子方法 8 9 /** cleanStack()方法里有用到 */ 10 abstract boolean isLive(); 11 12 public final void run() { 13 tryFire(ASYNC); 14 } 15 16 public final boolean exec() { 17 tryFire(ASYNC); 18 return true; 19 } 20 21 public final Void getRawResult() { 22 return null; 23 } 24 25 public final void setRawResult(Void v) { 26 } 27 }
static final int SYNC = 0; 同步
static final int ASYNC = 1; 异步
static final int NESTED = -1; 嵌套
继承了ForkJoinTask, 实现了Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask接口,它有诸多子类,如下图
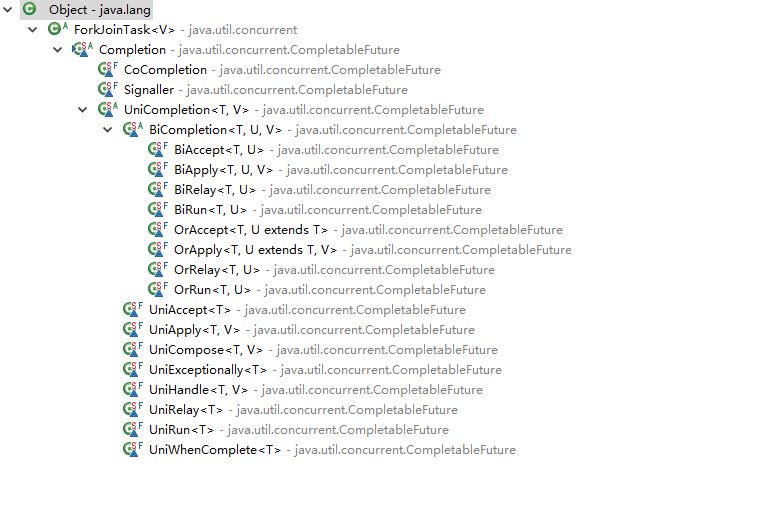
后面的方法都对应着不同的子类。
先看一个子类UniCompletion
1 abstract static class UniCompletion<T,V> extends Completion { 2 Executor executor; // 执行器 3 CompletableFuture<V> dep; // 依赖的任务 4 CompletableFuture<T> src; // 被依赖的任务 5 6 UniCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep, 7 CompletableFuture<T> src) { 8 this.executor = executor; this.dep = dep; this.src = src; 9 } 10 11 final boolean claim() { // 如果当前任务可以被执行,返回true,否则,返回false; 保证任务只被执行一次 12 Executor e = executor; 13 if (compareAndSetForkJoinTaskTag((short)0, (short)1)) { 14 if (e == null) 15 return true; 16 executor = null; // 设置为不可用 17 e.execute(this); 18 } 19 return false; 20 } 21 22 final boolean isLive() { return dep != null; } 23 }
claim()方法保证任务只被执行一次。
whenComplete
whenComplete()/whenCompleteAsync()
1 public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) { 2 return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action); 3 } 4 5 public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) { 6 return uniWhenCompleteStage(asyncPool, action); 7 }
xxx和xxxAsync方法的区别是,有没有asyncPool作为入参,有的话,任务直接入参,不检查任务是否完成。uniWhenCompleteStage方法有说明。
uniWhenCompleteStage(Executor e, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f)
1 private CompletableFuture<T> uniWhenCompleteStage(Executor e, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f) { 2 if (f == null) 3 throw new NullPointerException(); 4 CompletableFuture<T> d = new CompletableFuture<T>(); // 构建future 5 if (e != null || !d.uniWhenComplete(this, f, null)) { // 如果线程池不为空,直接构建任务入栈,并调用tryFire()方法;否则,调用uniWhenComplete()方法,检查依赖的那个任务是否完成,没有完成返回false, 6 // 完成了返回true, 以及后续一些操作。 7 UniWhenComplete<T> c = new UniWhenComplete<T>(e, d, this, f); // UniWhenComplete继承了UniCompletion 8 push(c); 9 c.tryFire(SYNC); // 先调一下钩子方法,检查一下任务是否结束 10 } 11 return d; 12 }
uniWhenComplete(CompletableFuture<T> a, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f, UniWhenComplete<T> c)
1 final boolean uniWhenComplete(CompletableFuture<T> a, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f, UniWhenComplete<T> c) { 2 Object r; 3 T t; 4 Throwable x = null; 5 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null) // 被依赖的任务还未完成 6 return false; 7 if (result == null) { // 被依赖的任务完成了 8 try { 9 if (c != null && !c.claim()) // 判断任务是否能被执行 10 return false; 11 if (r instanceof AltResult) { // 判断异常,AltResult类型很简单,里面只有一个属性Throwable ex; 12 x = ((AltResult) r).ex; 13 t = null; 14 } else { 15 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 16 T tr = (T) r; // 正常的结果 17 t = tr; 18 } 19 f.accept(t, x); // 执行任务 20 if (x == null) { 21 internalComplete(r); // 任务的结果设置为被依赖任务的结果 22 return true; 23 } 24 } catch (Throwable ex) { 25 if (x == null) 26 x = ex; // 记录异常 27 } 28 completeThrowable(x, r); // 设置异常和结果 29 } 30 return true; 31 }
push()
1 final void push(UniCompletion<?, ?> c) { 2 if (c != null) { 3 while (result == null && !tryPushStack(c)) 4 lazySetNext(c, null); // 失败重置c的next域 5 } 6 } 7 8 final boolean tryPushStack(Completion c) { 9 Completion h = stack; 10 lazySetNext(c, h); 11 return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, STACK, h, c); 12 } 13 14 static void lazySetNext(Completion c, Completion next) { 15 UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(c, NEXT, next); 16 }
UniWhenComplete
1 static final class UniWhenComplete<T> extends UniCompletion<T, T> { 2 BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> fn; 3 4 UniWhenComplete(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<T> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, 5 BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> fn) { 6 super(executor, dep, src); 7 this.fn = fn; 8 } 9 10 final CompletableFuture<T> tryFire(int mode) { // 钩子方法 11 CompletableFuture<T> d; // 依赖的任务 12 CompletableFuture<T> a; // 被依赖的任务 13 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.uniWhenComplete(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) // 如果是异步模式(mode = 1),就不判断任务是否结束 14 return null; // dep为空,说明已经调用过了 15 dep = null; 16 src = null; 17 fn = null; 18 return d.postFire(a, mode); // 钩子方法之后的处理 19 } 20 }
postFire(CompletableFuture<?> a, int mode)
1 final CompletableFuture<T> postFire(CompletableFuture<?> a, int mode) { 2 if (a != null && a.stack != null) { // 被依赖的任务存在,且stack不为空,先处理它 3 if (mode < 0 || a.result == null) // 如果是嵌套模式(mode = -1), 或者任务的结果为空,直接清空栈 4 a.cleanStack(); 5 else 6 a.postComplete(); // 否则,调用postComplete()方法 7 } 8 if (result != null && stack != null) { // 再处理当前任务 9 if (mode < 0) // 嵌套模式,直接返回自身(树 -> 链表,避免过深的递归调用) 10 return this; 11 else 12 postComplete(); // 调用postComplete()方法 13 } 14 return null; 15 }
cleanStack()
1 final void cleanStack() { // 过滤掉已经死掉的结点(Not isLive) 2 for (Completion p = null, q = stack; q != null;) { // q指针从头节点开始,向右移动,s一直执行q的下一个结点,p要么为空,要么指向遍历过的最后一个活着的结点,一旦发现q死掉了,就断开q, 连接p, s 3 Completion s = q.next; 4 if (q.isLive()) { // 还活着,p指向遍历过的最后一个结点,q向右移动 5 p = q; 6 q = s; 7 } else if (p == null) { // 说明第一个结点就是死掉的,cas stack, q指向stack 8 casStack(q, s); 9 q = stack; 10 } else { // 否则的话,连接p, s 11 p.next = s; 12 if (p.isLive()) // 再次判断p结点是否还或者(在这期间是否有别的线程改动了) 13 q = s; // 还活着,q继续向右移动 14 else { 15 p = null; // 过期的值,从新开始 16 q = stack; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 }
如下图
1. 第1个结点是无效结点,更新stack,更新指针
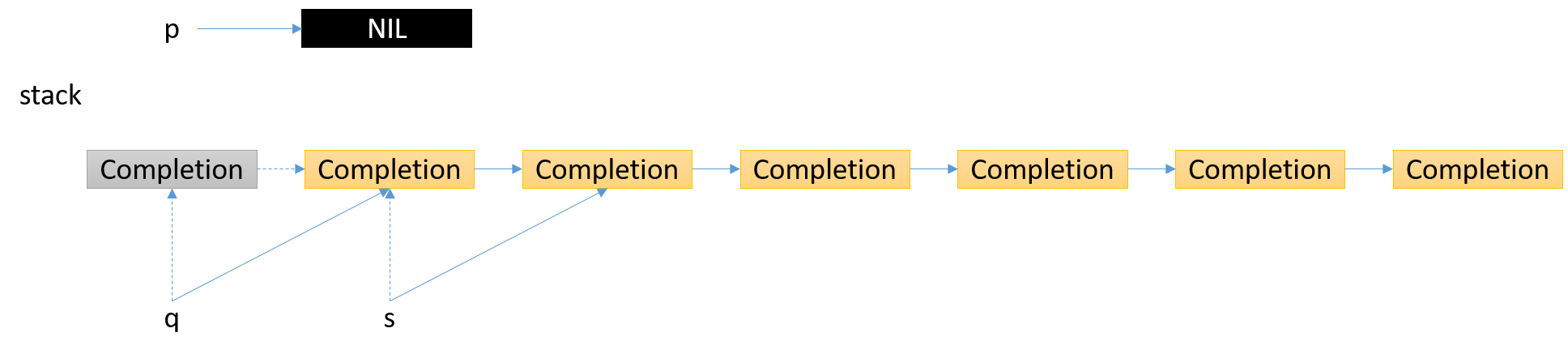
2. 第2个结点是有效结点,更新指针

3. 第3个结点是无效结点,更新指针
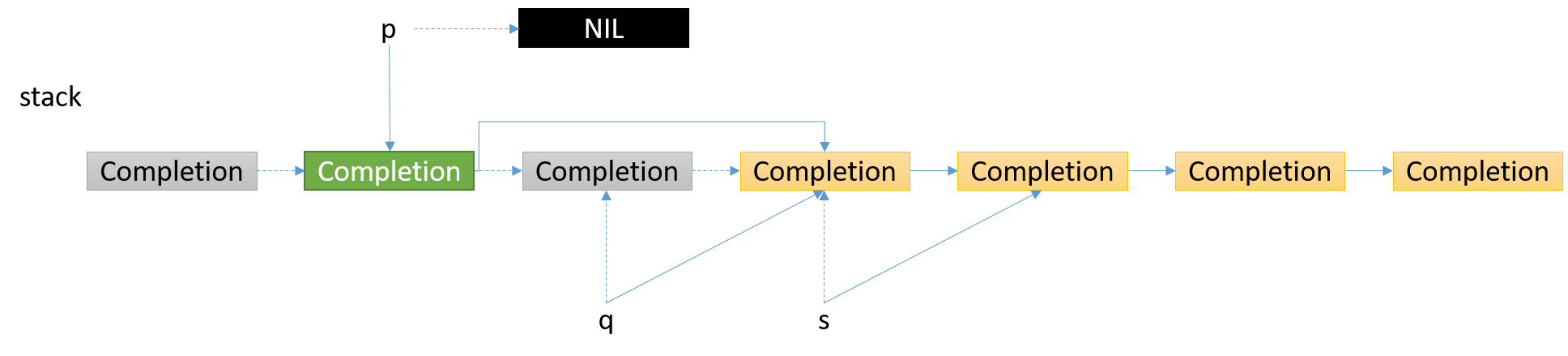
4. 第4个结点是有效结点,更新指针
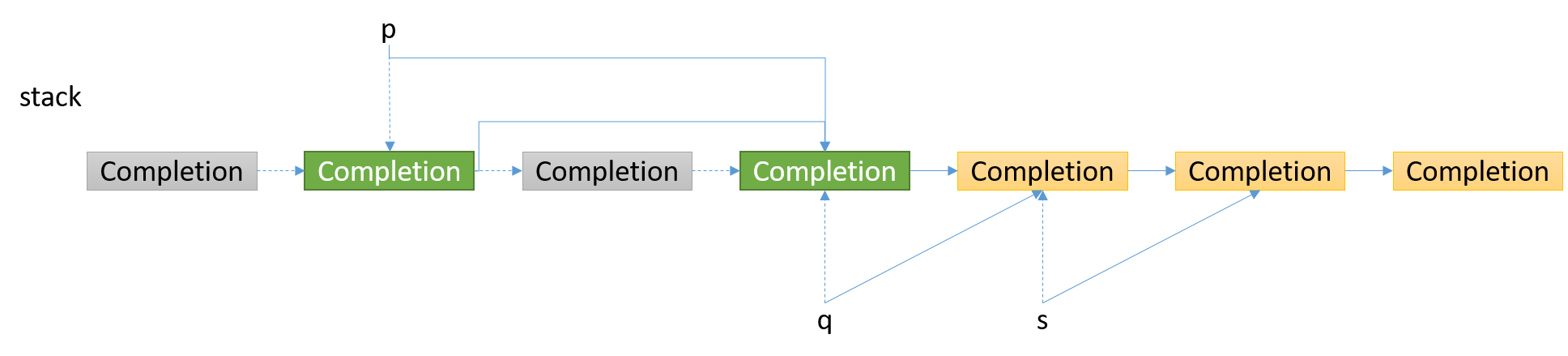
thenApply
1 public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T, ? extends U> fn) { 2 return uniApplyStage(null, fn); 3 } 4 5 public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends U> fn) { 6 return uniApplyStage(asyncPool, fn); 7 } 8 9 private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(Executor e, Function<? super T, ? extends V> f) { 10 if (f == null) 11 throw new NullPointerException(); 12 CompletableFuture<V> d = new CompletableFuture<V>(); 13 if (e != null || !d.uniApply(this, f, null)) { 14 UniApply<T, V> c = new UniApply<T, V>(e, d, this, f); 15 push(c); 16 c.tryFire(SYNC); 17 } 18 return d; 19 } 20 21 final <S> boolean uniApply(CompletableFuture<S> a, Function<? super S, ? extends T> f, UniApply<S, T> c) { 22 Object r; 23 Throwable x; 24 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null) 25 return false; 26 tryComplete: if (result == null) { 27 if (r instanceof AltResult) { 28 if ((x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) { 29 completeThrowable(x, r); // 有异常,直接跳出 30 break tryComplete; 31 } 32 r = null; 33 } 34 try { 35 if (c != null && !c.claim()) 36 return false; 37 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 38 S s = (S) r; 39 completeValue(f.apply(s)); 40 } catch (Throwable ex) { 41 completeThrowable(ex); 42 } 43 } 44 return true; 45 } 46 47 static final class UniApply<T, V> extends UniCompletion<T, V> { 48 Function<? super T, ? extends V> fn; 49 50 UniApply(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, 51 Function<? super T, ? extends V> fn) { 52 super(executor, dep, src); 53 this.fn = fn; 54 } 55 56 final CompletableFuture<V> tryFire(int mode) { 57 CompletableFuture<V> d; 58 CompletableFuture<T> a; 59 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.uniApply(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) 60 return null; 61 dep = null; 62 src = null; 63 fn = null; 64 return d.postFire(a, mode); 65 } 66 }
一样的套路,thenApply/thenApplyAsync -> uniApplyStage -> uniApply -> tryFire -> postFire
thenAccept
1 public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) { 2 return uniAcceptStage(null, action); 3 } 4 5 public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) { 6 return uniAcceptStage(asyncPool, action); 7 } 8 9 private CompletableFuture<Void> uniAcceptStage(Executor e, Consumer<? super T> f) { 10 if (f == null) 11 throw new NullPointerException(); 12 CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>(); 13 if (e != null || !d.uniAccept(this, f, null)) { 14 UniAccept<T> c = new UniAccept<T>(e, d, this, f); 15 push(c); 16 c.tryFire(SYNC); 17 } 18 return d; 19 } 20 21 final <S> boolean uniAccept(CompletableFuture<S> a, Consumer<? super S> f, UniAccept<S> c) { 22 Object r; 23 Throwable x; 24 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null) 25 return false; 26 tryComplete: if (result == null) { 27 if (r instanceof AltResult) { 28 if ((x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) { 29 completeThrowable(x, r); // 有异常直接跳出 30 break tryComplete; 31 } 32 r = null; 33 } 34 try { 35 if (c != null && !c.claim()) 36 return false; 37 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 38 S s = (S) r; 39 f.accept(s); 40 completeNull(); 41 } catch (Throwable ex) { 42 completeThrowable(ex); 43 } 44 } 45 return true; 46 } 47 48 static final class UniAccept<T> extends UniCompletion<T, Void> { 49 Consumer<? super T> fn; 50 51 UniAccept(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<Void> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, Consumer<? super T> fn) { 52 super(executor, dep, src); 53 this.fn = fn; 54 } 55 56 final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) { 57 CompletableFuture<Void> d; 58 CompletableFuture<T> a; 59 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.uniAccept(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) 60 return null; 61 dep = null; 62 src = null; 63 fn = null; 64 return d.postFire(a, mode); 65 } 66 }
thenAccept/thenAcceptAsync -> uniAcceptStage -> uniAccept -> tryFire -> postFire
thenRun
1 public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) { 2 return uniRunStage(null, action); 3 } 4 5 public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) { 6 return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action); 7 } 8 9 private CompletableFuture<Void> uniRunStage(Executor e, Runnable f) { 10 if (f == null) 11 throw new NullPointerException(); 12 CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>(); 13 if (e != null || !d.uniRun(this, f, null)) { 14 UniRun<T> c = new UniRun<T>(e, d, this, f); 15 push(c); 16 c.tryFire(SYNC); 17 } 18 return d; 19 } 20 21 final boolean uniRun(CompletableFuture<?> a, Runnable f, UniRun<?> c) { 22 Object r; 23 Throwable x; 24 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || f == null) 25 return false; 26 if (result == null) { 27 if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) 28 completeThrowable(x, r); 29 else 30 try { 31 if (c != null && !c.claim()) 32 return false; 33 f.run(); 34 completeNull(); 35 } catch (Throwable ex) { 36 completeThrowable(ex); 37 } 38 } 39 return true; 40 } 41 42 static final class UniRun<T> extends UniCompletion<T, Void> { 43 Runnable fn; 44 45 UniRun(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<Void> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, Runnable fn) { 46 super(executor, dep, src); 47 this.fn = fn; 48 } 49 50 final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) { 51 CompletableFuture<Void> d; 52 CompletableFuture<T> a; 53 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.uniRun(a = src, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) 54 return null; 55 dep = null; 56 src = null; 57 fn = null; 58 return d.postFire(a, mode); 59 } 60 }
thenRun/thenRunAsync -> uniRunStage -> uniRun -> tryFire -> postFire
thenAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) { return biAcceptStage(null, other, action); } public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action) { return biAcceptStage(asyncPool, other, action); }
biAcceptStage
private <U> CompletableFuture<Void> biAcceptStage(Executor e, CompletionStage<U> o, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> f) { CompletableFuture<U> b; if (f == null || (b = o.toCompletableFuture()) == null) throw new NullPointerException(); CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>(); if (e != null || !d.biAccept(this, b, f, null)) { BiAccept<T, U> c = new BiAccept<T, U>(e, d, this, b, f); bipush(b, c); c.tryFire(SYNC); } return d; }
bipush
1 final void bipush(CompletableFuture<?> b, BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> c) { 2 if (c != null) { 3 Object r; 4 while ((r = result) == null && !tryPushStack(c)) // a的result还没准备好,c压入栈 5 lazySetNext(c, null); // 失败重置c的next域 6 if (b != null && b != this && b.result == null) { // b的result也还没准备好 7 Completion q = (r != null) ? c : new CoCompletion(c); // 根据a的result决定是否构建CoCompletion, 如果a未结束,则构建一个CoCompletion, CoCompletion最后调用的也是BiCompletion的tryFire 8 while (b.result == null && !b.tryPushStack(q)) // 将q压入栈 9 lazySetNext(q, null); // 失败重置q的next域 10 } 11 } 12 }
CoCompletion
1 static final class CoCompletion extends Completion { 2 BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> base; 3 4 CoCompletion(BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> base) { 5 this.base = base; 6 } 7 8 final CompletableFuture<?> tryFire(int mode) { 9 BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> c; 10 CompletableFuture<?> d; 11 if ((c = base) == null || (d = c.tryFire(mode)) == null) // 调用的还是BiCompletion的tryFire方法 12 return null; 13 base = null; 14 return d; 15 } 16 17 final boolean isLive() { 18 BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> c; 19 return (c = base) != null && c.dep != null; 20 } 21 }
biAccept
1 final <R, S> boolean biAccept(CompletableFuture<R> a, CompletableFuture<S> b, BiConsumer<? super R, ? super S> f, 2 BiAccept<R, S> c) { 3 Object r, s; 4 Throwable x; 5 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || b == null || (s = b.result) == null || f == null) 6 return false; // a和b都完成了,才会往下走 7 tryComplete: if (result == null) { 8 if (r instanceof AltResult) { 9 if ((x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) { // a的异常检查 10 completeThrowable(x, r); 11 break tryComplete; 12 } 13 r = null; 14 } 15 if (s instanceof AltResult) { 16 if ((x = ((AltResult) s).ex) != null) { // b的异常检查 17 completeThrowable(x, s); 18 break tryComplete; 19 } 20 s = null; 21 } 22 try { 23 if (c != null && !c.claim()) 24 return false; 25 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 26 R rr = (R) r; 27 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 28 S ss = (S) s; 29 f.accept(rr, ss); // 执行任务 30 completeNull(); 31 } catch (Throwable ex) { 32 completeThrowable(ex); 33 } 34 } 35 return true; 36 }
BiAccept
1 static final class BiAccept<T, U> extends BiCompletion<T, U, Void> { 2 BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> fn; 3 4 BiAccept(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<Void> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, CompletableFuture<U> snd, 5 BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> fn) { 6 super(executor, dep, src, snd); 7 this.fn = fn; 8 } 9 10 final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) { 11 CompletableFuture<Void> d; 12 CompletableFuture<T> a; 13 CompletableFuture<U> b; 14 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.biAccept(a = src, b = snd, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) 15 return null; 16 dep = null; 17 src = null; 18 snd = null; 19 fn = null; 20 return d.postFire(a, b, mode); 21 } 22 } 23 24 abstract static class BiCompletion<T, U, V> extends UniCompletion<T, V> { 25 CompletableFuture<U> snd; // second source for action 26 27 BiCompletion(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<V> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, CompletableFuture<U> snd) { 28 super(executor, dep, src); 29 this.snd = snd; 30 } 31 }
thenAcceptBoth/thenAcceptBothAsync -> biAcceptStage -> biAccept -> tryFire -> postFire
acceptEither
1 public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action) { 2 return orAcceptStage(null, other, action); 3 } 4 5 public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action) { 6 return orAcceptStage(asyncPool, other, action); 7 } 8 9 private <U extends T> CompletableFuture<Void> orAcceptStage(Executor e, CompletionStage<U> o, 10 Consumer<? super T> f) { 11 CompletableFuture<U> b; 12 if (f == null || (b = o.toCompletableFuture()) == null) 13 throw new NullPointerException(); 14 CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>(); 15 if (e != null || !d.orAccept(this, b, f, null)) { 16 OrAccept<T, U> c = new OrAccept<T, U>(e, d, this, b, f); 17 orpush(b, c); 18 c.tryFire(SYNC); 19 } 20 return d; 21 } 22 23 final <R, S extends R> boolean orAccept(CompletableFuture<R> a, CompletableFuture<S> b, Consumer<? super R> f, 24 OrAccept<R, S> c) { 25 Object r; 26 Throwable x; 27 if (a == null || b == null || ((r = a.result) == null && (r = b.result) == null) || f == null) 28 return false; // a和b有一个完成了就往下走 29 tryComplete: if (result == null) { 30 try { 31 if (c != null && !c.claim()) 32 return false; 33 if (r instanceof AltResult) { // 异常 34 if ((x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) { 35 completeThrowable(x, r); 36 break tryComplete; 37 } 38 r = null; 39 } 40 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 41 R rr = (R) r; 42 f.accept(rr); // 执行 43 completeNull(); 44 } catch (Throwable ex) { 45 completeThrowable(ex); 46 } 47 } 48 return true; 49 } 50 51 static final class OrAccept<T, U extends T> extends BiCompletion<T, U, Void> { 52 Consumer<? super T> fn; 53 54 OrAccept(Executor executor, CompletableFuture<Void> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, CompletableFuture<U> snd, 55 Consumer<? super T> fn) { 56 super(executor, dep, src, snd); 57 this.fn = fn; 58 } 59 60 final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) { 61 CompletableFuture<Void> d; 62 CompletableFuture<T> a; 63 CompletableFuture<U> b; 64 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.orAccept(a = src, b = snd, fn, mode > 0 ? null : this)) 65 return null; 66 dep = null; 67 src = null; 68 snd = null; 69 fn = null; 70 return d.postFire(a, b, mode); 71 } 72 } 73 74 final void orpush(CompletableFuture<?> b, BiCompletion<?, ?, ?> c) { 75 if (c != null) { 76 while ((b == null || b.result == null) && result == null) { // a和b的result都没好,才会考虑入栈 77 if (tryPushStack(c)) { // 先入a的栈 78 if (b != null && b != this && b.result == null) { // 入a的栈成功,b的result还没好 79 Completion q = new CoCompletion(c); // a还未结束,用c构建CoCompletion 80 while (result == null && b.result == null && !b.tryPushStack(q)) // 再次判断,a和b的result都没好,才会考虑入栈 81 lazySetNext(q, null); // 失败置空q的next域 82 } 83 break; 84 } 85 lazySetNext(c, null); // 失败置空c的next域 86 } 87 } 88 }
acceptEither/acceptEitherAsync -> orAcceptStage -> orAccept -> tryFire -> postFire
allOf
1 public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) { 2 return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1); 3 } 4 5 static CompletableFuture<Void> andTree(CompletableFuture<?>[] cfs, int lo, int hi) { // 将一个数组构建成一棵树,二叉树,动态规划 6 CompletableFuture<Void> d = new CompletableFuture<Void>(); 7 if (lo > hi) // empty 8 d.result = NIL; 9 else { 10 CompletableFuture<?> a, b; 11 int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1; 12 if ((a = (lo == mid ? cfs[lo] : andTree(cfs, lo, mid))) == null 13 || (b = (lo == hi ? a : (hi == mid + 1) ? cfs[hi] : andTree(cfs, mid + 1, hi))) == null) 14 throw new NullPointerException(); 15 if (!d.biRelay(a, b)) { 16 BiRelay<?, ?> c = new BiRelay<>(d, a, b); 17 a.bipush(b, c); // both 18 c.tryFire(SYNC); 19 } 20 } 21 return d; 22 } 23 24 static final class BiRelay<T, U> extends BiCompletion<T, U, Void> { // for And 25 BiRelay(CompletableFuture<Void> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, CompletableFuture<U> snd) { 26 super(null, dep, src, snd); 27 } 28 29 final CompletableFuture<Void> tryFire(int mode) { 30 CompletableFuture<Void> d; 31 CompletableFuture<T> a; 32 CompletableFuture<U> b; 33 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.biRelay(a = src, b = snd)) 34 return null; 35 src = null; 36 snd = null; 37 dep = null; 38 return d.postFire(a, b, mode); 39 } 40 } 41 42 boolean biRelay(CompletableFuture<?> a, CompletableFuture<?> b) { 43 Object r, s; 44 Throwable x; 45 if (a == null || (r = a.result) == null || b == null || (s = b.result) == null) 46 return false; // a和b都结束了才往下执行 47 if (result == null) { 48 if (r instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult) r).ex) != null) 49 completeThrowable(x, r); 50 else if (s instanceof AltResult && (x = ((AltResult) s).ex) != null) 51 completeThrowable(x, s); 52 else 53 completeNull(); // 辅助结点,什么都不做 54 } 55 return true; 56 }
allOf -> andTree -> biRelay -> tryFire -> postFire
anyOf
1 public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) { 2 return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1); 3 } 4 5 static CompletableFuture<Object> orTree(CompletableFuture<?>[] cfs, int lo, int hi) { // 将一个数组构建成一棵树,二叉树,动态规划 6 CompletableFuture<Object> d = new CompletableFuture<Object>(); 7 if (lo <= hi) { 8 CompletableFuture<?> a, b; 9 int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1; 10 if ((a = (lo == mid ? cfs[lo] : orTree(cfs, lo, mid))) == null 11 || (b = (lo == hi ? a : (hi == mid + 1) ? cfs[hi] : orTree(cfs, mid + 1, hi))) == null) 12 throw new NullPointerException(); 13 if (!d.orRelay(a, b)) { 14 OrRelay<?, ?> c = new OrRelay<>(d, a, b); 15 a.orpush(b, c); 16 c.tryFire(SYNC); 17 } 18 } 19 return d; 20 } 21 22 static final class OrRelay<T, U> extends BiCompletion<T, U, Object> { // for Or 23 OrRelay(CompletableFuture<Object> dep, CompletableFuture<T> src, CompletableFuture<U> snd) { 24 super(null, dep, src, snd); 25 } 26 27 final CompletableFuture<Object> tryFire(int mode) { 28 CompletableFuture<Object> d; 29 CompletableFuture<T> a; 30 CompletableFuture<U> b; 31 if ((d = dep) == null || !d.orRelay(a = src, b = snd)) 32 return null; 33 src = null; 34 snd = null; 35 dep = null; 36 return d.postFire(a, b, mode); 37 } 38 } 39 40 final boolean orRelay(CompletableFuture<?> a, CompletableFuture<?> b) { 41 Object r; 42 if (a == null || b == null || ((r = a.result) == null && (r = b.result) == null)) 43 return false; // a和b有一个结束就往下进行 44 if (result == null) 45 completeRelay(r); 46 return true; 47 }
anyOf -> orTree -> orRelay -> tryFire -> postFire
数组构建树
allOf和anyOf都用到了数组构建成树的策略。
假设有一个任务Z(虚拟的,什么都不做),依赖一组任务[A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H]
对于allOf, 当这组任务都完成时,才会执行Z;对于anyOf, 当这组任务中有任何一个完成,就执行任务Z。
如果这组任务是数组结构或者链表结构,我们该如何解决呢?遍历数组或者是链表,当任务都完成或者有一个完成时,就执行Z,需要不停地遍历,这是轮询的方法,不合适。
整个基调是回调,是指,当一个任务完成时,会接着执行所有依赖于它的任务。
作为一个数组或者链表,该如何应用回调呢?谁在先,谁在后呢?因为不知道哪个任务会先完成,所以没法确定次序。而且这组任务之间也不应该相互依赖,它们只不过都是被Z依赖。
如果这组任务只有一个的话,那就演变成了X.thenXXX(Z), 如果这组任务有两个的话,allOf -> Both,anyOf -> Either
如果Z依赖Z1,Z2两个个任务,Z1和Z2依赖Z11,Z12和Z21,Z22四个任务,依次类推,当虚拟的任务的个数达到真实任务的个数的一半时,就让虚拟任务监听真实的任务,动态规划加二叉树,时间复杂度也只是logn级别的。
1 static String array2Tree(String[] cfs, int lo, int hi) { 2 String d = new String(cfs[lo] + cfs[hi]); 3 if (lo <= hi) { 4 String a, b; 5 int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1; // 二分 6 if (lo == mid) { // a作为左半部分的的结果 7 a = cfs[lo]; // 当只有不超过两个元素时,a直接取第一个值 8 } else { 9 a = array2Tree(cfs, lo, mid); 10 } 11 if (lo == hi) { // 当只有一个元素的时候,b取a的值 12 b = a; 13 } else { 14 if (hi == mid + 1) { // 右半部分只有两个元素时,b取第二个元素的值 15 b = cfs[hi]; 16 } else { 17 b = array2Tree(cfs, mid + 1, hi); 18 } 19 } 20 if (a == null || b == null) { 21 throw new NullPointerException(); 22 } 23 System.out.println("[" + a + "][" + b + "]->[" + d + "]"); 24 } 25 return d; 26 }
Console
[A][B]->[AB]
[C][D]->[CD]
[AB][CD]->[AD]
[E][F]->[EF]
[G][H]->[GH]
[EF][GH]->[EH]
[AD][EH]->[AH]
如下图
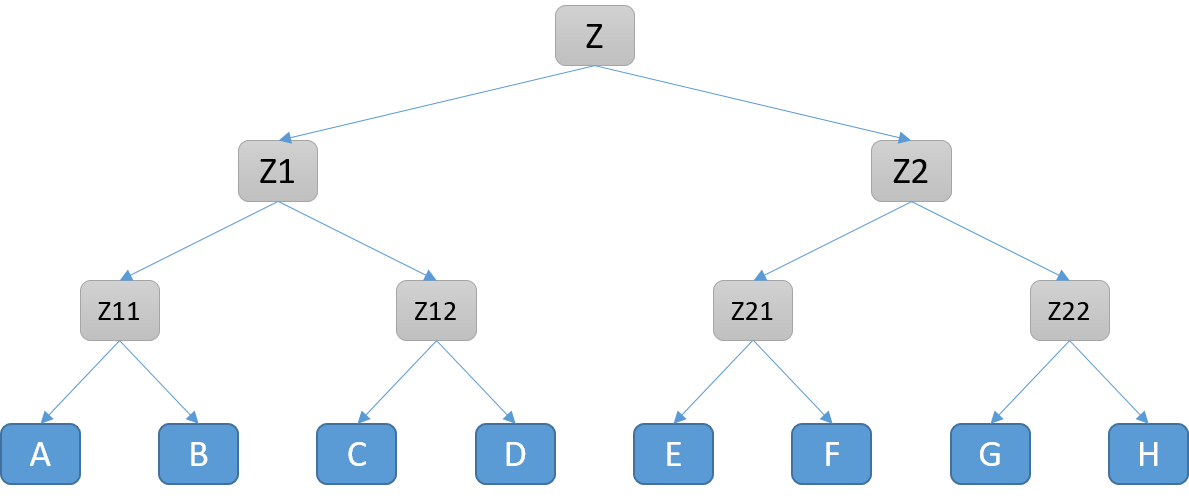
对于allOf, Z只要保证Z1和Z2都完成了就行,Z1和Z2分别保证Z11,Z12 和 Z21,Z22都完成了就像,而Z11,Z12,Z21,Z22则分别保证了A-H任务都完成。
对应anyOf, Z 只要保证Z1和Z2有一个完成了就像,Z1和Z2联合保证了Z11,Z12,Z21,Z22这4个任务只要有一个完成了就行,同理,Z11,Z12,Z21,Z22则联合保证了A-H中有一个任务完成了就行。
然后,Z就可以执行了,其实Z什么也没做,只是从这组任务里得出一个结果。
行文至此结束。
尊重他人的劳动,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/aniao/p/aniao_cf.html