1.初步了解:
(1)事件:指的是能够发生的什么事情。比如公司上市,这里的上市就是事件(比事情更正式。)。
(2)在c#中的定义:是类型的成员。是一种使对象或类具备了通知能力的成员。
(3)事件参数:经由事件发送过来的,与事件本身相关的消息,称为事件参数。
作用:比如,当手机的关注者收到通知之后,就会检查事件参数(这里的包含这个通知中具体是开会还是别的信息),根据事件参数中的内容采取相应的行动。
(4)微事件处理器:软对这种对响应做出的相应处理称为响应事件或者处理事件,处理事件中具体所做的事情就叫做事件处理器。
(5)事件=使对象或类具备通知的能力+可选的事件参数(就是指的传来的详细信息)
(6)使用环境:用于对象或类之间的动作协调与信息传递(消息推送)。
某某对象有什么事件,是指这个对象可以通过这个事件来通知别的对象,事件一发生,关心这个事件的对象就会做出响应进行相应的处理。
(7)事件模型(它是从现实生活中抽象出来的一个客观存在)
发生->响应中的5个部分:闹钟响了你起床,孩子饿了你做饭。这2个例子都只有4部分,闹钟,响了,你,起床;孩子,饿了,你,做饭。还缺最后一部分,就是订阅关系。就是说你关注着某个事件。比如说为什么别人的闹钟响你不起床呢,因为你指订阅了自己的闹钟的事件,并且对事件做出了响应。
发生->响应中的5个动作(步骤):(1)我有一个事件。(2)一个人或一群人关心这个事件(3)我的事件发生了(4)关心这个事件的人依次接到通知(5)被通知到的人根据拿到的事件信息(又称事件数据,事件参数,通知)对事件进行响应(又称事件处理器)
(8)事件多用于桌面手机等的客户端编程。
2.事件的应用
事件不会主动发生,一定是事件的拥有者的内部逻辑触发的。
(1)事件模型的5个组成部分
·事件的拥有者(event source,对象)
·事件成员(event,成员)
·事件的响应者(event subscriber,对象)
·事件处理器(event handler,成员)--本质是一个回调方法
·事件订阅 把事件处理器和事件关联起来,本质上是一种以委托类型为基础的约定。用于订阅事件的事件处理器必须和事件遵守同一个约定。这个约定既约定了事件能够把什么样的消息发送给事件处理器,也约束了事件处理器能够处理什么样的消息。如果想订阅的事件和事件处理器遵守的约定是一样的,那就能够匹配。这个约定就是委托。所以常常说事件是基于委托的。
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //timer事件拥有者 Timer timer = new Timer(); //boy是事件响应者 Boy boy = new Boy(); timer.Interval = 1000; //+=表示事件订阅,其中Elapsed是事件 timer.Elapsed += boy.Action; timer.Start(); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class Boy { /// <summary> /// 事件处理器 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">这是事件的拥有者,事件的source,或者事件的发送者(这三个说法都一样)</param> /// <param name="e">事件参数</param> internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("elapsedEventArgs"); } }
(2)下面是事件的拥有者和响应者是不同的对象。

下面的代码是上图中的格式,事件的响应者和拥有者是不同的对象。
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //form是事件拥有者 Form form = new Form(); //controller是事件响应者 Controller controller = new Controller(form); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class Controller { private Form form; public Controller(Form form) { if(form!=null) { this.form = form; //事件是Click。 //事件处理器订阅事件FormClicked。 this.form.Click += this.FormClicked; } } /// <summary> /// 事件处理器 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.form.Text = "test"; } }
(3)事件的拥有者和响应者是同一对象。
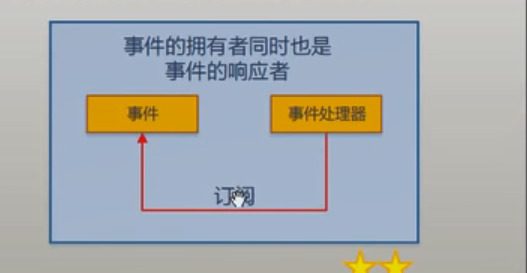
代码如下:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //form是事件拥有者 MyForm form = new MyForm(); form.Click += form.FormClicked; Console.ReadKey(); } } public class MyForm:Form { /// <summary> /// 事件处理器 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> internal void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Text = "test"; } }
(4)事件的拥有者是事件的相应者的一个字段成员,事件的响应者用方法订阅者自己的成员的某个事件。
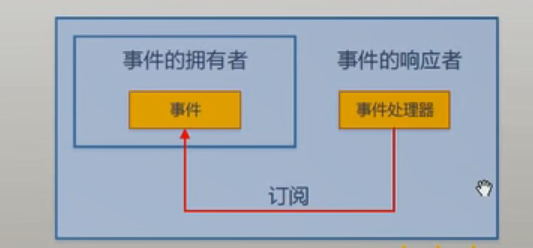
实现点击按钮,在文本框中显示文本信息
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //form是事件拥有者,也是事件的响应者 MyForm form = new MyForm(); form.ShowDialog(); Console.ReadKey(); } } public class MyForm:Form { private TextBox textBox; private Button button; public MyForm() { this.textBox = new TextBox(); this.button = new Button(); this.Controls.Add(textBox); this.Controls.Add(button); //Click是事件,ButtonCliked订阅了事件Click this.button.Click += this.ButtonCliked; } /// <summary> /// 事件处理器 /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">这是事件的拥有者,事件的source,或者事件的发送者</param> /// <param name="e">事件参数</param> private void ButtonCliked(object sender, EventArgs e) { if(sender==this.button) { this.textBox.Text = "test"; } } }
3.事件的声明
事件是基于委托的。
第一层意思:就是说事件需要委托来做约束,这个约束既规定了事件能够发送什么样的消息给事件的响应者,也规定了事件的响应者返回什么样的消息,所以说这个事件的事件响应器必须和这个事件匹配上才能订阅这个事件。
第二层意思:当事件的响应者给事件的拥有者提供了能够匹配的事件处理器之后,需要找个地方将事件处理器记录保存下来,能够记录和引用方法的任务也只有委托能够实现。
总的来说,事件不管是从表层约束来讲,还是底层实现来讲,都是依赖于委托的。
(1)完整声明
比如去餐馆吃饭,这时候会有服务员来订阅你点菜的事件,当点菜的事件发生,服务员之后就会上菜。实际上服务员拿自己的事件处理器来处理你点菜的事件。现在我们声明实现一个点菜的事件。
namespace TestClass { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //customer是事件拥有者, Customer customer = new Customer(); //waitor是事件的响应者 Waitor waitor = new Waitor(); //Order是事件,Action是事件处理器 //订阅事件 customer.Order += waitor.Action; //订阅完事件,下面需要执行这个事件 customer.Action(); customer.PayTheBill(); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// 如果一个委托是为了声明一个事件准备的,那么需要后缀加上EventHandler /// 这个委托和类是平级的,因为委托本质上是类。 /// </summary> /// <param name="customer"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e); /// <summary> /// 菜单信息类 /// 如果某个类是作为EventArgs事件参数来使用的话,那就需要继承EventArgs /// </summary> public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs { /// <summary> /// 菜名 /// </summary> public string DishName; public string Size; } public class Customer { /// <summary> /// 账单 /// </summary> public double Bill; private OrderEventHandler orderEventHandler; /// <summary> /// 创建一个事件Order点菜 /// 这个事件是由OrderEventHandler委托进行约束的。 /// </summary> public event OrderEventHandler Order { add { this.orderEventHandler += value; } remove { this.orderEventHandler -= value; } } public void PayTheBill() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void WalkIn() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void SitDown() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } /// <summary> /// 思考吃什么 /// </summary> public void Think() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); //先判断有没有订阅这个事件 if(this.orderEventHandler!=null) { OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs(); orderEventArgs.DishName = "Noodles"; orderEventArgs.Size = "Size"; this.orderEventHandler(this,orderEventArgs); } } public void Action() { Console.ReadLine(); this.WalkIn(); this.SitDown(); this.Think(); } } /// <summary> /// 服务生 /// </summary> public class Waitor { public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e) { Console.Write($"DishName={e.DishName}"); double price = 10; switch(e.Size) { case "small": price *= 0.5; break; case "large": price *= 1.5; break; default: break; } customer.Bill += price; } } }
注意上面的代码,之所以使用EventHandler后缀,用意有3个:第一个是别人看到后就会知道这个委托是专门用来生成事件的。第二个是说明这个委托是用来约束事件处理器的。第三个是指这个委托将来是专门用来存储事件处理器的。
简化声明:
namespace TestClass { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //customer是事件拥有者, Customer customer = new Customer(); //waitor是事件的响应者 Waitor waitor = new Waitor(); //Order是事件,Action是事件处理器 //订阅事件 customer.Order += waitor.Action; //订阅完事件,下面需要执行这个事件 customer.Action(); customer.PayTheBill(); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// 如果一个委托是为了声明一个事件准备的,那么需要后缀加上EventHandler /// 这个委托和类是平级的,因为委托本质上是类。 /// </summary> /// <param name="customer"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e); /// <summary> /// 菜单信息类 /// 如果某个类是作为EventArgs事件参数来使用的话,那就需要继承EventArgs /// </summary> public class OrderEventArgs:EventArgs { /// <summary> /// 菜名 /// </summary> public string DishName; public string Size; } public class Customer { /// <summary> /// 账单 /// </summary> public double Bill; /// <summary> /// 创建一个事件Order点菜 /// 这个事件是由OrderEventHandler委托进行约束的。 /// </summary> public event OrderEventHandler Order; public void PayTheBill() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void WalkIn() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void SitDown() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } /// <summary> /// 思考吃什么 /// </summary> public void Think() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); //先判断有没有订阅这个事件 if(this.Order != null) { OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs(); orderEventArgs.DishName = "Noodles"; orderEventArgs.Size = "Size"; this.Order(this,orderEventArgs); } } public void Action() { Console.ReadLine(); this.WalkIn(); this.SitDown(); this.Think(); } } /// <summary> /// 服务生 /// </summary> public class Waitor { public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e) { Console.Write($"DishName={e.DishName}"); double price = 10; switch(e.Size) { case "small": price *= 0.5; break; case "large": price *= 1.5; break; default: break; } customer.Bill += price; } } }
4.有了委托字段/属性,为什么还需要事件?
为了程序的逻辑更加的‘有道理’,更加安全,防止‘借刀杀人’
比如在餐馆中,明明你没有点别的菜,但是别人给点了,记到了自己上面。
如下:
namespace TestClass { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //customer是事件拥有者, Customer customer = new Customer(); //waitor是事件的响应者 Waitor waitor = new Waitor(); //Order是事件,Action是事件处理器 //订阅事件 customer.Order += waitor.Action; //订阅完事件,下面需要执行这个事件 //customer.Action(); #region 不用事件,使用委托 OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs() { DishName = "test1", Size="small" }; OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs1 = new OrderEventArgs() { DishName = "test2", Size = "large" }; Customer badCustomer = new Customer(); badCustomer.Order += waitor.Action; badCustomer.Order(customer, orderEventArgs1); badCustomer.Order(customer, orderEventArgs); #endregion customer.PayTheBill(); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// 如果一个委托是为了声明一个事件准备的,那么需要后缀加上EventHandler /// 这个委托和类是平级的,因为委托本质上是类。 /// </summary> /// <param name="customer"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> public delegate void OrderEventHandler(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e); /// <summary> /// 菜单信息类 /// 如果某个类是作为EventArgs事件参数来使用的话,那就需要继承EventArgs /// </summary> public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs { /// <summary> /// 菜名 /// </summary> public string DishName; public string Size; } public class Customer { /// <summary> /// 账单 /// </summary> public double Bill; /// <summary> /// 创建一个事件Order点菜 /// 这个事件是由OrderEventHandler委托进行约束的。 /// </summary> //public event OrderEventHandler Order; #region 不用事件,使用委托 //创建委托字段 public OrderEventHandler Order; #endregion public void PayTheBill() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void WalkIn() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void SitDown() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } /// <summary> /// 思考吃什么 /// </summary> public void Think() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); //先判断有没有订阅这个事件 if (this.Order != null) { OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs(); orderEventArgs.DishName = "Noodles"; orderEventArgs.Size = "Size"; this.Order(this, orderEventArgs); } } public void Action() { Console.ReadLine(); this.WalkIn(); this.SitDown(); this.Think(); } } /// <summary> /// 服务生 /// </summary> public class Waitor { public void Action(Customer customer, OrderEventArgs e) { Console.Write($"DishName={e.DishName}"); double price = 10; switch (e.Size) { case "small": price *= 0.5; break; case "large": price *= 1.5; break; default: break; } customer.Bill += price; } } }
需要注意的是,在开发的时候,很多项目是很多人一起做,如果没有做限制的话,很可能会被滥用。如果是通过事件的话,就会确保只有订阅了这个事件的事件响应者才会和这个事件有联系。事件的触发只能是事件的拥有者才能触发,比委托更安全。
把上面代码中 public event OrderEventHandler Order;这行代码的event去掉,就会报错,这种使用有问题( badCustomer.Order(customer, orderEventArgs1);): 事件“Customer.Order”只能出现在 += 或 -= 的左边(从类型“Customer”中使用时除外) 。
5.事件的本质是委托字段的包装器
(1)这个包装器对委托字段的访问起限制作用
(2)封装的一个重要功能就是隐藏
(3)事件对外界隐藏了委托字段的大部分功能,仅暴露添加/移除事件处理器的功能。(所以上面代码将委托字段改成事件(加上event)之后就会报错,事件对于本类的外界来说,只暴露了添加/移除事件处理器的功能)
6.通用的事件约束
下面是一个通用的事件约束
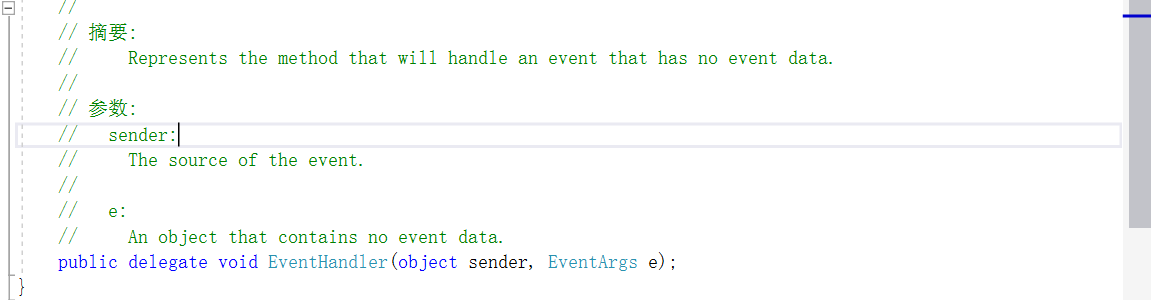
代码:
namespace TestClass { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //customer是事件拥有者, Customer customer = new Customer(); //waitor是事件的响应者 Waitor waitor = new Waitor(); //Order是事件,Action是事件处理器 //订阅事件 customer.Order += waitor.Action; //订阅完事件,下面需要执行这个事件 customer.Action(); customer.PayTheBill(); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// 菜单信息类 /// 如果某个类是作为EventArgs事件参数来使用的话,那就需要继承EventArgs /// </summary> public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs { /// <summary> /// 菜名 /// </summary> public string DishName; public string Size; } public class Customer { /// <summary> /// 账单 /// </summary> public double Bill; /// <summary> /// 创建一个事件Order点菜 /// 这个事件是由EventHandler委托进行约束的。 /// </summary> public event EventHandler Order; public void PayTheBill() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void WalkIn() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void SitDown() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } /// <summary> /// 思考吃什么 /// </summary> public void Think() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); //先判断有没有订阅这个事件 if (this.Order != null) { OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs(); orderEventArgs.DishName = "Noodles"; orderEventArgs.Size = "Size"; this.Order(this, orderEventArgs); } } public void Action() { Console.ReadLine(); this.WalkIn(); this.SitDown(); this.Think(); } } /// <summary> /// 服务生 /// </summary> public class Waitor { public void Action(object obj, EventArgs args) { Customer customer = (Customer)obj; OrderEventArgs e = args as OrderEventArgs; Console.Write($"DishName={e.DishName}"); double price = 10; switch (e.Size) { case "small": price *= 0.5; break; case "large": price *= 1.5; break; default: break; } customer.Bill += price; } } }
7.触发事件Foo,一般谢伟OnFoo,而且级别一般是protected级别,防止“借刀杀人”
所以修改后的代码:
namespace TestClass { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //customer是事件拥有者, Customer customer = new Customer(); //waitor是事件的响应者 Waitor waitor = new Waitor(); //Order是事件,Action是事件处理器 //订阅事件 customer.Order += waitor.Action; //订阅完事件,下面需要执行这个事件 customer.Action(); customer.PayTheBill(); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// 菜单信息类 /// 如果某个类是作为EventArgs事件参数来使用的话,那就需要继承EventArgs /// </summary> public class OrderEventArgs : EventArgs { /// <summary> /// 菜名 /// </summary> public string DishName; public string Size; } public class Customer { /// <summary> /// 账单 /// </summary> public double Bill; /// <summary> /// 创建一个事件Order点菜 /// 这个事件是由EventHandler委托进行约束的。 /// </summary> public event EventHandler Order; public void PayTheBill() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void WalkIn() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } public void SitDown() { Console.WriteLine($"支付账单:{this.Bill}"); } /// <summary> /// 思考吃什么 /// </summary> public void Think() { Console.WriteLine("Thinking"); this.OnOrder("chicken","large"); } protected void OnOrder(string name,string size) { //先判断有没有订阅这个事件 if (this.Order != null) { OrderEventArgs orderEventArgs = new OrderEventArgs(); orderEventArgs.DishName = name; orderEventArgs.Size = size; this.Order(this, orderEventArgs); } } public void Action() { Console.ReadLine(); this.WalkIn(); this.SitDown(); this.Think(); } } /// <summary> /// 服务生 /// </summary> public class Waitor { public void Action(object obj, EventArgs args) { Customer customer = (Customer)obj; OrderEventArgs e = args as OrderEventArgs; Console.Write($"DishName={e.DishName}"); double price = 10; switch (e.Size) { case "small": price *= 0.5; break; case "large": price *= 1.5; break; default: break; } customer.Bill += price; } } }
8.事件的命名约定
(1)带有时态的动词或者动词短语
(2)正在做什么用进行时,完成做什么就用完成时。

引于:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV13b411b7Ht?p=21