委托,事件这个两个不知道看过多少次了,总是摸不透。这一次又把他们集中来展现,希望下次能完全明白。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace dazilianxi { public class SmartCar { private int distance; public string brand="福特"; public string type="翼虎"; public delegate void DetectDistanceEventHandler(object sender,DetectDistanceEventArgs e);//声明委托 public event DetectDistanceEventHandler DetectDistance;//声明事件 //事件一旦被触发就调用所有的注册方法 //设计成虚方法以便让子类来继承,这样子类就可以不被观察者监视 public virtual void OnDetectDistance(DetectDistanceEventArgs e) { if (DetectDistance!=null) { DetectDistance(this,e); } } public void KeepSafety() { for (int i = 100; i > 48;i-- ) { distance = i; if (distance<50){ DetectDistanceEventArgs d = new DetectDistanceEventArgs(distance); OnDetectDistance(d);//触发事件 } } } } public class DetectDistanceEventArgs:EventArgs { public readonly int distance; public DetectDistanceEventArgs(int distance) { this.distance = distance; } } public class Alarm { public void MarkAlert(object sender,DetectDistanceEventArgs e) { SmartCar car = (SmartCar)sender; Console.WriteLine("开始开始,与前方车距{0}米,请保持车距",e.distance); Console.WriteLine("前方车牌号为{0},车型是{1}",car.brand,car.type); Console.WriteLine(); } } public class Display { public static void ShowAlert(object sender, DetectDistanceEventArgs e) { SmartCar car = (SmartCar)sender; Console.WriteLine("与前方车距{0}米,请保持车距", e.distance); Console.WriteLine("前方车牌号为{0},车型是{1}", car.brand, car.type); Console.WriteLine(); } } }
SmartCar car = new SmartCar();//这个是事件的引发者 Alarm al = new Alarm(); car.DetectDistance+=al.MarkAlert; //注册事件 car.DetectDistance += Display.ShowAlert;//注册事件 car.KeepSafety();//执行方法 Console.ReadKey();
委托异步调用
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; namespace dazilianxi { public delegate string delecooking(string food1,string food2); public class Cooking { public string Cook(string food1,string food2) { Thread.CurrentThread.Name = "王大厨"; Console.WriteLine("厨师开始炒菜!"); for (int i = 1; i <= 2;i++ ) { Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(i)); Console.WriteLine("{0},炒菜时间{1}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,i); } Console.WriteLine("好了,菜做好了"); return food1 + food2; } } }
Console.WriteLine("客人点菜!"); Cooking co = new Cooking(); //string result = co.Cook("鱼香","肉丝"); //Console.WriteLine("好了,请慢用{0}",result); //Console.WriteLine("客人吃完了"); delecooking del = new delecooking(co.Cook);//给委托注册方法 string data = "希望您能喜欢"; AsyncCallback callBack = new AsyncCallback(OnCookComplete); IAsyncResult asyncResult = del.BeginInvoke("西红柿", "鸡蛋", callBack, data); Console.WriteLine("客人做点其他事……"); // string result = del.EndInvoke(asyncResult); // Console.WriteLine("{0}好了,请慢用!", result); Console.ReadKey();
//回调需要执行的方法 static void OnCookComplete(IAsyncResult asyncResult) { AsyncResult result = (AsyncResult)asyncResult; //从异步结果中可以拿到委托 delecooking del = (delecooking)result.AsyncDelegate; string data = (string)asyncResult.AsyncState; //从异步结果中可以拿到BeginInvoke方法中的object参数 string r = del.EndInvoke(asyncResult); Console.WriteLine("{0}好了,请慢用,{1}", r,data); }
事件定义在引发者类里面。
public delegate void maojiaodelegate (object Sender, EventArgs e); /// <summary> /// 触发对象 观察者 人醒来 /// </summary> public class BigMaster { private Mao _cat; public BigMaster(Mao cat) { _cat = cat; _cat.onjiao += new maojiaodelegate(onxinglaile); } public void onxinglaile(object Sender, EventArgs e) { xinglaile(); } public void xinglaile() { Console.WriteLine("xinglai"); } } /// <summary> /// 事件引发者 被观察者 猫叫 /// </summary> public class Mao { public event maojiaodelegate onjiao; public void catjiao( EventArgs e) { if (onjiao != null) { onjiao(this, e); } } public void catjiao() { // Console.WriteLine("jiao"); EventArgs e=new EventArgs(); catjiao(e); } } /// <summary> /// 触发对象 观察者 老鼠跑了 /// </summary> public class Lashu { private Mao _cat; public Lashu(Mao cat) { _cat = cat; _cat.onjiao += new maojiaodelegate(onrunningla); } public void onrunningla(object Sender,EventArgs e) { runningla(); } public void runningla() { Console.WriteLine("pao"); } }
Mao mao = new Mao(); mao.catjiao(); BigMaster p = new BigMaster(mao); Lashu lao = new Lashu(mao);
Demo 委托 Code highlighting produced by Actipro CodeHighlighter (freeware)http://www.CodeHighlighter.com/--> 1 using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace DelegateDemo { class Class1 { delegate double processDelegate(double db1, double db2); static double Multiply(double db1, double db2) { return db1 * db2; } static double Divide(double db1, double db2) { return db1 / db2; } static void NamedMethod(string strInput,double dbNum1,double dbNum2) { processDelegate process; if (strInput == "M") process = new processDelegate(Multiply); else process = new processDelegate(Divide); Console.WriteLine("结果为:{0}", process(dbNum1, dbNum2)); }
//匿名的方法 static void AnonymousMethod(string strInput, double dbNum1, double dbNum2) { processDelegate process; if (strInput == "M") process = delegate(double db1, double db2){return db1 * db2;}; else process = delegate(double db1, double db2) { return db1 / db2; }; Console.WriteLine("结果为:{0}", process(dbNum1, dbNum2)); } /// <summary> /// 应用程序的主入口点。 /// </summary> [STAThread] static void Main(string[] args) { // // TODO: 在此处添加代码以启动应用程序 Console.WriteLine("请输入两个小数,用逗号分割"); string strInput = Console.ReadLine(); int commmaPos = strInput.IndexOf(','); double dbNum1 = Convert.ToDouble(strInput.Substring(0, commmaPos)); double dbNum2 = Convert.ToDouble(strInput.Substring(commmaPos + 1)); Console.WriteLine("输入M表示乘法,或者D表示除法"); strInput = (Console.ReadLine()).ToUpper(); //使用命名方法 Console.WriteLine("使用命名方法委托"); NamedMethod(strInput,dbNum1,dbNum2); //使用匿名方法 Console.WriteLine("使用匿名方法委托"); AnonymousMethod(strInput, dbNum1, dbNum2); } } }
委托实例:http://www.cnblogs.com/liulun/archive/2009/10/25/1589523.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/liulun/archive/2009/05/29/1491912.html
事件多播:http://www.cnblogs.com/liulun/archive/2009/09/24/1573571.html
另外:
http://www.cnblogs.com/annabook/p/4583357.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2007/09/23/903360.html
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace xiancheng { class Program { delegate void mytest(int a,int b); static void Main(string[] args) { mytest tee = delegate(int x,int y) { int result = x + y; Console.WriteLine("这是匿名委托用法结果是: "+result); }; tee(2, 8); mytest tee2 = new mytest(getresult); tee2(9,8); //拉姆达 mytest tee3 = (x,y)=> { int result = x + y; Console.WriteLine("这是拉姆达匿名委托用法结果是: " + result); }; tee3(88, 12);
mytest tee4 = new mytest((x, y) => {
int result = x + y;
Console.WriteLine("这是拉姆达匿名委托用法结果是: " + result);
});
tee4(5,45);
mytest tee5 = getresult;
tee5(90, 8);
Console.ReadKey(); } public static void getresult(int x, int y) { int result = x + y; Console.WriteLine("这不是匿名委托方法使用结果是: "+result) ; } } }
输出 10,17,100,50,98
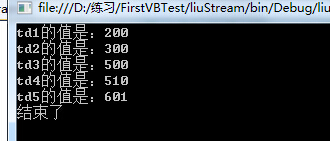
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace liuStream { public class weituo { public delegate double testdelegate(int num); // private int x; public static double chengfa(int x) { return x * 5; } public static double chufa(int x) { return x / 100; } public static double add(int x) { return x + 100; } public static double jiafa(int x) { return 100-x; } public void getruslut() { testdelegate td1 = add;//居然不报错 testdelegate td2 = new testdelegate(add); testdelegate td3 = (x) => { return x+100; }; testdelegate td4 = delegate(int x) { return x+10; }; testdelegate td5 = new testdelegate((x) => { return x+1; }); Console.WriteLine("td1的值是:"+ td1(100)); Console.WriteLine("td2的值是:"+td2(200)); Console.WriteLine("td3的值是:"+ td3(400)); Console.WriteLine("td4的值是:"+ td4(500)); Console.WriteLine("td5的值是:"+ td5(600)); } public weituo() { } } }
调用:
weituo te = new weituo(); te.getruslut(); Console.WriteLine("结束了"); Console.ReadKey();
结果:
Lambda表达式
(1)源起
.net的设计者发现在使用匿名方法时,
仍旧有一些多余的字母或单词的编码工作
比如delegate关键字
于是进一步简化了匿名方法的写法
(2)使用
List<int> arr = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
arr.ForEach(new Action<int>(delegate(int a) { Console.WriteLine(a); }));
arr.ForEach(new Action<int>(a => Console.WriteLine(a)));
匿名方法的代码如下:
delegate(int a) { Console.WriteLine(a); }
使用lambda表达式的代码如下:
a => Console.WriteLine(a)
这里解释一下这个lambda表达式
<1>
a是输入参数,编译器可以自动推断出它是什么类型的,
如果没有输入参数,可以写成这样:
() => Console.WriteLine("ddd")
<2>
=>是lambda操作符
<3>
Console.WriteLine(a)是要执行的语句。
如果是多条语句的话,可以用{}包起来。
如果需要返回值的话,可以直接写return语句