要专业系统地学习EF前往《你必须掌握的Entity Framework 6.x与Core 2.0》这本书的作者(汪鹏,Jeffcky)的博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/CreateMyself/
EF的优点之一在于我们得实体模型不用匹配存储模型
Entity Spliting
实体拆分就是将一个实体进行配置后,映射后会在数据库中生成多张表
来个类,里面包含图书和水果的属性

public class Model1
{
public string Model1Id { get; set; }
public string FruitName { get; set; }
public decimal FruitPrice { get; set; }
public string BookName { get; set; }
public decimal BookPrice { get; set; }
public DateTime AddTime { get; set; }
}
配置到两张表

protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Model1>().Map(m =>
{
m.Properties(p => new
{
p.Model1Id,
p.BookName,
p.BookPrice,
p.AddTime
});
m.ToTable("tb_Books");
}).Map(m =>
{
m.Properties(p => new
{
p.FruitName,
p.FruitPrice
});
m.ToTable("tb_Fruits");
});
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
}
生成的表结构如下
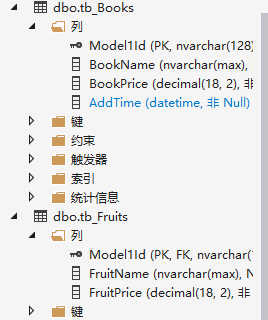
添加一个水果,会生成两条插入数据,因为两个表都要插入数据,对Model进行查询的时候会进行连表查询
这个还是有一点局限,因为只有一个model,查询的时候不能针对Fruit和Book进行查询
Table Spliting
多个实体映射为一张表
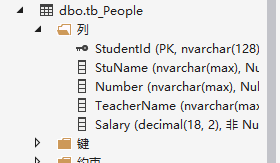
学生类Student

public class Student
{
public string StudentId { get; set; }
public string StuName { get; set; }
public string Number { get; set; }
public virtual Teacher Teacher { get; set; }
}
老师类

public class Teacher
{
public string TeacherId { get; set; }
public string TeacherName { get; set; }
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
public Student Student { get; set; }
}
配置

modelBuilder.Entity<Student>().ToTable("tb_People").HasKey(x => x.StudentId)
.HasRequired(x =>x.Teacher).WithRequiredPrincipal(x =>x.Student);
modelBuilder.Entity<Teacher>().ToTable("tb_People").HasKey(x => x.TeacherId);
生成表结构如下,和TPH一样