前言
在此,只是对下面这条链接的实现:
https://www.cnblogs.com/AlexanderZhao/p/12369732.html
正文
测试分类:
1.单元测试
2.集成测试
3.皮下测试
4.UI测试
测试的三个阶段:AAA
Arrange: 在这里做一些先决的设定。例如创建对象实例,数据,输入等。
Act: 在这里执行生产代码并返回结果。例如调用方法或者设置属性。
Assert:在这里检查结果,会产生测试通过或者失败两种结果。

Assert方法应用
bool 值:
Patient patient = new Patient();
var result = patient.IsNew;
Assert.True(result);
Assert.False(result);
string 类型:
[Fact]
public async void Test1()
{
Patient patient = new Patient();
Assert.Equal("xxx",patient.FistName);
Assert.NotEqual("xxx",patient.LastName);
Assert.StartsWith("xxx",patient.LastName);
Assert.EndsWith("xxx",patient.LastName);
Assert.Contains("xxx",patient.LastName);
Assert.Matches(@"xxx",patient.LastName);
}
数字类型:
Patient patient = new Patient();
var result = patient.Age;
Assert.Equal(4.9f,result);
Assert.InRange(result,3.9,6.1);
判断null 和 not null
var p = new Patient();
Assert.Null(p.FirstName);
Assert.NotNull(_patient);
集合:
Patient patient = new Patient();
var diseases = new List<string>
{
"感冒",
"发烧",
"水痘",
"腹泻"
};
Assert.Contains("感冒",patient.History);
Assert.DoesNotContain("感冒", patient.History);
// any
Assert.Contains(patient.History,x=>x.StartsWith("水"));
// 遍历 all
Assert.All(patient.History, x => { Assert.True(x.Length > 2); });
Assert.Equal(diseases,patient.History);
对象:
Patient patient = new Patient();
Patient patient1 = new Patient();
// 类型是否相同
Assert.IsNotType<Patient>(patient);
Assert.IsType<Patient>(patient);
// 两个实例是否是同一个
Assert.Same(patient,patient1);
Assert.NotSame(patient, patient1);
//是否继承Patient
Assert.IsAssignableFrom<Patient>(patient);
错误性验证:
Patient patient = new Patient();
// 判断是否出现指定的异常
var ex = Assert.Throws<InvalidOperationException>(()=> { patient.NotAllowed(); });
// 进一步判断异常消息
Assert.Equal("not able to create", ex.Message);
判断是否触发事件:
/// <summary>
/// 判断是否触发事件
/// </summary>
[Fact]
public void RaizeSleepEvent()
{
var p = new Patient();
Assert.Raises<EventArgs>(
handler=>p.PatientSlept+=handler,
handler=>p.PatientSlept -= handler,
() => p.Sleep());
}
判断属性改变是否触发事件#
/// <summary>
/// 测试属性改变事件是否触发
/// </summary>
[Fact]
public void RaisePropertyChangedEvent()
{
var p = new Patient();
Assert.PropertyChanged(p, nameof(p.HeartBeatRate),
() => p.IncreaseHeartBeatRate());
}
进阶
分组测试:
[Fact]
[Trait("Category", "New")]
public void BeNewWhenCreated()
{
var patient = new Patient();
patient.IsNew = true;
var result = patient.IsNew;
Assert.True(result);
}
[Fact]
[Trait("Category", "add")]
public void BeNewWhenCreated1()
{
var patient = new Patient();
var result = patient.IsNew;
Assert.True(result);;
}
dotnet test --filter “Category=New” //运行单个分类测试
dotnet test --filter “Category=New|Category=Add”//运行多个分类测试
dotnet test --filter Category --logger:trx //输出测试日志
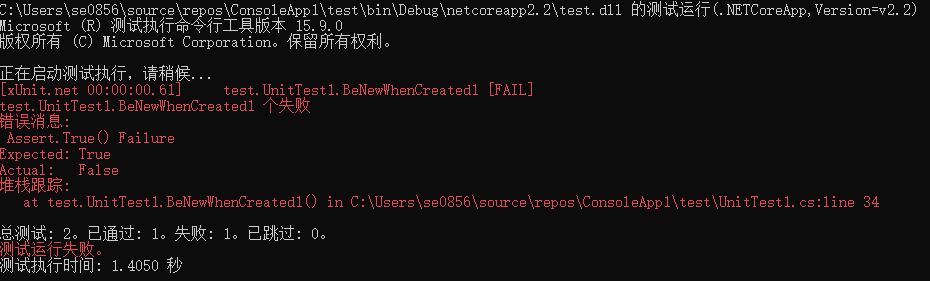
忽略测试#
使用特性:[Fact(Skip="不跑这个测试")],可以忽略测试,忽略测试图标为黄色警告
自定义测试输出内容#
使用ITestOutputHelper可以自定义在测试时的输出内容
dotnet test --filter Category --logger:trx会输出测试日志trx结尾的文件
public class PatientShould:IClassFixture<LongTimeFixture>,IDisposable
{
private readonly ITestOutputHelper _output;
private readonly Patient _patient;
private readonly LongTimeTask _task;
public PatientShould(ITestOutputHelper output,LongTimeFixture fixture)
{
this._output = output;
_patient = new Patient();
//_task = new LongTimeTask();
_task = fixture.Task;
}
[Fact]
[Trait("Category","New")]
public void BeNewWhenCreated()
{
_output.WriteLine("第一个测试");
// Arrange
//var patient = new Patient();
// Act
var result = _patient.IsNew;
// Assert
Assert.True(result);
//Assert.False(result);
}
}
减少重复代码#
减少new对象,可以在构造函数中new,在方法中使用。
测试类实现IDispose接口,测试完释放资源,注意每个测试结束后都会调用Dispose方法。
共享上下文#
同一个测试类#
在执行一个方法时,需要很长事件,而在构造函数中new时,每个测试跑的时候都会new对象或者执行方法,这是导致测试很慢。解决方法:
创建一个类:
using Demo2;
using System;
namespace Demo2Test
{
public class LongTimeFixture : IDisposable
{
public LongTimeTask Task { get; }
public LongTimeFixture()
{
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
}
}
测试类实现IClassFixture
public class PatientShould:IClassFixture<LongTimeFixture>,IDisposable
{
private readonly ITestOutputHelper _output;
private readonly Patient _patient;
private readonly LongTimeTask _task;
public PatientShould(ITestOutputHelper output,LongTimeFixture fixture)
{
this._output = output;
_patient = new Patient();
//_task = new LongTimeTask();
_task = fixture.Task;//获取方法
}
}
不同的测试类#
1.在上一个的继承上,先建立一个TaskCollection类,实现ICollectionFixture
using Xunit;
namespace Demo2Test
{
[CollectionDefinition("Lone Time Task Collection")]
public class TaskCollection:ICollectionFixture<LongTimeFixture>
{
}
}
使用,加上[Collection("Lone Time Task Collection")]
[Collection("Lone Time Task Collection")]
public class PatientShould:IClassFixture<LongTimeFixture>,IDisposable
{
private readonly ITestOutputHelper _output;
private readonly Patient _patient;
private readonly LongTimeTask _task;
public PatientShould(ITestOutputHelper output,LongTimeFixture fixture)
{
this._output = output;
_patient = new Patient();
//_task = new LongTimeTask();
_task = fixture.Task;//获取方法
}
}
数据共享
- 使用[Theory],可以写有构造参数的测试方法,使用InlineData传递数据#
[Theory]
[InlineData(1,2,3)]
[InlineData(2,2,4)]
[InlineData(3,3,6)]
public void ShouldAddEquals(int operand1,int operand2,int expected)
{
//Arrange
var sut = new Calculator(); //sut-system under test
//Act
var result = sut.Add(operand1, operand2);
//Assert
Assert.Equal(expected, result);
}
2. 使用[MemberData]特性,可以在多个测试中使用#
先添加CalculatorTestData类:
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DemoTest
{
public class CalculatorTestData
{
private static readonly List<object[]> Data = new List<object[]>
{
new object[]{ 1,2,3},
new object[]{ 1,3,4},
new object[]{ 2,4,6},
new object[]{ 0,1,1},
};
public static IEnumerable<object[]> TestData => Data;
}
}
使用MemberData
/// <summary>
/// 数据共享-MemberData
/// </summary>
/// <param name="operand1"></param>
/// <param name="operand2"></param>
/// <param name="expected"></param>
[Theory]
[MemberData(nameof(CalculatorTestData.TestData),MemberType =typeof(CalculatorTestData))]
public void ShouldAddEquals2(int operand1, int operand2, int expected)
{
//Arrange
var sut = new Calculator(); //sut-system under test
//Act
var result = sut.Add(operand1, operand2);
//Assert
Assert.Equal(expected, result);
}
3. 使用外部数据
先创建一个类,准备数据,这里是读取的csv文件的数据
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
namespace DemoTest.Data
{
/// <summary>
/// 读取文件并返回数据集合
/// </summary>
public class CalculatorCsvData
{
public static IEnumerable<object[]> TestData
{
get
{
//把csv文件中的数据读出来,转换
string[] csvLines = File.ReadAllLines("Data\TestData.csv");
var testCases = new List<object[]>();
foreach (var csvLine in csvLines)
{
IEnumerable<int> values = csvLine.Trim().Split(',').Select(int.Parse);
object[] testCase = values.Cast<object>().ToArray();
testCases.Add(testCase);
}
return testCases;
}
}
}
}
2.csv数据
Copy
1,2,3
1,3,4
2,4,6
0,1,1
/// <summary>
/// 数据共享-MemberData-外部数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="operand1"></param>
/// <param name="operand2"></param>
/// <param name="expected"></param>
[Theory]
[MemberData(nameof(CalculatorCsvData.TestData), MemberType = typeof(CalculatorCsvData))]
public void ShouldAddEquals3(int operand1, int operand2, int expected)
{
//Arrange
var sut = new Calculator(); //sut-system under test
//Act
var result = sut.Add(operand1, operand2);
//Assert
Assert.Equal(expected, result);
}
-
使用自定义特性,继承自DataAttribute#
自定义特性
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Reflection;
using Xunit.Sdk;
namespace DemoTest.Data
{
public class CalculatorDataAttribute : DataAttribute
{
public override IEnumerable<object[]> GetData(MethodInfo testMethod)
{
yield return new object[] { 0, 100, 100 };
yield return new object[] { 1, 99, 100 };
yield return new object[] { 2, 98, 100 };
yield return new object[] { 3, 97, 100 };
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 数据共享-自定义特性继承自DataAttribute
/// </summary>
/// <param name="operand1"></param>
/// <param name="operand2"></param>
/// <param name="expected"></param>
[Theory]
[CalculatorDataAttribute]
public void ShouldAddEquals4(int operand1, int operand2, int expected)
{
//Arrange
var sut = new Calculator(); //sut-system under test
//Act
var result = sut.Add(operand1, operand2);
//Assert
Assert.Equal(expected, result);
}