前言
整理了一下.net core 一些常见的库的源码阅读,共32个库,记100余篇。
以下只是个人的源码阅读,如有错误或者思路不正确,望请指点。
正文
github 地址为:
https://github.com/stefanprodan/AspNetCoreRateLimit
一般个人习惯先阅读readme的简介。

上面大概翻译是:
AspNetCoreRateLimit 是ASP.NET Core 访问速率限制的解决方案,设计基于ip地址和客户端id用于控制用于web api和 mvc app的客户端访问速率。
这个包包含了IpRateLimitMiddleware and a ClientRateLimitMiddleware两个中间件,用这两个中间件你根据不同的场景能设置几种不同的限制,
比如限制一个客户端或者一个ip在几秒或者15分钟内访问最大限制。您可以定义这些限制来处理对某个API的所有请求,也可以将这些限制限定在指定范围的每个API URL或HTTP请求路径上。
上面说了这么多就是用来限流的,针对客户端id和ip进行限流。
因为一般用的是ip限流,看下ip限制怎么使用的,毕竟主要还是拿来用的嘛。
本来还想根据文档先写个小demo,然后发现官方已经写了demo。
直接看demo(只看ip限制部分的)。
先来看下ConfigureServices:
services.Configure<IpRateLimitOptions>(Configuration.GetSection("IpRateLimiting"));
services.Configure<IpRateLimitPolicies>(Configuration.GetSection("IpRateLimitPolicies"));
services.AddSingleton<IRateLimitConfiguration, RateLimitConfiguration>();
services.AddInMemoryRateLimiting();
从上面看,那么配置ip 限制的有两个配置,一个配置是IpRateLimitOptions,另外一个配置是IpRateLimitPolicies。
那么为什么要设计成两个配置呢?一个配置不是更香吗?
官方设计理念是这样的:
IpRateLimiting Configuration and general rules appsettings.json
IpRateLimitPolicies Override general rules for specific IPs appsettings.json


原来IpRateLimiting 是限制普遍的ip,而IpRateLimitPolicies 是限制一些特殊的ip。
比如说有些api对内又对外的,普遍的ip对外限制是1分钟300次,如果有个大客户特殊需求且固定ip的,需要限制是1分钟是10000次的,那么就可以这样特殊处理,而不用另外写code来维护,成本问题。
故而我们写中间件组件的时候也可以参考这个来做,特殊的怎么处理,普遍的怎么处理,当然也不能盲目的设计。
然后看:AddInMemoryRateLimiting
public static IServiceCollection AddInMemoryRateLimiting(this IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton<IIpPolicyStore, MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore>();
services.AddSingleton<IClientPolicyStore, MemoryCacheClientPolicyStore>();
services.AddSingleton<IRateLimitCounterStore, MemoryCacheRateLimitCounterStore>();
services.AddSingleton<IProcessingStrategy, AsyncKeyLockProcessingStrategy>();
return services;
}
里面注入了MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore、MemoryCacheClientPolicyStore、MemoryCacheRateLimitCounterStore、AsyncKeyLockProcessingStrategy。
分别看下这几个东西。
MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore:
public class MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore : MemoryCacheRateLimitStore<IpRateLimitPolicies>, IIpPolicyStore
{
private readonly IpRateLimitOptions _options;
private readonly IpRateLimitPolicies _policies;
public MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore(
IMemoryCache cache,
IOptions<IpRateLimitOptions> options = null,
IOptions<IpRateLimitPolicies> policies = null) : base(cache)
{
_options = options?.Value;
_policies = policies?.Value;
}
public async Task SeedAsync()
{
// on startup, save the IP rules defined in appsettings
if (_options != null && _policies != null)
{
await SetAsync($"{_options.IpPolicyPrefix}", _policies).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
}
这个是用例存储IpRateLimitPolicies(ip限制)。
MemoryCacheIpPolicyStore 这个名字起的有点意思,MemoryCache 是内存缓存,IpPolicy ip策略,store 存储。
分别是存储空间、物品、功能的组合。所以这个库应该是外国人写的,一般来说中国人会这样改:IpPolicyMemoryCacheStore,估计是因为强调故而把MemoryCache放到前面去了。
这里我刚开始有点不理解,本来已经可以读取到了options,那么按照options操作就很方便了。
那么为啥要用缓存到内存中呢?后来大体的通读了一下,是因为_policies(特殊制定的ip规则)很多地方都要使用到,一方面是为了解耦,另外一方面呢,是因为下面这个。
[HttpPost]
public void Post()
{
var pol = _ipPolicyStore.Get(_options.IpPolicyPrefix);
pol.IpRules.Add(new IpRateLimitPolicy
{
Ip = "8.8.4.4",
Rules = new List<RateLimitRule>(new RateLimitRule[] {
new RateLimitRule {
Endpoint = "*:/api/testupdate",
Limit = 100,
Period = "1d" }
})
});
_ipPolicyStore.Set(_options.IpPolicyPrefix, pol);
}
是可以动态设置特殊ip的一些配置的。 那么里面也考虑到了分布式的一些行为,比如把缓存放到redis这种隔离缓存中。
如果将_policies 封装到memory cache 中,那么和redis cache形成了一套适配器。个人认为是从设计方面考虑的。
然后看下这个方法,里面就是以IpRateLimiting的IpPolicyPrefix 作为key,然后存储了IpRateLimitPolicies。
public async Task SeedAsync()
{
// on startup, save the IP rules defined in appsettings
if (_options != null && _policies != null)
{
await SetAsync($"{_options.IpPolicyPrefix}", _policies).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
具体的SetAsync 如下:
public Task SetAsync(string id, T entry, TimeSpan? expirationTime = null, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var options = new MemoryCacheEntryOptions
{
Priority = CacheItemPriority.NeverRemove
};
if (expirationTime.HasValue)
{
options.SetAbsoluteExpiration(expirationTime.Value);
}
_cache.Set(id, entry, options);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
然后这里值得注意的是_options.IpPolicyPrefix,这个值如果是分布式那么应该值得关注一下,因为我们有不同应用服务,如果希望不同的应用服务用到不同的ip限制,那么IpPolicyPrefix 最好改成应用名,而不是使用默认值。
那么看下MemoryCacheClientPolicyStore:
public class MemoryCacheClientPolicyStore : MemoryCacheRateLimitStore<ClientRateLimitPolicy>, IClientPolicyStore
{
private readonly ClientRateLimitOptions _options;
private readonly ClientRateLimitPolicies _policies;
public MemoryCacheClientPolicyStore(
IMemoryCache cache,
IOptions<ClientRateLimitOptions> options = null,
IOptions<ClientRateLimitPolicies> policies = null) : base(cache)
{
_options = options?.Value;
_policies = policies?.Value;
}
public async Task SeedAsync()
{
// on startup, save the IP rules defined in appsettings
if (_options != null && _policies?.ClientRules != null)
{
foreach (var rule in _policies.ClientRules)
{
await SetAsync($"{_options.ClientPolicyPrefix}_{rule.ClientId}", new ClientRateLimitPolicy { ClientId = rule.ClientId, Rules = rule.Rules }).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
}
}
这个就是client id的限制的缓存的,和上面一样就不看了。
MemoryCacheRateLimitCounterStore:
public class MemoryCacheRateLimitCounterStore : MemoryCacheRateLimitStore<RateLimitCounter?>, IRateLimitCounterStore
{
public MemoryCacheRateLimitCounterStore(IMemoryCache cache) : base(cache)
{
}
}
这里面没有啥子。但是从名字上猜测,里面是缓存每个ip请求次数的当然还有时间,主要起缓存作用。
最后一个:AsyncKeyLockProcessingStrategy
public class AsyncKeyLockProcessingStrategy : ProcessingStrategy
{
private readonly IRateLimitCounterStore _counterStore;
private readonly IRateLimitConfiguration _config;
public AsyncKeyLockProcessingStrategy(IRateLimitCounterStore counterStore, IRateLimitConfiguration config)
: base(config)
{
_counterStore = counterStore;
_config = config;
}
/// The key-lock used for limiting requests.
private static readonly AsyncKeyLock AsyncLock = new AsyncKeyLock();
public override async Task<RateLimitCounter> ProcessRequestAsync(ClientRequestIdentity requestIdentity, RateLimitRule rule, ICounterKeyBuilder counterKeyBuilder, RateLimitOptions rateLimitOptions, CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
var counter = new RateLimitCounter
{
Timestamp = DateTime.UtcNow,
Count = 1
};
var counterId = BuildCounterKey(requestIdentity, rule, counterKeyBuilder, rateLimitOptions);
// serial reads and writes on same key
using (await AsyncLock.WriterLockAsync(counterId).ConfigureAwait(false))
{
var entry = await _counterStore.GetAsync(counterId, cancellationToken);
if (entry.HasValue)
{
// entry has not expired
if (entry.Value.Timestamp + rule.PeriodTimespan.Value >= DateTime.UtcNow)
{
// increment request count
var totalCount = entry.Value.Count + _config.RateIncrementer?.Invoke() ?? 1;
// deep copy
counter = new RateLimitCounter
{
Timestamp = entry.Value.Timestamp,
Count = totalCount
};
}
}
// stores: id (string) - timestamp (datetime) - total_requests (long)
await _counterStore.SetAsync(counterId, counter, rule.PeriodTimespan.Value, cancellationToken);
}
return counter;
}
}
估摸着是执行具体计数逻辑的,那么等执行中间件的时候在看。
后面有写入了一个:services.AddSingleton<IRateLimitConfiguration, RateLimitConfiguration>();
那么这个RateLimitConfiguration 是做什么的呢?
public class RateLimitConfiguration : IRateLimitConfiguration
{
public IList<IClientResolveContributor> ClientResolvers { get; } = new List<IClientResolveContributor>();
public IList<IIpResolveContributor> IpResolvers { get; } = new List<IIpResolveContributor>();
public virtual ICounterKeyBuilder EndpointCounterKeyBuilder { get; } = new PathCounterKeyBuilder();
public virtual Func<double> RateIncrementer { get; } = () => 1;
public RateLimitConfiguration(
IOptions<IpRateLimitOptions> ipOptions,
IOptions<ClientRateLimitOptions> clientOptions)
{
IpRateLimitOptions = ipOptions?.Value;
ClientRateLimitOptions = clientOptions?.Value;
}
protected readonly IpRateLimitOptions IpRateLimitOptions;
protected readonly ClientRateLimitOptions ClientRateLimitOptions;
public virtual void RegisterResolvers()
{
string clientIdHeader = GetClientIdHeader();
string realIpHeader = GetRealIp();
if (clientIdHeader != null)
{
ClientResolvers.Add(new ClientHeaderResolveContributor(clientIdHeader));
}
// the contributors are resolved in the order of their collection index
if (realIpHeader != null)
{
IpResolvers.Add(new IpHeaderResolveContributor(realIpHeader));
}
IpResolvers.Add(new IpConnectionResolveContributor());
}
protected string GetClientIdHeader()
{
return ClientRateLimitOptions?.ClientIdHeader ?? IpRateLimitOptions?.ClientIdHeader;
}
protected string GetRealIp()
{
return IpRateLimitOptions?.RealIpHeader ?? ClientRateLimitOptions?.RealIpHeader;
}
}
重点看:
public virtual void RegisterResolvers()
{
string clientIdHeader = GetClientIdHeader();
string realIpHeader = GetRealIp();
if (clientIdHeader != null)
{
ClientResolvers.Add(new ClientHeaderResolveContributor(clientIdHeader));
}
// the contributors are resolved in the order of their collection index
if (realIpHeader != null)
{
IpResolvers.Add(new IpHeaderResolveContributor(realIpHeader));
}
IpResolvers.Add(new IpConnectionResolveContributor());
}
这里只看ip部分:
protected string GetRealIp()
{
return IpRateLimitOptions?.RealIpHeader ?? ClientRateLimitOptions?.RealIpHeader;
}
那么这个IpHeaderResolveContributor是什么呢?
public class IpHeaderResolveContributor : IIpResolveContributor
{
private readonly string _headerName;
public IpHeaderResolveContributor(
string headerName)
{
_headerName = headerName;
}
public string ResolveIp(HttpContext httpContext)
{
IPAddress clientIp = null;
if (httpContext.Request.Headers.TryGetValue(_headerName, out var values))
{
clientIp = IpAddressUtil.ParseIp(values.Last());
}
return clientIp?.ToString();
}
}
原来是配置是从header的哪个位置获取ip。官网demo中给的是"RealIpHeader": "X-Real-IP"。从header部分的RealIpHeader获取。
同样,官方也默认提供了IpResolvers.Add(new IpConnectionResolveContributor());。
public class IpConnectionResolveContributor : IIpResolveContributor
{
public IpConnectionResolveContributor()
{
}
public string ResolveIp(HttpContext httpContext)
{
return httpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress?.ToString();
}
}
从httpContext.Connection.RemoteIpAddress 中获取ip,那么问题来了,RemoteIpAddress 是如何获取的呢? 到底X-Real-IP 获取的ip准不准呢?会在.net core 细节篇中介绍。
回到原始。现在已经注入了服务,那么如何把中间件注入进去呢?
在Configure 中:
app.UseIpRateLimiting();
将会执行中间件:IpRateLimitMiddleware
public class IpRateLimitMiddleware : RateLimitMiddleware<IpRateLimitProcessor>
{
private readonly ILogger<IpRateLimitMiddleware> _logger;
public IpRateLimitMiddleware(RequestDelegate next,
IProcessingStrategy processingStrategy,
IOptions<IpRateLimitOptions> options,
IRateLimitCounterStore counterStore,
IIpPolicyStore policyStore,
IRateLimitConfiguration config,
ILogger<IpRateLimitMiddleware> logger
)
: base(next, options?.Value, new IpRateLimitProcessor(options?.Value, counterStore, policyStore, config, processingStrategy), config)
{
_logger = logger;
}
protected override void LogBlockedRequest(HttpContext httpContext, ClientRequestIdentity identity, RateLimitCounter counter, RateLimitRule rule)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"Request {identity.HttpVerb}:{identity.Path} from IP {identity.ClientIp} has been blocked, quota {rule.Limit}/{rule.Period} exceeded by {counter.Count - rule.Limit}. Blocked by rule {rule.Endpoint}, TraceIdentifier {httpContext.TraceIdentifier}. MonitorMode: {rule.MonitorMode}");
}
}
查看:RateLimitMiddleware
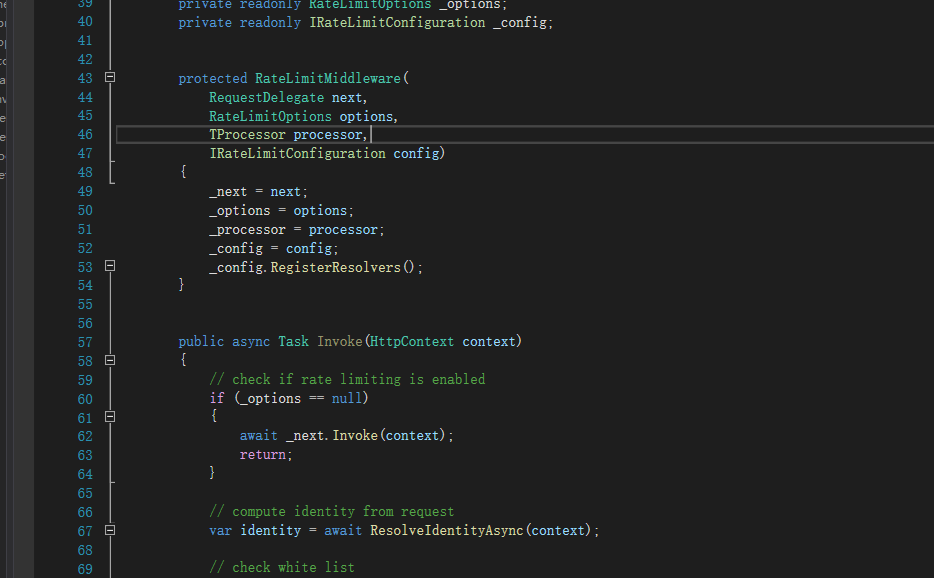
里面就是具体的invoke中间件代码了。
结
因为篇幅有限,后一节invoke逐行分析其如何实现的。
以上只是个人看源码的过程,希望能得到各位的指点,共同进步。
另外.net core 细节篇整理进度为40%。