目录
1. 前言
分析Thrift的结构动机是为了实现服务端能取到客户端的IP,因此需要对它的结构、调用流程有些了解。另外,请注意本文针对的是TNonblockingServer,不包含TThreadPoolServer、TThreadedServer和TSimpleServer。
thrift对网络连接没有使用内存池,最直接简单的性能优化是绑定Google gperftools中的TCMalloc。
2. 示例Service
|
service EchoService { string hello(1: string greetings); } class EchoHandler: public EchoServiceIf { private: virtual void hello(std::string& _return, const std::string& greetings); }; |
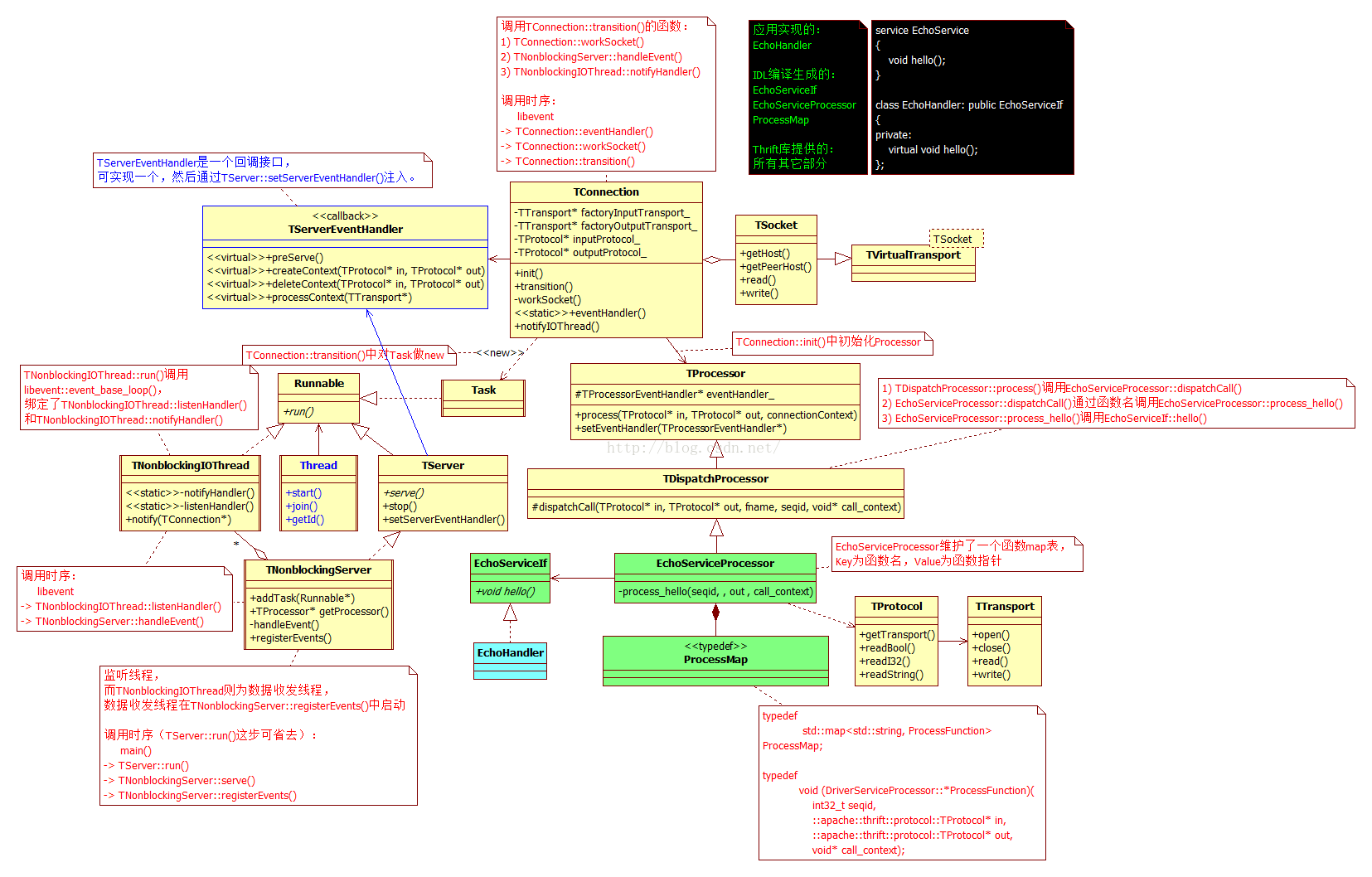
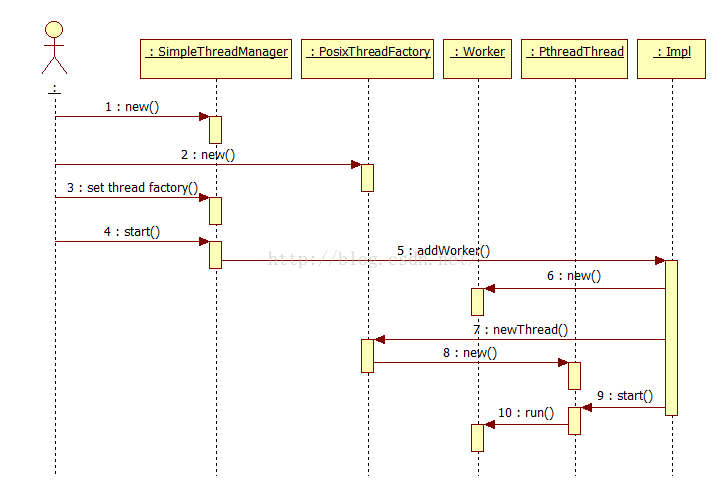
3. 网络部分类图
Thrift线程模型为若干IO线程TNonblockingIOThread(负责收发TCP连接的数据),以及主线程(负责监听TCP连接及接受连接请求)组成。
主线程不一定就是进程的主线程,哪个线程调用了TServer::run()或TServer::serve()就是本文所说的主线程。就当前最新版本(0.9.2)的Thrift而言,调用TServer::run()或TServer::serve()均可以,原因是TServer::run()除无条件的调用外TServer::serve(),没有做任何其它事。对TServer::serve()的调用实际是对TServer的实现类TNonblockingServer的serve()的调用。
简而言之,TNonblockingIOThread负责数据的收发,而TNonblockingServer负责接受连接请求。
在使用中需要注意,调用TServer::run()或TServer::serve()的线程或进程会被阻塞,阻塞进入libevent的死循环,Linux上是死循环调用epoll_wait()。
4. 线程模式
Thrift将线程分成两类:
4.1. IO线程
IO线程负责监听和接受连接请求,和接收客户端发送过来的数据,收到完整请求后,以Task方式传递给工作线程,由工作线程回调。
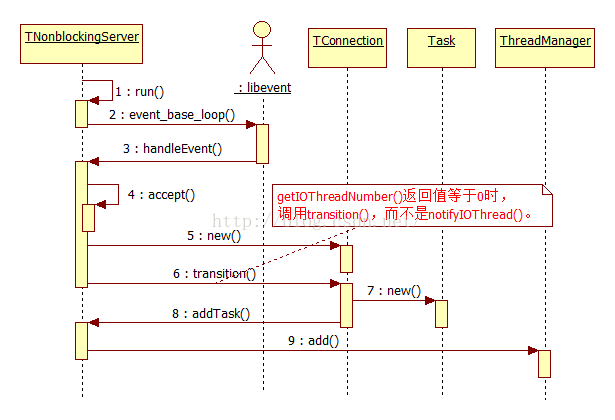
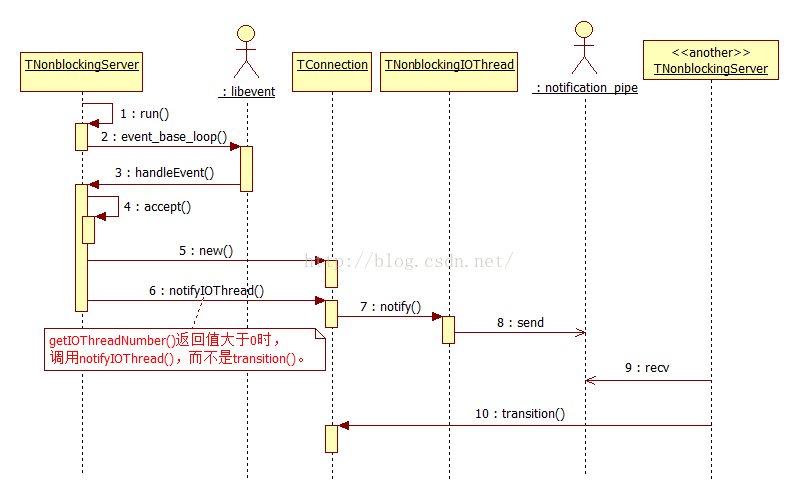
IO线程针对TNonblockingServer,TNonblockingServer提供方法setNumIOThreads()来设置IO线程个数。第一个IO线程总是独占调用TServer::server()或TServer::run()的线程。
IO线程在accept一个连接后,会创建一个TConnection实例(在TNonblockingServer::TConnection::transition()中),而TConnection会创建一个Task(在TNonblockingServer::TConnection::transition()中完成),由TNonblockingServer将Task传递给ThreadManager。
纠正:上图中的TNonblockingServer应当为TNonblockingIOThread。
注意函数TNonblockingServer::handleEvent()的下小段代码,getIOThreadNumber()并不是表示取得IO线程个数,而是该线程在线程组中的ID,可以这么认为等于0时表示0号线程:
|
void TNonblockingServer::handleEvent(int fd, short which) { if (clientConnection->getIOThreadNumber() == 0) { clientConnection->transition(); } else { clientConnection->notifyIOThread(); // 最终也会调用transition() } } |
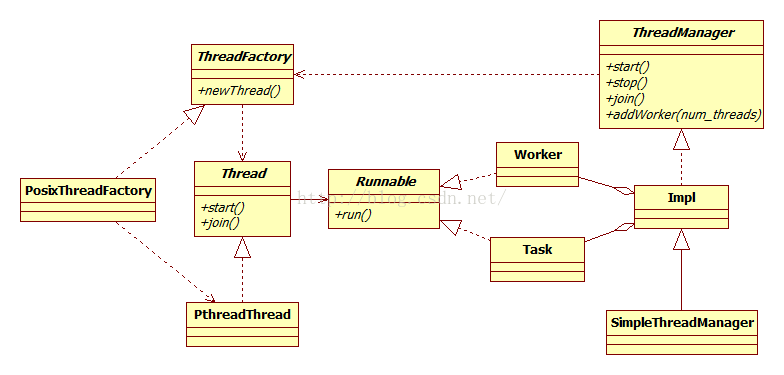
4.2. 工作线程
工作线程负责回调和对客户端响应。
4.2.1. 工作线程类图
4.2.2. 工作线程启动过程
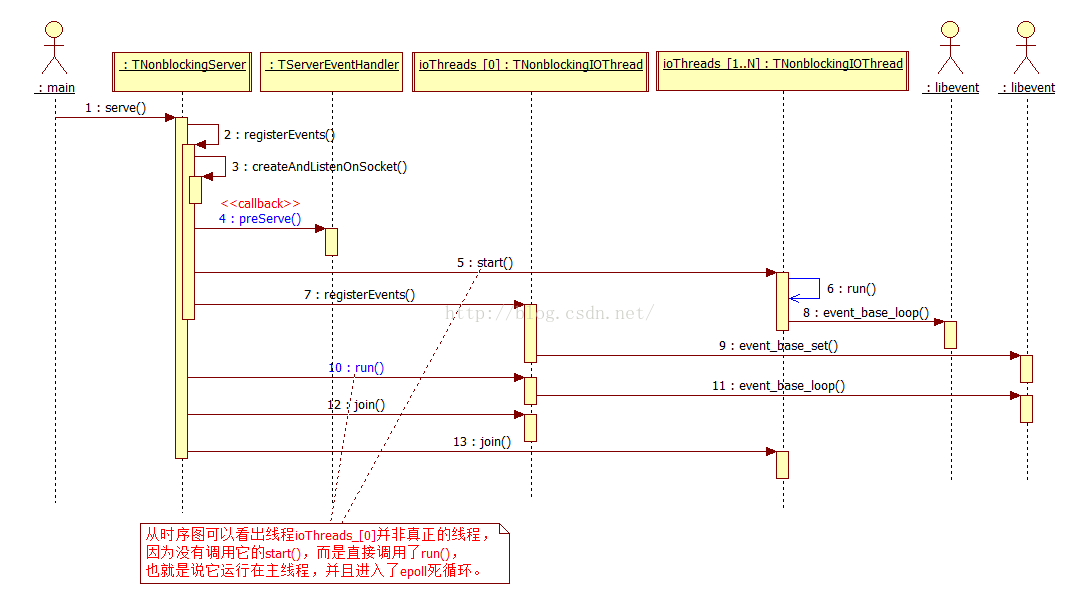
5. 一个RPC函数被调用时序图
5.1. 启动准备
准备的工作包括:
1) 启动监听连接
2) 启动收发数据线程
3) 初始化运行环境
在这里,可以看到第一次对TServerEventHandler的回调:
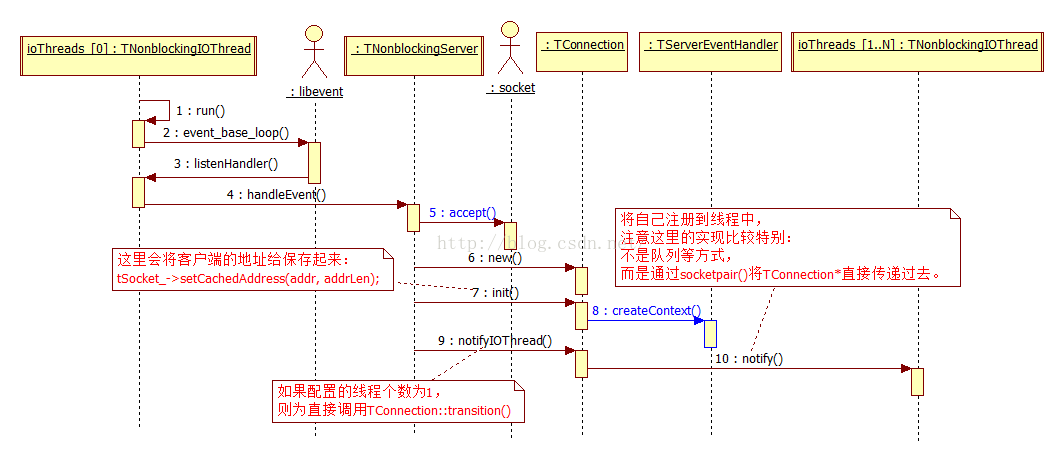
5.2. 接受连接
从接受连接的时序过程可以看出:在该连接TConnection接收数据之前,先调用了TServerEventHandler::createContext(),这个就是获取客户端IP的机会之一,但是当前的实现没有将相关的信息作为参数传递给TServerEventHandler::createContext()。
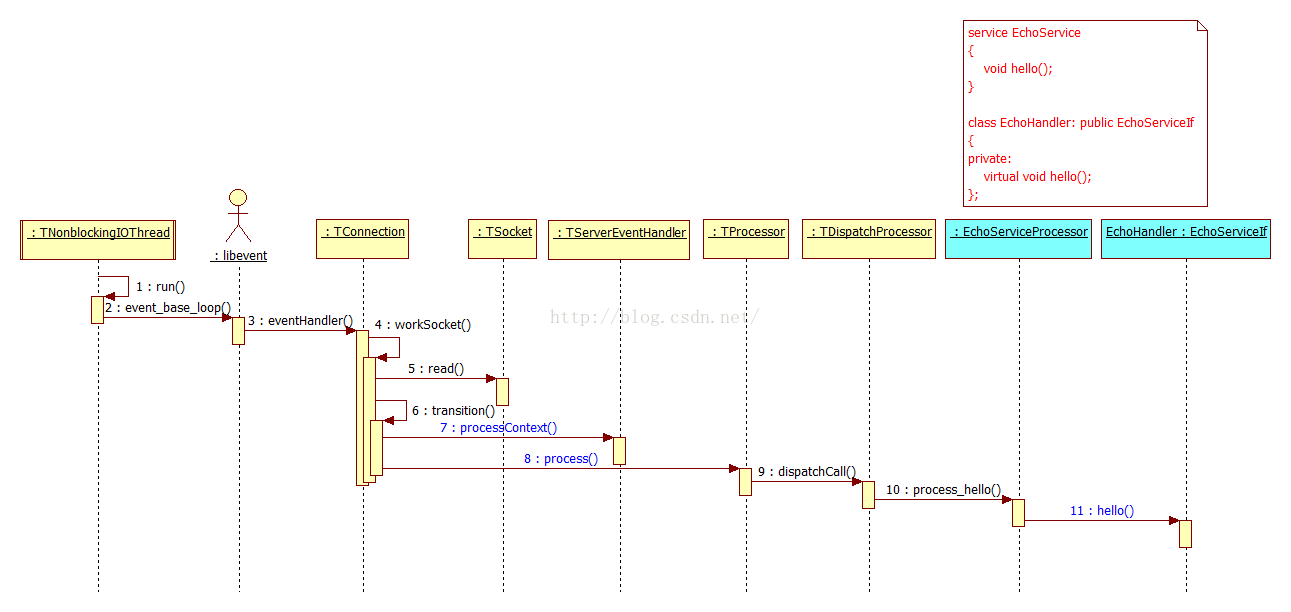
5.3. 收发数据:执行调用
这过程中对TServerEventHandler::processContext(connectionContext_, getTSocket())进行了回调,并传递了TSocket。
5.4. 服务端回调代码解读
下面是thrift编译生成的代码片段,为服务端的代码:
|
// TProtocol为协议接口,常用实现类为TBinaryProtocol等 void EchoServiceProcessor::process_hello(int32_t seqid, // 消息序列号 ::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol* iprot, // 输入参数 ::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol* oprot, // 输出参数 void* callContext) { // eventHandler_类型为TProcessorEventHandler,是一个被回调对象 void* ctx = NULL; if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { ctx = this->eventHandler_->getContext("EchoService.hello", callContext); } ::apache::thrift::TProcessorContextFreer freer(this->eventHandler_.get(), ctx, "EchoService.hello"); if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { this->eventHandler_->preRead(ctx, "HelloService.hello"); // 回调TProcessorEventHandler } EchoService_hello_args args; // 输入参数 args.read(iprot); // 反序列化输入参数 iprot->readMessageEnd(); uint32_t bytes = iprot->getTransport()->readEnd(); if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { this->eventHandler_->postRead(ctx, "EchoService.hello", bytes); // 回调TProcessorEventHandler } // EchoService_hello_result是thrift编译生成的类 EchoService_hello_result result; // 输出参数,也就是thrift文件中定义的返回值 try { iface_->hello(result.success, args.greetings); // 这里就是回调用户自己写的代码了 result.__isset.success = true; } catch (const std::exception& e) { if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { this->eventHandler_->handlerError(ctx, "EchoService.hello"); // 回调TProcessorEventHandler } // 下段是异常时的返回,客户端应当catch它 ::apache::thrift::TApplicationException x(e.what()); // writeMessageBegin序列化消息头 oprot->writeMessageBegin("hello", ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_EXCEPTION, seqid); x.write(oprot); // 将x序列化到oprot oprot->writeMessageEnd(); oprot->getTransport()->writeEnd(); oprot->getTransport()->flush(); return; } if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { this->eventHandler_->preWrite(ctx, "EchoService.hello"); // 回调TProcessorEventHandler } // 下段为序列化输出参数,也注是返回值啦 oprot->writeMessageBegin("hello", ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_REPLY, seqid); // 序列化消息头 result.write(oprot); // 序列化result到oprot oprot->writeMessageEnd(); bytes = oprot->getTransport()->writeEnd(); oprot->getTransport()->flush(); if (this->eventHandler_.get() != NULL) { this->eventHandler_->postWrite(ctx, "EchoService.hello", bytes); // 回调TProcessorEventHandler } } |
5.5. 客户端回调代码解读
下面是thrift编译生成的代码片段,为客户端的代码:
|
// 同步调用实现 // hello就是客户端直接调用的 void EchoServiceClient::hello(std::string& _return, const std::string& greetings) { send_hello(greetings); // 序列化输入参数,并发送给服务端 recv_hello(_return); // 接收服务端的返回,并反序列化 } // 向服务端发起调用 void EchoServiceClient::send_hello(const std::string& greetings) { int32_t cseqid = 0; oprot_->writeMessageBegin("hello", ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_CALL, cseqid); // 类EchoService_hello_pargs也是thrift编译生成的类,所有的参数都是它的数据成员 EchoService_hello_pargs args; args.greetings = &greetings; args.write(oprot_); // 序列化 oprot_->writeMessageEnd(); oprot_->getTransport()->writeEnd(); oprot_->getTransport()->flush(); } // 接收服务端的响应 void EchoServiceClient::recv_hello(std::string& _return) { int32_t rseqid = 0; std::string fname; // 函数名 ::apache::thrift::protocol::TMessageType mtype; iprot_->readMessageBegin(fname, mtype, rseqid); if (mtype == ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_EXCEPTION) { ::apache::thrift::TApplicationException x; x.read(iprot_); iprot_->readMessageEnd(); iprot_->getTransport()->readEnd(); throw x; // 抛出异常 } if (mtype != ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_REPLY) { iprot_->skip(::apache::thrift::protocol::T_STRUCT); iprot_->readMessageEnd(); iprot_->getTransport()->readEnd(); } if (fname.compare("hello") != 0) { iprot_->skip(::apache::thrift::protocol::T_STRUCT); iprot_->readMessageEnd(); iprot_->getTransport()->readEnd(); } EchoService_hello_presult result; result.success = &_return; result.read(iprot_); // 反序列化 iprot_->readMessageEnd(); iprot_->getTransport()->readEnd(); if (result.__isset.success) { // _return pointer has now been filled return; } throw ::apache::thrift::TApplicationException(::apache::thrift::TApplicationException::MISSING_RESULT, "hello failed: unknown result"); } |
5.6. 服务端dispatchCall的实现
thrift编译生成的类Ec hoServiceProcessor,实现了接口apache::thrift::TDispatchProcessor的dispatchCall()方法:
|
bool EchoServiceProcessor::dispatchCall(::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol* iprot, // 输入参数 ::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol* oprot, // 输出参数 const std::string& fname, // 被调用的函数名 int32_t seqid, // 序列号 void* callContext) { ProcessMap::iterator pfn; // typedef void (EchoServiceProcessor::*ProcessFunction)(int32_t, // ::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol*, // ::apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol*, // void*); // typedef std::map<std::string, ProcessFunction> ProcessMap; pfn = processMap_.find(fname); // 根据函数名,找到函数(ProcessMap processMap_;) if (pfn == processMap_.end()) { // 没有找到时,抛出异常 iprot->skip(::apache::thrift::protocol::T_STRUCT); iprot->readMessageEnd(); iprot->getTransport()->readEnd(); ::apache::thrift::TApplicationException x(::apache::thrift::TApplicationException::UNKNOWN_METHOD, "Invalid method name: '"+fname+"'"); oprot->writeMessageBegin(fname, ::apache::thrift::protocol::T_EXCEPTION, seqid); x.write(oprot); oprot->writeMessageEnd(); // 序列化后,调用了Transport,而Transport调用了网络send oprot->getTransport()->writeEnd(); oprot->getTransport()->flush(); return true; } // 找到,则进行回调 (this->*(pfn->second))(seqid, iprot, oprot, callContext); return true; } |
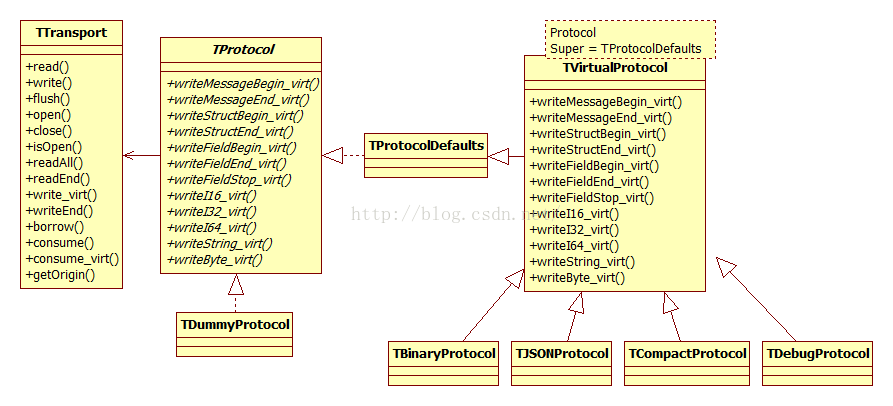
6. TProtocol
TProtocol提供序列化和反序列化能力,定义了消息包的编码和解码协议,它的实现有以下几种:
1) TBinaryProtocol 二进制编解码
2) TDebugProtocol 用于调试的,可读的文本编解码
3) TJSONProtocol 基于json的编解码
4) TCompactProtocol 压缩的二进制编解码
如果需要为thrift增加一种数据类型,则需要修改TProtocol,增加对新数据类型的序列化和反序列化实现。
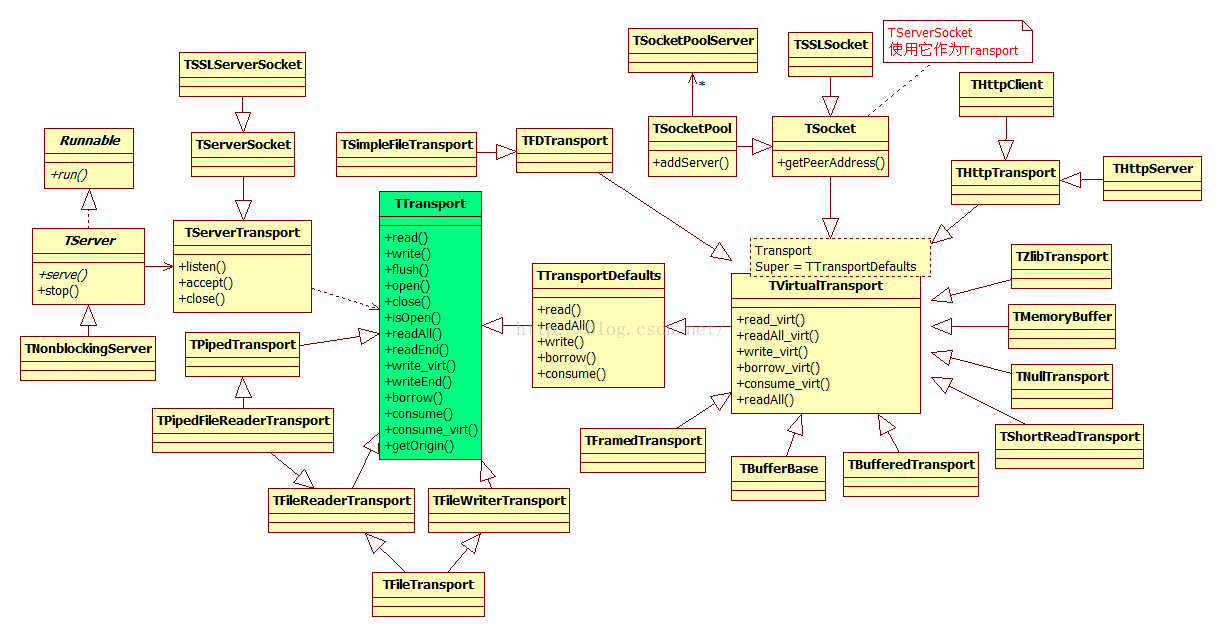
7. TTransport
TTransport负责收发数据,可以简单的是对Socket的包装,但是也支持非Socket,比如Pipe。其中TSocket为TServerSocket使用的Transport。
8. TProtocol&TTransport
对于TNonblockingServer默认使用的是输入和输出Transport,都是以TMemoryBuffer为TTransport。
TProtocol本身没有缓冲区等,它只是序列化和反序列化。然而它依赖于TTransport,通过TTransport发送数据。以TBinaryProtocol为例:
|
// 序列化int16_t值 template <class Transport_> uint32_t TBinaryProtocolT<Transport_>::writeI16(const int16_t i16) { int16_t net = (int16_t)htons(i16); this->trans_->write((uint8_t*)&net, 2); // 看到没?这里调用的是TTransport return 2; } |
对比看下TTransport::write的实现:
|
// TSocket是一种TTransport void TSocket::write(const uint8_t* buf, uint32_t len) { uint32_t sent = 0; // 从下面的实现可以看出发送是同步的 while (sent < len) { uint32_t b = write_partial(buf + sent, len - sent); // 这里实际调用的是系统的send() if (b == 0) { // This should only happen if the timeout set with SO_SNDTIMEO expired. // Raise an exception. throw TTransportException(TTransportException::TIMED_OUT, "send timeout expired"); } sent += b; } } |
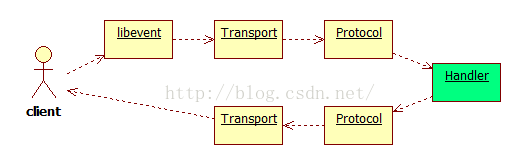
9. 数据流向关系
客户端发送数据时,会触发libevent事件,然后调用Transport收数据。包完整后,调用Protocol反序列化,接着就调用服务端的代码。
前半部分在IO线程中完成,后半部分在工作线程中完成。
10. 取客户端IP
为取得客户端的IP,有三个办法:
1) 网上博文http://blog.csdn.net/hbuxiaoshe/article/details/38942869介绍的方法也是可行的,不过让人有些纠结;
2) 修改Thrift的实现,为TServerEventHandler::createContext()增加一个参数,将TSocket作为参数传递,这样就可以非常轻易的取得客户端的IP了。最简单的修改为:
|
class TServerEventHandler { public: virtual void* createContext(boost::shared_ptr<TProtocol> input, boost::shared_ptr<TProtocol> output, TTransport* transport); // 对于TNonblockingServer实际传递为TSocket }; |
3) 不修改Thrift的实现。
在“收发数据:执行调用”的流程中,可以发现有对TServerEventHandler::processContext()的调用,而这里真好将TSocket作为第二个参数进行了传递,因此可以直接利用。
TServerEventHandler::createContext()和TServerEventHandler::processContext()的不同在于:前者只在建立连接时被调用一次,而后者每一个RPC调用时都会调用一次。
|
#ifndef MOOON_NET_THRIFT_HELPER_H #define MOOON_NET_THRIFT_HELPER_H #include <mooon/net/config.h> #include <mooon/sys/log.h> #include <mooon/utils/scoped_ptr.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include <boost/scoped_ptr.hpp> #include <thrift/concurrency/PosixThreadFactory.h> #include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h> #include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h> #include <thrift/server/TNonblockingServer.h> #include <thrift/transport/TSocketPool.h> #include <thrift/transport/TTransportException.h> NET_NAMESPACE_BEGIN // 用来判断thrift是否已经连接,包括两种情况: // 1.从未连接过,也就是还未打开过连接 // 2.连接被对端关闭了 inline bool thrift_not_connected( apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException::TTransportExceptionType type) { return (apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException::NOT_OPEN == type) || (apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException::END_OF_FILE == type); } inline bool thrift_not_connected( apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException& ex) { apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException::TTransportExceptionType type = ex.getType(); return thrift_not_connected(type); } // thrift客户端辅助类 // // 使用示例: // mooon::net::CThriftClientHelper<ExampleServiceClient> client(rpc_server_ip, rpc_server_port); // try // { // client.connect(); // client->foo(); // } // catch (apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException& transport_ex) // { // MYLOG_ERROR("thrift exception: %s ", transport_ex.what()); // } // catch (apache::thrift::transport::TApplicationException& app_ex) // { // MYLOG_ERROR("thrift exception: %s ", app_ex.what()); // } // catch (apache::thrift::TException& tx) // { // MYLOG_ERROR("thrift exception: %s ", tx.what()); // } // Transport除默认的TFramedTransport (TBufferTransports.h),还可选择: // TBufferedTransport (TBufferTransports.h) // THttpTransport // TZlibTransport // TFDTransport (TSimpleFileTransport) // // Protocol除默认的apache::thrift::protocol::TBinaryProtocol,还可选择: // TCompactProtocol // TJSONProtocol // TDebugProtocol template <class ThriftClient, class Protocol=apache::thrift::protocol::TBinaryProtocol, class Transport=apache::thrift::transport::TFramedTransport> class CThriftClientHelper { public: // host thrift服务端的IP地址 // port thrift服务端的端口号 // connect_timeout_milliseconds 连接thrift服务端的超时毫秒数 // receive_timeout_milliseconds 接收thrift服务端发过来的数据的超时毫秒数 // send_timeout_milliseconds 向thrift服务端发送数据时的超时毫秒数 CThriftClientHelper(const std::string &host, uint16_t port, int connect_timeout_milliseconds=2000, int receive_timeout_milliseconds=2000, int send_timeout_milliseconds=2000); ~CThriftClientHelper(); // 连接thrift服务端 // // 出错时,可抛出以下几个thrift异常: // apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException // apache::thrift::TApplicationException // apache::thrift::TException void connect(); // 断开与thrift服务端的连接 // // 出错时,可抛出以下几个thrift异常: // apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException // apache::thrift::TApplicationException // apache::thrift::TException void close(); ThriftClient* get() { return _client.get(); } ThriftClient* get() const { return _client.get(); } ThriftClient* operator ->() { return get(); } ThriftClient* operator ->() const { return get(); } const std::string& get_host() const { return _host; } uint16_t get_port() const { return _port; } private: std::string _host; uint16_t _port; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::transport::TSocketPool> _sock_pool; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::transport::TTransport> _socket; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::transport::TFramedTransport> _transport; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocol> _protocol; boost::shared_ptr<ThriftClient> _client; }; //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // thrift服务端辅助类 // // 使用示例: // mooon::net::CThriftServerHelper<CExampleHandler, ExampleServiceProcessor> _thrift_server; // try // { // _thrift_server.serve(listen_port); // } // catch (apache::thrift::TException& tx) // { // MYLOG_ERROR("thrift exception: %s ", tx.what()); // } // ProtocolFactory除了默认的TBinaryProtocolFactory,还可选择: // TCompactProtocolFactory // TJSONProtocolFactory // TDebugProtocolFactory // // Server除默认的TNonblockingServer外,还可选择: // TSimpleServer // TThreadedServer // TThreadPoolServer template <class ThriftHandler, class ServiceProcessor, class ProtocolFactory=apache::thrift::protocol::TBinaryProtocolFactory, class Server=apache::thrift::server::TNonblockingServer> class CThriftServerHelper { public: // 启动rpc服务,请注意该调用是同步阻塞的,所以需放最后调用 // port thrift服务端的监听端口号 // num_threads thrift服务端开启的线程数 // // 出错时,可抛出以下几个thrift异常: // apache::thrift::transport::TTransportException // apache::thrift::TApplicationException // apache::thrift::TException // 参数num_io_threads,只有当Server为TNonblockingServer才有效 void serve(uint16_t port, uint8_t num_worker_threads=1, uint8_t num_io_threads=1); void serve(const std::string &ip, uint16_t port, uint8_t num_worker_threads, uint8_t num_io_threads=1); void stop(); private: boost::shared_ptr<ThriftHandler> _handler; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::TProcessor> _processor; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::protocol::TProtocolFactory> _protocol_factory; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::server::ThreadManager> _thread_manager; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::concurrency::PosixThreadFactory> _thread_factory; boost::shared_ptr<apache::thrift::server::TServer> _server; }; //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // 被thrift回调的写日志函数,由set_thrift_log_write_function()调用它 inline void write_log_function(const char* log) { MYLOG_INFO("%s", log); } // 将thrift输出写入到日志文件中 inline void set_thrift_log_write_function() { if (log != NULL) { apache::thrift::GlobalOutput.setOutputFunction(write_log_function); } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// template <class ThriftClient, class Protocol, class Transport> CThriftClientHelper<ThriftClient, Protocol, Transport>::CThriftClientHelper( const std::string &host, uint16_t port, int connect_timeout_milliseconds, int receive_timeout_milliseconds, int send_timeout_milliseconds) : _host(host) , _port(port) { set_thrift_log_write_function(); _sock_pool.reset(new apache::thrift::transport::TSocketPool()); _sock_pool->addServer(host, (int)port); _sock_pool->setConnTimeout(connect_timeout_milliseconds); _sock_pool->setRecvTimeout(receive_timeout_milliseconds); _sock_pool->setSendTimeout(send_timeout_milliseconds); _socket = _sock_pool; // Transport默认为apache::thrift::transport::TFramedTransport _transport.reset(new Transport(_socket)); // Protocol默认为apache::thrift::protocol::TBinaryProtocol _protocol.reset(new Protocol(_transport)); _client.reset(new ThriftClient(_protocol)); } template <class ThriftClient, class Protocol, class Transport> CThriftClientHelper<ThriftClient, Protocol, Transport>::~CThriftClientHelper() { close(); } template <class ThriftClient, class Protocol, class Transport> void CThriftClientHelper<ThriftClient, Protocol, Transport>::connect() { if (!_transport->isOpen()) { _transport->open(); } } template <class ThriftClient, class Protocol, class Transport> void CThriftClientHelper<ThriftClient, Protocol, Transport>::close() { if (_transport->isOpen()) { _transport->close(); } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// template <class ThriftHandler, class ServiceProcessor, class ProtocolFactory, class Server> void CThriftServerHelper<ThriftHandler, ServiceProcessor, ProtocolFactory, Server>::serve(uint16_t port, uint8_t num_worker_threads, uint8_t num_io_threads) { serve("0.0.0.0", port, num_worker_threads, num_io_threads); } template <class ThriftHandler, class ServiceProcessor, class ProtocolFactory, class Server> void CThriftServerHelper<ThriftHandler, ServiceProcessor, ProtocolFactory, Server>::serve(const std::string &ip, uint16_t port, uint8_t num_worker_threads, uint8_t num_io_threads) { set_thrift_log_write_function(); _handler.reset(new ThriftHandler); _processor.reset(new ServiceProcessor(_handler)); // ProtocolFactory默认为apache::thrift::protocol::TBinaryProtocolFactory _protocol_factory.reset(new ProtocolFactory()); _thread_manager = apache::thrift::server::ThreadManager::newSimpleThreadManager(num_worker_threads); _thread_factory.reset(new apache::thrift::concurrency::PosixThreadFactory()); _thread_manager->threadFactory(_thread_factory); _thread_manager->start(); // Server默认为apache::thrift::server::TNonblockingServer Server* server = new Server(_processor, _protocol_factory, port, _thread_manager); if (sizeof(Server) == sizeof(apache::thrift::server::TNonblockingServer)) server->setNumIOThreads(num_io_threads); _server.reset(server); _server->run(); // 这里也可直接调用serve(),但推荐run() } template <class ThriftHandler, class ServiceProcessor, class ProtocolFactory, class Server> void CThriftServerHelper<ThriftHandler, ServiceProcessor, ProtocolFactory, Server>::stop() { _server->stop(); } NET_NAMESPACE_END #endif // MOOON_NET_THRIFT_HELPER_H |
11. 日志输出
默认thrift日志打屏,但其实可以让它输出到自己的日志文件中。这个功能通过全局对象apache::thrift::GlobalOutput来实现,在Thrift.h中声明了GlobalOutput,它的定义在Thrift.cpp文件中。
类TOutput提供了方法setOutputFunction()用来设置日志输出函数:
|
class TOutput{ public: inline void setOutputFunction(void (*function)(const char *)); }; |
调用setOutputFunction()设置回调函数,即可将日志输出到自己的日志文件中,遗憾的是不能自动区分日志级别。更佳的做法是定义一个抽象接口,然后让使用者注入接口实现,如mooon中ILogger:
https://github.com/eyjian/mooon/blob/master/common_library/include/mooon/sys/log.h。
具体做法,可以参考:https://github.com/eyjian/mooon/blob/master/common_library/include/mooon/net/thrift_helper.h。
附:问题
如何让Thrift只在指定的IP上监听,而不是监听0.0.0.0?