像Hibernate这种ORM框架,相较于JDBC操作,需要有更复杂的机制来实现映射、对象状态管理等,因此在性能和效率上有一定的损耗。
在保证避免映射产生低效的SQL操作外,缓存是提升Hibernate的关键之一。
加入缓存可以避免数据库调用带来的连接创建与销毁、数据打包拆包、SQL执行、网络传输,良好的缓存机制和合理的缓存模式能带来性能的极大提升,EHCache就提供了这种良好的缓存机制。
在考虑给系统加入缓存进行优化前,复用SessionFactory是Hibernate优化最优先、最基础的性能优化方法,参考上一篇《Hibernate性能优化之SessionFactory重用》。
Hibernate的缓存机制
缓存的级别一般分为三种,每一种缓存的范围更大:
事务级缓存:Hibernate中称为一级缓存,在一个Session中共享缓存对象;
应用级缓存:Hibernate中称为二级缓存,在一个SessionFactory中共享缓存对象,SessionFactory在整个应用范围内重用;
分布式缓存:部署为单独的实例,如Redis、Memcache等。
Hibernate的按以下方式进行缓存:
当Hibernate根据ID访问数据对象的时候,首先从Session一级缓存中查;
查不到,如果配置了二级缓存,那么从二级缓存中查;
如果都查不到,再查询数据库,把结果按照ID放入到缓存删除、更新、增加数据的时候,同时更新缓存。
Hibernate默认不启用二级缓存,EHCache是Hibernate中的二级缓存插件,使用Hibernate的系统可以直接使用EHCache缓存。
为什么要直接使用EHCache
回头来看那句话:良好的缓存机制和合理的缓存模式能带来性能的极大提升。
Hibernate的缓存模式是什么?
根据ID来缓存对象,也就是Session的get、load操作时。
这种缓存模式的弊端有两点:
1、应用场景太单一,系统中大量的列表式查询缓存起不到作用;
2、一些系统中通过ThreadLocal在线程中重用Session,每个线程可能需要大量处理不用的业务逻辑,缓存命中率很低;如果不重用Session,一般的场景缓存命中率更低。
既然EHCache已经提供了良好的缓存机制,结合自己系统的业务来优化缓存模式才是最佳的。
如何使用EHCache
EHCache是Hibernate中的二级缓存插件,使用Hibernate的系统可以直接使用EHCache缓存,不需要再添加其他jar包。
新建EHCache配置文件,具体的配置含义可以查手册:
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="ehcache.xsd"> <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" maxElementsOnDisk="0" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="0" timeToLiveSeconds="0" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="50" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LFU" /> <cache name="restCache" maxElementsInMemory="100" maxElementsOnDisk="0" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="119" timeToLiveSeconds="119" diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="50" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="FIFO" /> </ehcache>
EHCache的一个优点是线程安全的,适合多线程的使用场景,能简化开发人员的使用。
因此我写了一个单例模式,避免每次在方法里写getCache,这个类也涵盖了EHCache的基本使用:
public class EHCacheFactory { private final CacheManager manager; private final Cache cache; private EHCacheFactory() { manager = CacheManager.create(getClass().getResource("/ehcache.xml")); cache = manager.getCache("restCache"); } public Element getCache(String strKey) { return EHCacheFactory.getInstance().getCache().get(strKey); } public void setCache(String strKey, String strVal) { EHCacheFactory.getInstance().getCache().put(new Element(strKey, strVal)); } public Cache getCache() { return cache; } private static class SingletonHolder { private final static EHCacheFactory INSTANCE = new EHCacheFactory(); } public static EHCacheFactory getInstance() { return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE; } }
我的系统是JAVA REST,在需要缓冲的REST接口中加入了EHCache缓存,通过URL参数作为缓存键值,REST接口返回的json数据作为缓存值,这种缓存模式非常适合REST。
使用ab进行了简单的性能测试:
在一个简答查询接口中,性能提升一倍;
在一个略复杂接口中,执行4、5个查询,加入缓存后性能提升20倍。
介绍在Hibernate中使用查询缓存、一级缓存、二级缓存,
整合Spring在HibernateTemplate中使用查询缓存。
EhCache是Hibernate的二级缓存技术之一,可以把查询出来的数据存储在内存或者磁盘,节省下次同样查询语句再次查询数据库,大幅减轻数据库压力;
EhCache的使用注意点
当用Hibernate的方式修改表数据(save,update,delete等等),这时EhCache会自动把缓存中关于此表的所有缓存全部删除掉(这样能达到同步)。但对于数据经常修改的表来说,可能就失去缓存的意义了(不能减轻数据库压力);
在比较少更新表数据的情况下,EhCache一般要使用在比较少执行write操作的表(包括update,insert,delete等)[Hibernate的二级缓存也都是这样];对并发要求不是很严格的情况下,两台机子中的缓存是不能实时同步的;
首先要在hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件中添加配置,在hibernate.cfg.xml中的mapping标签上面加以下内容:
<!-- Hibernate 3.3 and higher -->
<!--
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.SingletonEhCacheRegionFactory</property>
-->
<!-- hibernate3.0-3.2 cache config-->
<!--
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.EhCacheProvider</property>
-->
<property name="hibernate.cache.provider_class">net.sf.ehcache.hibernate.SingletonEhCacheProvider</property>
<!-- Enable Second-Level Cache and Query Cache Settings -->
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</property>
如果你是整合在spring配置文件中,那么你得配置你的applicationContext.xml中相关SessionFactory的配置
<prop key="hibernate.cache.use_query_cache">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</prop> <prop key="hibernate.cache.provider_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheProvider</prop>
然后在hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件中加入使用缓存的属性
<!-- class-cache config --> <class-cache class="com.hoo.hibernate.entity.User" usage="read-write" />
当然你也可以在User.hbm.xml映射文件需要Cache的配置class节点下,加入类似如下格式信息:
<class name="com.hoo.hibernate.entity.User" table="USER" lazy="false">
<cache usage="transactional|read-write|nonstrict-read-write|read-only" />
注意:cache节点元素应紧跟class元素
关于选择缓存策略依据:
ehcache不支持transactional,其他三种可以支持。
read- only:无需修改, 可以对其进行只读缓存,注意:在此策略下,如果直接修改数据库,即使能够看到前台显示效果,但是将对象修改至cache中会报error,cache不会发生作用。另:删除记录会报错,因为不能在read-only模式的对象从cache中删除。
read-write:需要更新数据,那么使用读/写缓存比较合适,前提:数据库不可以为serializable transaction isolation level(序列化事务隔离级别)
nonstrict-read-write:只偶尔需要更新数据(也就是说,两个事务同时更新同一记录的情况很不常见),也不需要十分严格的事务隔离,那么比较适合使用非严格读/写缓存策略。
如果你使用的注解方式,没有User.hbm.xml,那么你也可以用注解方式配置缓存
@Cache(usage = CacheConcurrencyStrategy.READ_WRITE) public class User implements Serializable { }
在Dao层使用cache,代码如下
Session s = HibernateSessionFactory.getSession(); Criteria c = s.createCriteria(User.class); c.setCacheable(true);//这句必须要有 System.out.println("第一次读取"); List<User> users = c.list(); System.out.println(users.size()); HibernateSessionFactory.closeSession(); s = HibernateSessionFactory.getSession(); c = s.createCriteria(User.class); c.setCacheable(true);//这句必须要有 System.out.println("第二次读取"); users = c.list(); System.out.println(users.size()); HibernateSessionFactory.closeSession();
你会发现第二次查询没有打印sql语句,而是直接使用缓存中的对象。
如果你的Hibernate和Spring整合在一起,那么你可以用HibernateTemplate来设置cache
getHibernateTemplate().setCacheQueries(true); return getHibernateTemplate().find("from User");
当你整合Spring时,如果你的HibernateTemplate模板配置在Spring的Ioc容器中,那么你可以这样启用query cache
<bean id="hibernateTemplate" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTemplate"> <property name="sessionFactory"> <ref bean="sessionFactory" /> </property> <property name="cacheQueries"> <value>true</value> </property> </bean>
此后,你在dao模块中注入sessionFactory的地方都注入hibernateTemplate即可。
以上讲到的都是Spring和Hibernate的配置,下面主要结合上面使用的ehcache,来完成ehcache.xml的配置。如果你没有配置ehcache,默认情况下使用defaultCache的配置。
<cache name="com.hoo.hibernate.entity.User" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600" overflowToDisk="true" /> <!-- hbm文件查找cache方法名的策略:如果不指定hbm文件中的region="ehcache.xml中的name的属性值",则使用name名为com.hoo.hibernate.entity.User的cache,如果不存在与类名匹配的cache名称,则用 defaultCache。 如果User包含set集合,则需要另行指定其cache 例如User包含citySet集合,则需要 添加如下配置到ehcache.xml中 --> <cache name="com.hoo.hibernate.entity.citySet" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="300" timeToLiveSeconds="600" overflowToDisk="true" />
如果你使用了Hibernate的查询缓存,需要在ehcache.xml中加入下面的配置
<cache name="org.hibernate.cache.UpdateTimestampsCache" maxElementsInMemory="5000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" /> <cache name="org.hibernate.cache.StandardQueryCache" maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" />
调试时候使用log4j的log4j.logger.org.hibernate.cache=debug,更方便看到ehcache的操作过程,主要用于调试过程,实际应用发布时候,请注释掉,以免影响性能。
使用ehcache,打印sql语句是正常的,因为query cache设置为true将会创建两个缓存区域:一个用于保存查询结果集 (org.hibernate.cache.StandardQueryCache); 另一个则用于保存最近查询的一系列表的时间戳(org.hibernate.cache.UpdateTimestampsCache)。请注意:在查询缓存中,它并不缓存结果集中所包含的实体的确切状态;它只缓存这些实体的标识符属性的值、以及各值类型的结果。需要将打印sql语句与最近的cache内 容相比较,将不同之处修改到cache中,所以查询缓存通常会和二级缓存一起使用。
二级缓存是属于SessionFactory级别的缓存机制,是属于进程范围的缓存。一级缓存是Session级别的缓存,是属于事务范围的缓存,由Hibernate管理,一般无需进行干预。
Hibernate支持以下的第三方的缓存框架:
| Cache | Interface | Supported strategies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HashTable (testing only) |
|
|||
| EHCache |
|
|||
| OSCache |
|
|||
| SwarmCache |
|
|||
| JBoss Cache 1.x |
|
|||
| JBoss Cache 2.x |
|
2、下载第三方ehcache.jar
ehcache.jar包的话,有两种,一种是org.ehcache,另一种是net.sf.ehache。Hibernate集成的是net.sf.ehcache!!所以应该下载net.sf.ehcache。如果使用org.ehcache的jar包,hibernate是不支持的!!
下载下来的jar包,需要放到项目当中,在本案例,是放到SSHWebProject项目的WebRoot/WEB-INF/lib目录下,需要注意的是,ehcache.jar包依赖commons-logging.jar,你还得看看你项目中有没有commons-logging.jar!!
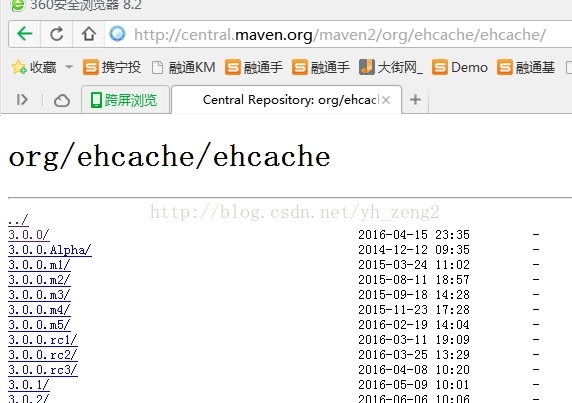
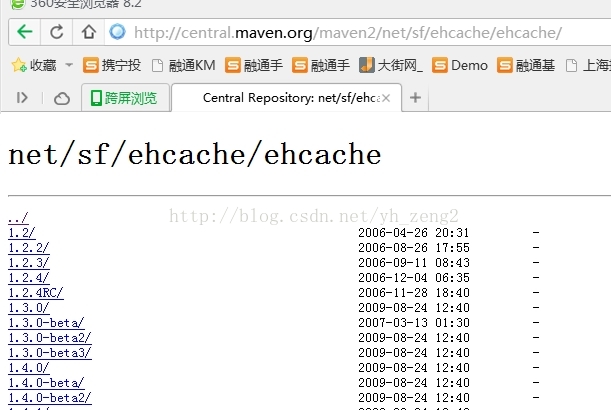
3、开启hibernate的二级缓存
想是否使用hibernate.cfg.xml配置文件,会导致配置使用二级缓存的方式不一样,一般是由于项目集成了Spring框架,所以配置二级缓存的话,
就分以下两种情况:
1)项目有hibernate.cfg.xml
1-1)开启Hibernate缓存二级缓存功能
修改hibernate.cfg.xml,添加以下内容
Users.hbm.xml,添加以下内容:
2)集成了Spring框架之后,没有hibenate.cfg.mlx文件
1-1)开启Hibernate缓存二级缓存功能
修改applicationContext.xml文件,在sessionFactory Bean中添加以下hibernateProperties,如下:
1-2)配置哪些实体类的对象需要存放到二级缓存
本案例中,以edu.po.Users用户对象为例子,对应的实体映射文件为Users.hbm.xml。
在hbm文件(实体映射文件)中配置
Users.hbm.xml,添加以下内容:
<cache usage="read-write"/>
4、配置ehcache.xml文件
将ehcache.jar包中的ehcache-failsafe.xml 改名为 ehcache.xml 放入 src,因为hibernate默认找classpath*:ehcache.xml
本案例,对<diskStore>和<defaultCache>进行修改,如下
<diskStore path="d:/EhCacheData"/>
<!-- maxElementsInMemory: 内存中最大对象数量 ,超过数量,数据会被缓存到硬盘 eternal:缓存的对象是否有有效期(即是否永久存在)。如果为true,timeouts属性被忽略 timeToIdleSeconds:缓存的对象在过期前的空闲时间,单位秒 timeToLiveSeconds:存活时间,对象不管是否使用,到了时间回收,单位秒 overflowToDisk:当内存中缓存对象数量达到 maxElementsInMemory 限制时,是否可以写到硬盘 maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘缓存最大对象数量 diskPersistent:在java虚拟机(JVM)重启或停掉的时候,是否持久化磁盘缓存,默认是false diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:清除磁盘缓存中过期对象的监听线程的运行间隔,默认是120秒 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当内存缓存的对象数量达到最大,有新的对象要加入的时候, 移除缓存中对象的策略。默认是LRU,可选的有LFU和FIFO --> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="10000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="true" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU" />
5、demo
SpringBeanUtils.java:
package utils; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; /** * Title: SpringBeanUtils.java * Description: 获取Spring的Bean实例对象的工具类 * @author yh.zeng * @date 2017-6-27 */ public class SpringBeanUtils { private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SpringBeanUtils.class); static String filePath ="WebRoot/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml"; static ApplicationContext CONTEXT ; static{ try{ CONTEXT = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(filePath); }catch(Exception e){ logger.error(StringUtils.getExceptionMessage(e)); } } /** * 获取Bean * @param uniqueIdentifier Bean的唯一标识,可以是ID也可以是name * @return */ public static Object getBean(String uniqueIdentifier){ return CONTEXT.getBean(uniqueIdentifier); } /** * 获取SessionFacotry对象 * @param uniqueIdentifier SessionFactory Bean的唯一标识,可以是ID也可以是name * @return */ public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory(String uniqueIdentifier){ return (SessionFactory) CONTEXT.getBean(uniqueIdentifier); } public static String getFilePath() { return filePath; } public static void setFilePath(String filePath) { SpringBeanUtils.filePath = filePath; CONTEXT = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(filePath); } }
HibernateEhCacheTest.java:
注意:查询缓存和查看Cache(缓存)统计信息的功能,需要做另外配置,见博客Hibernate开启查询缓存、Hibernate开启收集缓存统计信息
项目demo: https://github.com/zengyh/SSHWebProject.git

