模拟类
Description
In a modernized warehouse, robots are used to fetch the goods. Careful planning is needed to ensure that the robots reach their destinations without crashing into each other. Of course, all warehouses are rectangular, and all robots occupy a circular floor space with a diameter of 1 meter. Assume there are N robots, numbered from 1 through N. You will get to know the position and orientation of each robot, and all the instructions, which are carefully (and mindlessly) followed by the robots. Instructions are processed in the order they come. No two robots move simultaneously; a robot always completes its move before the next one starts moving.
A robot crashes with a wall if it attempts to move outside the area of the warehouse, and two robots crash with each other if they ever try to occupy the same spot.
Input
The first line of input is K, the number of test cases. Each test case starts with one line consisting of two integers, 1 <= A, B <= 100, giving the size of the warehouse in meters. A is the length in the EW-direction, and B in the NS-direction.
The second line contains two integers, 1 <= N, M <= 100, denoting the numbers of robots and instructions respectively.
Then follow N lines with two integers, 1 <= Xi <= A, 1 <= Yi <= B and one letter (N, S, E or W), giving the starting position and direction of each robot, in order from 1 through N. No two robots start at the same position.
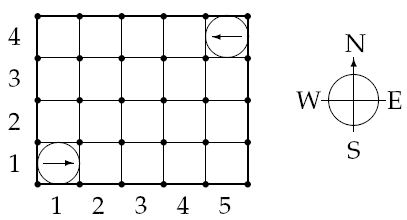
Figure 1: The starting positions of the robots in the sample warehouse
Finally there are M lines, giving the instructions in sequential order.
An instruction has the following format:
< robot #> < action> < repeat>
Where is one of
L: turn left 90 degrees,
R: turn right 90 degrees, or
F: move forward one meter,
and 1 <= < repeat> <= 100 is the number of times the robot should perform this single move.
Output
Output one line for each test case:
Robot i crashes into the wall, if robot i crashes into a wall. (A robot crashes into a wall if Xi = 0, Xi = A + 1, Yi = 0 or Yi = B + 1.)
Robot i crashes into robot j, if robots i and j crash, and i is the moving robot.
OK, if no crashing occurs.
Only the first crash is to be reported.
Sample Input
4
5 4
2 2
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 7
2 F 7
5 4
2 4
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 3
2 F 1
1 L 1
1 F 3
5 4
2 2
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 L 96
1 F 2
5 4
2 3
1 1 E
5 4 W
1 F 4
1 L 1
1 F 20
Sample Output
Robot 1 crashes into the wall
Robot 1 crashes into robot 2
OK
Robot 1 crashes into robot 2
Source
Nordic 2005
//
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int cases;
cin >> cases;
int width, height;
int robots, instructions;
unsigned char rbs[101][3]; // x, y, direction
unsigned char ins[101][3]; // robot #, action, repeat
int status; //0 ok, 1 crash into wall, 2 crash to robot
int robnum, crashnum, repeat;
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < cases; ++i)
{
cin >> width >> height;
cin >> robots >> instructions;
for (int j = 1; j <= robots; ++j)
{
cin >> x >> y >> rbs[j][2];
rbs[j][0] = x;
rbs[j][1] = y;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= instructions; ++j)
{
cin >> robnum >> ins[j][1] >> repeat;
ins[j][0] = robnum;
ins[j][2] = repeat;
}
status = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= instructions; ++j)
{
robnum = ins[j][0];
repeat = ins[j][2];
if (ins[j][1]=='F')
{
switch (rbs[robnum][2])
{
case 'N':
x = 0; y = 1;
break;
case 'S':
x = 0; y = -1;
break;
case 'E':
x = 1; y = 0;
break;
case 'W':
x = -1; y = 0;
break;
}
for (int k = 1; k <= repeat; ++k)
{
if (status != 0) break;
if (rbs[robnum][0] + x * k >= 1 && rbs[robnum][0] + x * k <= width
&& rbs[robnum][1] + y * k >= 1 && rbs[robnum][1] + y * k <= height)
{
for (int l = 1; l <= robots; ++l)
if (rbs[robnum][0] + x * k == rbs[l][0] && rbs[robnum][1] + y * k == rbs[l][1])
{
status = 2;
crashnum = l;
break;
};
}
else
{
status = 1;
}
};
if (status == 0)
{
rbs[robnum][0] += x * repeat;
rbs[robnum][1] += y * repeat;
}
else
break;
}
else if (ins[j][1]=='L')
{
for (int k = 1; k <= repeat; ++k)
{
switch (rbs[robnum][2])
{
case 'N':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'W';
break;
case 'S':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'E';
break;
case 'E':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'N';
break;
case 'W':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'S';
break;
}
}
}
else
{
for (int k = 1; k <= repeat; ++k)
{
switch (rbs[robnum][2])
{
case 'N':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'E';
break;
case 'S':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'W';
break;
case 'E':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'S';
break;
case 'W':
rbs[robnum][2] = 'N';
break;
}
}
}
}
if (status == 0) cout << "OK\n";
else if (status == 1)
{
cout << "Robot " <<robnum <<" crashes into the wall\n";
}
else if (status == 2)
{
cout << "Robot " <<robnum <<" crashes into robot " << crashnum << "\n";
}
}
return 0;
}