本笔记摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/liyangLife/p/4797583.html,记录一下学习过程以备后续查用。
一、文件系统
1.1文件系统类的介绍
文件操作类大都在System.IO命名空间里,FileSystemInfo类是所有文件系统类的基类。FileInfo与File表示文件系统中的文件,DirectoryInfo与Directory
表示文件系统中的文件夹,Path表示文件系统中的路径,DriveInfo提供对有关驱动器信息的访问。
注意,XXXInfo与XXX类的区别是:XXX是静态类,XXXInfo类可以实例化。还有个较为特殊的类System.MarshalByRefObject允许在支持远程处理的
应用程序中跨应用程序域边界访问对象。
1.2FileInfo与File类

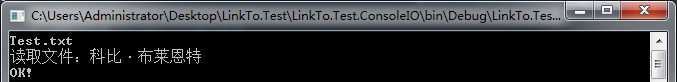
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region FileInfo与File类 //创建文件 FileInfo file = new FileInfo(@"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt"); FileStream fs = file.Create(); //关闭文件流,这个很重要。 fs.Close(); Console.WriteLine("创建时间:" + file.CreationTime); Console.WriteLine("文件路径:" + file.DirectoryName); //打开追加流 StreamWriter sw = file.AppendText(); //追加数据 sw.Write("科比·布莱恩特"); //释放资源,关闭文件。 sw.Dispose(); //移动 File.Move(file.FullName, @"E:学习笔记Test.txt"); Console.WriteLine("文件创建并操作完成。"); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

1.3DirectoryInfo与Directory类

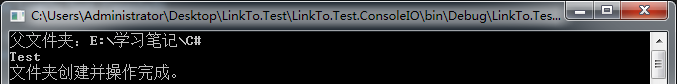
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region FileInfo与File类 ////创建文件 //FileInfo file = new FileInfo(@"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt"); //FileStream fs = file.Create(); ////关闭文件流,这个很重要。 //fs.Close(); //Console.WriteLine("创建时间:" + file.CreationTime); //Console.WriteLine("文件路径:" + file.DirectoryName); ////打开追加流 //StreamWriter sw = file.AppendText(); ////追加数据 //sw.Write("科比·布莱恩特"); ////释放资源,关闭文件。 //sw.Dispose(); ////移动 //File.Move(file.FullName, @"E:学习笔记Test.txt"); //Console.WriteLine("文件创建并操作完成。"); //Console.Read(); #endregion #region DirectoryInfo与Directory类 //创建文件夹 DirectoryInfo directory = new DirectoryInfo(@"E:学习笔记C#Test"); directory.Create(); Console.WriteLine("父文件夹:" + directory.Parent.FullName); //输出父目录下的所有文件夹与文件 FileSystemInfo[] infos = directory.Parent.GetFileSystemInfos(); foreach (FileSystemInfo info in infos) { Console.WriteLine(info.Name); } //删除文件夹 Directory.Delete(directory.FullName); Console.WriteLine("文件夹创建并操作完成。"); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
1.4Path类

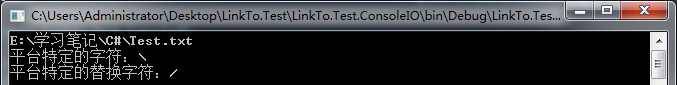
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region Path类 //连接 Console.WriteLine(Path.Combine(@"E:学习笔记C#", @"Test.txt")); Console.WriteLine("平台特定的字符:" + Path.DirectorySeparatorChar); Console.WriteLine("平台特定的替换字符:" + Path.AltDirectorySeparatorChar); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
1.5DriveInfo类

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region DriveInfo类 DriveInfo[] drives = DriveInfo.GetDrives(); foreach (DriveInfo drive in drives) { if (drive.IsReady) { Console.WriteLine("驱动器名称:" + drive.Name); Console.WriteLine("驱动器类型:" + drive.DriveFormat); Console.WriteLine("总容量:" + drive.TotalFreeSpace); Console.WriteLine("可用容量:" + drive.AvailableFreeSpace + " "); } } Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

二、文件操作
2.1文件的移动、复制、删除

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 文件的移动、复制、删除 string path = @"E:学习笔记Test.txt"; File.WriteAllText(path, "测试数据"); Console.WriteLine("文件已写入。"); File.Move(path, @"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt"); Console.WriteLine("文件已移动。"); File.Copy(@"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt", path); Console.WriteLine("文件已复制。"); File.Delete(@"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt"); Console.WriteLine("文件已删除。"); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
2.2判断路径是文件还是文件夹

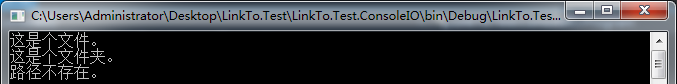
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 判断路径是文件还是文件夹 IsFile(@"E:学习笔记Test.txt"); IsFile(@"E:学习笔记"); IsFile(@"E:学习笔记XXX"); Console.Read(); #endregion } /// <summary> /// 判断路径是文件还是文件夹 /// </summary> /// <param name="path"></param> static void IsFile(string path) { if (File.Exists(path)) { Console.WriteLine("这是个文件。"); } else if (Directory.Exists(path)) { Console.WriteLine("这是个文件夹。"); } else { Console.WriteLine("路径不存在。"); } } }
运行结果如下:
三、文件读写与数据流
3.1文件读取

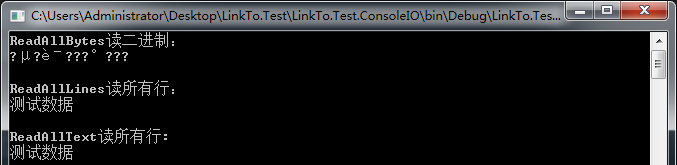
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 文件读取 string path = @"E:学习笔记Test.txt"; byte[] bytes = File.ReadAllBytes(path); Console.WriteLine("ReadAllBytes读二进制:"); foreach (byte b in bytes) { Console.Write((char)b); } Console.WriteLine(Environment.NewLine); string[] strs = File.ReadAllLines(path, Encoding.UTF8); Console.WriteLine("ReadAllLines读所有行:"); foreach (string s in strs) { Console.WriteLine(s + " "); } string str = File.ReadAllText(path, Encoding.UTF8); Console.WriteLine("ReadAllText读所有行: " + str); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
3.2文件写入

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 文件写入 string path = @"E:学习笔记Test.txt"; File.WriteAllBytes(path, new byte[] { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }); //写入二进制 Console.WriteLine("WriteAllBytes写入二进制成功。"); string[] array = { "123", "456", "789" }; File.WriteAllLines(path, array, Encoding.UTF8); //写入所有行 Console.WriteLine("WriteAllLines写入所有行成功。"); File.WriteAllText(path, "Hello World", Encoding.UTF8); //写入字符串 Console.WriteLine("WriteAllText写入字符串成功。 "); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
3.3数据流
FileStream:文件流,可以读写二进制文件。
StreamReader:流读取器,使其以一种特定的编码从字节流中读取字符。
StreamWriter:流写入器,使其以一种特定的编码向流中写入字符。
BufferedStream:缓冲流,给另一流上的读写操作添加一个缓冲层。
3.3.1使用FileStream读写二进制文件

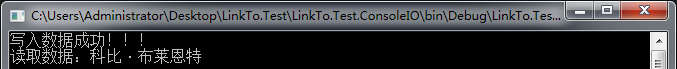
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 使用FileStream读写二进制文件 string path = @"E:学习笔记C#Test.txt"; //以写文件的方式创建文件 FileStream file = new FileStream(path, FileMode.CreateNew, FileAccess.Write); string str = "科比·布莱恩特"; byte[] bytes = Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(str); //写入二进制 file.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); file.Dispose(); Console.WriteLine("写入数据成功!!!"); //以读文件的方式打开文件 file = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); byte[] temp = new byte[bytes.Length]; //读取二进制 file.Read(temp, 0, temp.Length); Console.WriteLine("读取数据:" + Encoding.Unicode.GetString(temp)); file.Dispose(); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
3.3.2StreamWriter与StreamReader
使用StreamWriterStreamReader就不用担心文本文件的编码方式,所以它们很适合读写文本文件。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region StreamWriter与StreamReader string path = @"E:学习笔记C#Test1.txt"; //以写文件的方式创建文件 FileStream file = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(file); sw.WriteLine("科比·布莱恩特"); sw.Dispose(); Console.WriteLine("写入数据成功!!!"); //以读文件的方式打开文件 file = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(file); Console.WriteLine("读取数据:" + sr.ReadToEnd()); sr.Dispose(); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

四、内存映射文件
MemoryMappedFile类(.NET4新增):
应用程序需要频繁地或随机地访问文件时,最好使用MemoryMappedFile类(映射内存的文件)。使用这种方式允许把文件的一部分或者全部加载到一段
虚拟内存上,这些文件内容会显示给应用程序,就好像这个文件包含在应用程序的主内存中一样。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 内存映射文件 MemoryMappedFile mmFile = MemoryMappedFile.CreateFromFile(@"E:学习笔记C#Test2.txt", FileMode.OpenOrCreate, "MapName", 1024 * 1024); //内存映射文件的视图 //或使用数据流操作内存文件MemoryMappedViewStream stream = mmFile.CreateViewStream(); MemoryMappedViewAccessor mmViewAccessor = mmFile.CreateViewAccessor(); string str = "科比·布莱恩特"; int length = Encoding.UTF8.GetByteCount(str); //写入数据 mmViewAccessor.WriteArray<byte>(0, Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str), 0, length); byte[] bytes = new byte[length]; mmViewAccessor.ReadArray<byte>(0, bytes, 0, bytes.Length); Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes)); //释放资源 mmFile.Dispose(); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

五、文件安全
5.1ACL介绍
ACL是存在于计算机中的一张表(访问控制表),它使操作系统明白每个用户对特定系统对象--例如文件目录或单个文件的存取权限,每个对象拥有一个在
访问控制表中定义的安全属性。每个系统用户对于这张表拥有一个访问权限,最一般的访问权限包括读文件(包括所有目录中的文件)、写一个或多个文件
和执行一个文件(如果它是一个可执行文件或者是程序的时候)。
5.2读取文件的ACL

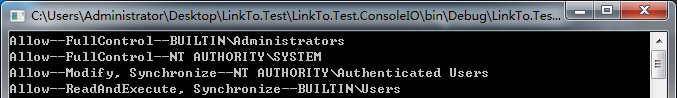
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 读取文件的ACL FileStream file = new FileStream(@"E:学习笔记Test.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); //得到文件访问控制属性 FileSecurity filesec = file.GetAccessControl(); //输出文件的访问控制项 foreach (FileSystemAccessRule filerule in filesec.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount))) { Console.WriteLine(filerule.AccessControlType + "--" + filerule.FileSystemRights + "--" + filerule.IdentityReference); } file.Dispose(); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:
5.3读取文件夹的ACL

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 读取文件夹的ACL DirectoryInfo dir = new DirectoryInfo(@"E:学习笔记C#"); //得到文件访问控制属性 DirectorySecurity filesec = dir.GetAccessControl(); //输出文件的访问控制项 foreach (FileSystemAccessRule filerule in filesec.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount))) { Console.WriteLine(filerule.AccessControlType + "--" + filerule.FileSystemRights + "--" + filerule.IdentityReference); } Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

5.4修改ACL

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 修改ACL FileStream file = new FileStream(@"E:学习笔记Test.txt", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); //得到文件访问控制属性 FileSecurity filesec = file.GetAccessControl(); //输出文件访问控制项 PrintACL(filesec.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount))); FileSystemAccessRule rule = new FileSystemAccessRule ( new NTAccount(@"AtomyStudioAdministrator"), //计算机账户名 FileSystemRights.Delete, //操作权限 AccessControlType.Allow //能否访问受保护的对象 ); filesec.AddAccessRule(rule); //增加ACL项 PrintACL(filesec.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount))); //输出文件访问控制项 filesec.RemoveAccessRule(rule); //移除ACL项 PrintACL(filesec.GetAccessRules(true, true, typeof(NTAccount))); //输出文件访问控制项 file.Dispose(); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下:

六、读写注册表
6.1注册表介绍
Windows注册表是帮助Windows控制硬件、软件、用户环境和Windows界面的一套数据文件,运行regedit可以看到有5个注册表配置单元(实际有7个):
HKEY-CLASSES-ROOT: 文件关联和COM信息
HKEY-CURRENT-USER: 用户轮廓
HKEY-LOCAL-MACHINE: 本地机器系统全局配置子键
HKEY-USERS: 已加载用户轮廓子键
HKEY-CURRENT-CONFIG: 当前硬件配置
6.2.NET操作注册表的类
在.NET中提供了Registry类、RegistryKey类来实现对注册表的操作。
6.2.1Registry类
封装了注册表的七个基本主键:
Registry.ClassesRoot 对应于HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT主键
Registry.CurrentUser 对应于HKEY_CURRENT_USER主键
Registry.LocalMachine 对应于HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE主键
Registry.User 对应于HKEY_USER主键
Registry.CurrentConfig 对应于HEKY_CURRENT_CONFIG主键
Registry.DynDa 对应于HKEY_DYN_DATA主键
Registry.PerformanceData 对应于HKEY_PERFORMANCE_DATA主键
6.2.2RegistryKey类
封装了对注册表的基本操作,包括读取、写入,删除。
1)读取的函数:
OpenSubKey() 主要是打开指定的子键
GetSubKeyNames() 获得主键下面的所有子键的名称,它的返回值是一个字符串数组。
GetValueNames() 获得当前子键中的所有的键名称,它的返回值也是一个字符串数组。
GetValue() 指定键的键值。
2)写入的函数:
CreateSubKey() 增加一个子键
SetValue() 设置一个键的键值
3)删除的函数:
DeleteSubKey() 删除一个指定的子键
DeleteSubKeyTree() 删除该子键以及该子键以下的全部子键
6.3示例

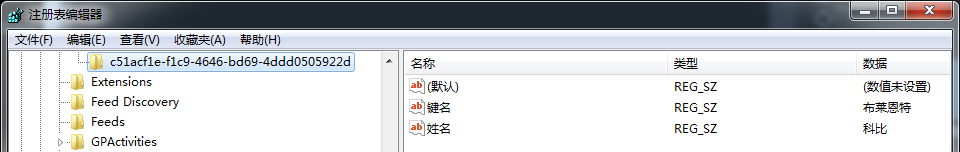
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 读写注册表 string path = @"SOFTWAREMicrosoftInternet ExplorerExtension Compatibility"; //以只读方式 RegistryKey registryKey = Registry.LocalMachine.OpenSubKey(path, true); if (registryKey != null) { Console.WriteLine(registryKey.Name + "--" + registryKey.SubKeyCount + "--" + registryKey.ValueCount); string subRegistryKey = Guid.NewGuid().ToString(); //增加一个子键 registryKey.CreateSubKey(subRegistryKey); RegistryKey newRegistryKey = Registry.LocalMachine.OpenSubKey(path + @"" + subRegistryKey, true); //设置一个键的键值 newRegistryKey.SetValue("姓名", "科比"); //设置一个键的键值 newRegistryKey.SetValue("键名", "布莱恩特"); Console.WriteLine(registryKey.Name + "--" + registryKey.SubKeyCount + "--" + registryKey.ValueCount); registryKey.Close(); newRegistryKey.Close(); } Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果生成值为:
七、读写独立的存储器
7.1IsolatedStorageFile类
使用IsolatedStorageFile类可以读写独立的存储器。
独立的存储器可以看成一个虚拟磁盘,在其中可以保存只由创建他们的应用程序或其应用程序实例共享的数据项。
独立的存储器的访问类型有两种:第一种是一个应用程序的多个实例在同一个独立存储器中工作,第二种是一个应用程序的多个实例在各自不同的独立存
储器中工作。
7.2示例

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 读写独立的存储器 //写文件 IsolatedStorageFileStream fileStream = new IsolatedStorageFileStream(@"Test.txt", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write); string str = "科比·布莱恩特"; byte[] bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(str); //写数据 fileStream.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); fileStream.Dispose(); //读文件 IsolatedStorageFile file = IsolatedStorageFile.GetUserStoreForDomain(); string[] fileNames = file.GetFileNames(@"Test.txt"); foreach (string fileName in fileNames) { Console.WriteLine(fileName); fileStream = new IsolatedStorageFileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(fileStream); Console.WriteLine("读取文件:" + sr.ReadToEnd()); sr.Dispose(); //删除文件 file.DeleteFile(fileName); } file.Dispose(); Console.WriteLine("OK!"); Console.Read(); #endregion } }
运行结果如下: