词法分析程序(Lexical Analyzer)要求:
- 从左至右扫描构成源程序的字符流
- 识别出有词法意义的单词(Lexemes)
- 返回单词记录(单词类别,单词本身)
- 滤掉空格
- 跳过注释
- 发现词法错误
程序结构:
输入:字符流(什么输入方式,什么数据结构保存)
处理:
–遍历(什么遍历方式)
–词法规则
输出:单词流(什么输出形式)
–二元组
单词类别:
1.标识符(10)
2.无符号数(11)
3.保留字(一词一码)
4.运算符(一词一码)
5.界符(一词一码)
|
单词符号 |
种别码 |
单词符号 |
种别码 |
|
begin |
1 |
: |
17 |
|
if |
2 |
:= |
18 |
|
then |
3 |
< |
20 |
|
while |
4 |
<= |
21 |
|
do |
5 |
<> |
22 |
|
end |
6 |
> |
23 |
|
l(l|d)* |
10 |
>= |
24 |
|
dd* |
11 |
= |
25 |
|
+ |
13 |
; |
26 |
|
- |
14 |
( |
27 |
|
* |
15 |
) |
28 |
|
/ |
16 |
# |
0 |
import re
strs = "then do / 100 if x : x + 3)#" + " "
# strs = input('请输入程序代码:')+" " #补位
types = {'begin': 1,
'if': 2,
'then': 3,
'while': 4,
'do': 5,
'end': 6,
'l(l|d)*': 10,
'dd*': 11,
'+': 13,
'-': 14,
'*': 15,
'/': 16,
':': 17,
':=': 18,
'<': 20,
'<=': 21,
'<>': 22,
'>': 23,
'>=': 24,
'=': 25,
';': 26,
'(': 27,
')': 28,
'#': 0
}
if __name__ == '__main__':
index = 0
while index < len(strs):
keyIndex = 0
for key in types.keys():
if index + len(key) < len(strs):
if strs[index:index + len(key)] == key and not re.match('^[=a-zA-Z0-9_-]$', strs[index + len(key)]):
if not (strs[index] == '=' and re.match('^[<>]$', strs[index - 1])):
ss = strs[index:index + len(key)]
print((ss, types.get(ss)))
elif re.match('^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+', strs[index:]):
ss = re.match('^([a-zA-Z0-9_]+)', strs[index:]).group()
if not types.get(ss):
if re.match('[a-zA-Z]+', ss):
print((ss, '标识符'))
elif re.match('d+', ss):
print((ss, '数字'))
else:
print((ss, '其他'))
index += len(ss)
keyIndex += 1
index += 1
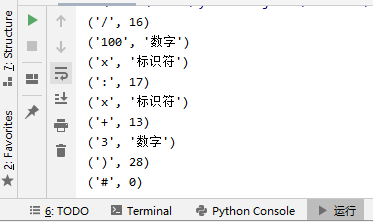
运行结果:
这篇博客是转载这位大神 Rakers:https://www.cnblogs.com/Rakers1024/p/11640718.html