http://www.dba-oracle.com/t_steps_for_oracle_performance_tuning.htm
Question: I am new to Oracle tuning, and I want to know the steps for Oracle performance tuning.
Answer: As of Oracle 11g, Oracle has codified a top-down tuning approach, with the first steps being very broad, and successive steps becoming more focused. Oracle performance tuning is very complex, and where there are some generic steps for performance tuning, the world is not always that simple. Here are the steps for a top-down Oracle performance tuning approach:
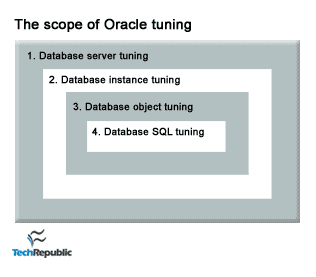
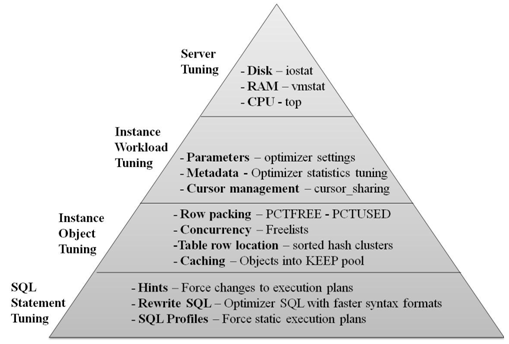
Oracle tuning involves the following steps, with each step getting more specific and targeted:
- Server & network tuning—This is always the first step, as not amount of tuning will help a poor server environment.
- Instance tuning—Tuning
the Oracle SGA is the next step, and all of the Oracle initialization
parameters must be reviewed to ensure that the database has been properly
configured for it's workload. In some cases, a database may have a
bi-modal workload (online vs. batch) and the instance parms are adjusted
as-needed during this step.
- Object tuning—This
step of performance tuning looks at the setting for Oracle tables and
indexes. Table and index settings such as PCTFREE, PCTUSED, and FREELISTS
can have a dramatic impact on Oracle performance.
- SQL tuning—This is last step in tuning, and the most time-consuming tuning operation because there can be many thousands of individual SQL statements that access the Oracle database. If you have carefully optimized the workload as a whole from step 2, there you will only need to tune "outlier" SQL statements. Within this step, there are sub-steps:
Remove unnecessary large-table full-table scans—In this tuning step you evaluate the SQL
based on the number of rows returned by the query. Standard b-tree indexes can
be added to tables, and bitmapped and function-based indexes can also eliminate
full-table scans.
Cache small-table full-table scans—In this step we ensure that a
dedicated data buffer is available for the rows.
Verify optimal index usage—This step is critical because you may have
"missing" indexes in your database, causing excessive I/O.
Materialize your aggregations and summaries for static tables - One
features of the Oracle SQLAccess advisor is recommendations for new
indexes and suggestions for materialized views.