本教程介绍如何从文件读取流和向文件写入流。这就需要用到 C++ 中另一个标准库 fstream,它定义了三个新的数据类型:
| 数据类型 | 描述 |
| ofstream | 该数据类型表示输出文件流,用于创建文件并向文件写入信息。 |
| ifstream | 该数据类型表示输入文件流,用于从文件中读取信息。 |
| fstream | 该数据类型通常表示文件流,且同时具有ofstream和ifstream两种功能,这意味着它可以创建文件,向文件写入信息,从文件读取信息。 |
要在 C++ 中进行文件处理,必须在 C++ 源代码文件中包含头文件 <iostream> 和 <fstream>。
打开文件:open() 函数是 fstream、ifstream 和 ofstream 对象的一个成员。
void open(const char *filename, ios::openmode mode);
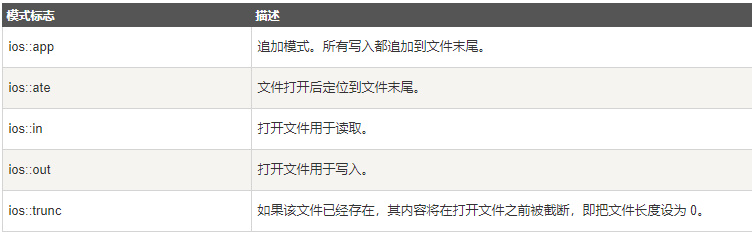
如果您想要以写入模式打开文件,并希望截断文件,以防文件已存在
ofstream outfile; outfile.open("file.dat", ios::out | ios::trunc );
如果想要打开一个文件用于读写,可以使用下面的语法:
ifstream afile; afile.open("file.dat", ios::out | ios::in );
关闭文件:close() 函数是 fstream、ifstream 和 ofstream 对象的一个成员。
当 C++ 程序终止时,它会自动关闭刷新所有流,释放所有分配的内存,并关闭所有打开的文件。但程序员应该养成一个好习惯,在程序终止前关闭所有打开的文件。
void close();
写入文件和读取文件:
在 C++ 编程中,我们使用流插入运算符( << )向文件写入信息,就像使用该运算符输出信息到屏幕上一样。唯一不同的是,在这里您使用的是 ofstream 或 fstream 对象,而不是 cout 对象。
在 C++ 编程中,我们使用流提取运算符( >> )从文件读取信息,就像使用该运算符从键盘输入信息一样。唯一不同的是,在这里您使用的是 ifstream 或 fstream 对象,而不是 cin 对象。
实例
#include <fstream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main () { char data[100]; // 以写模式打开文件 ofstream outfile; outfile.open("afile.dat"); cout << "Writing to the file" << endl; cout << "Enter your name: "; cin.getline(data, 100); // 向文件写入用户输入的数据 outfile << data << endl; cout << "Enter your age: "; cin >> data; cin.ignore(); // 再次向文件写入用户输入的数据 outfile << data << endl; // 关闭打开的文件 outfile.close(); // 以读模式打开文件 ifstream infile; infile.open("afile.dat"); cout << "Reading from the file" << endl; infile >> data; // 在屏幕上写入数据 cout << data << endl; // 再次从文件读取数据,并显示它 infile >> data; cout << data << endl; // 关闭打开的文件 infile.close(); return 0; }
当上面的代码被编译和执行时,会产生下列输入和输出:
$./a.out Writing to the file Enter your name: Zara Enter your age: 9 Reading from the file Zara 9
文件位置指针
istream 和 ostream 都提供了用于重新定位文件位置指针的成员函数。这些成员函数包括关于 istream 的 seekg("seek get")和关于 ostream 的 seekp("seek put")。
seekg 和 seekp 的参数通常是一个长整型。第二个参数可以用于指定查找方向。查找方向可以是 ios::beg(默认的,从流的开头开始定位),也可以是 ios::cur(从流的当前位置开始定位),也可以是 ios::end(从流的末尾开始定位)。