实验六 接口的定义与使用
实验时间 2018-10-18
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握接口定义方法;
(2) 掌握实现接口类的定义要求;
(3) 掌握实现了接口类的使用要求;
(4) 掌握程序回调设计模式;
(5) 掌握Comparator接口用法;
(6) 掌握对象浅层拷贝与深层拷贝方法;
(7) 掌握Lambda表达式语法;
(8) 了解内部类的用途及语法要求。
学习总结:
1. 接口:用interface声明,是抽象方法和常量值定义的集 合。从本质上讲,接口是一种特殊的抽象类。
(1)在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类 的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成。 l 接口中不包括变量和有具体实现的方法。
(2)接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义,接口中只进 行方法的声明,不提供方法的实现。
(3)通常接口的名字以able或ible结尾;
(4)接口中的所有常量必须是public static final,方法必须是public abstract,这是 系统默认的,不管你在定义接口时,写不写 修饰符都是一样的.
(5)接口的实现:一个类使用了某个接口,那么这个类必须实现该 接口的所有方法,即为这些方法提供方法体。一个类可以实现多个接口,接口间应该用逗号分 隔开。
(6)接口的使用:接口不能构造接口对象,但可以声明接口变量以指向一个实现了该接口的类对象。
(7)可以用instanceof检查对象是否实现了某个接口。
(8)抽象类:用abstract来声明,没有具体实例对象的类,不 能用new来创建对象。
2. 接口示例
(1)回调(callback):一种程序设计模式,在这种模 式中,可指出某个特定事件发生时程序应该采取 的动作。
(2)Comparator接口所在包: java.util.*
(3)Object类的Clone方法:当拷贝一个对象变量时,原始变量与拷贝变量 引用同一个对象。这样,改变一个变量所引用 的对象会对另一个变量产生影响。
(4)如果要创建一个对象新的copy,它的最初状态与 original一样,但以后可以各自改变状态,就需 要使用Object类的clone方法。
(5)Object.clone()方法返回一个Object对象。必须进行强 制类型转换才能得到需要的类型。
(6)浅层拷贝与深层拷贝
(7)Java中对象克隆的实现:在子类中实现Cloneable接口。
(8)在子类的clone方法中,调用super.clone()。
3. lambda表达式
(1)Java Lambda 表达式是 Java 8 引入的一个新的功能,主 要用途是提供一个函数化的语法来简化编码。
(2)Lambda 表达式的语法基本结构 (arguments) -> body
(3)有如下几种情况: 1、参数类型可推导时,不需要指定类型,如 (a) -> System.out.println(a)
2、 只有一个参数且类型可推导时,不强制写 (), 如 a -> System.out.println(a)
3、 参数指定类型时,必须有括号,如 (int a) -> System.out.println(a)
4、参数可以为空,如 () -> System.out.println(“hello”)
5、 body 需要用 {} 包含语句,当只有一条语句时 {} 可省略
4.内部类:是定义在一个类内部的类。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第6章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
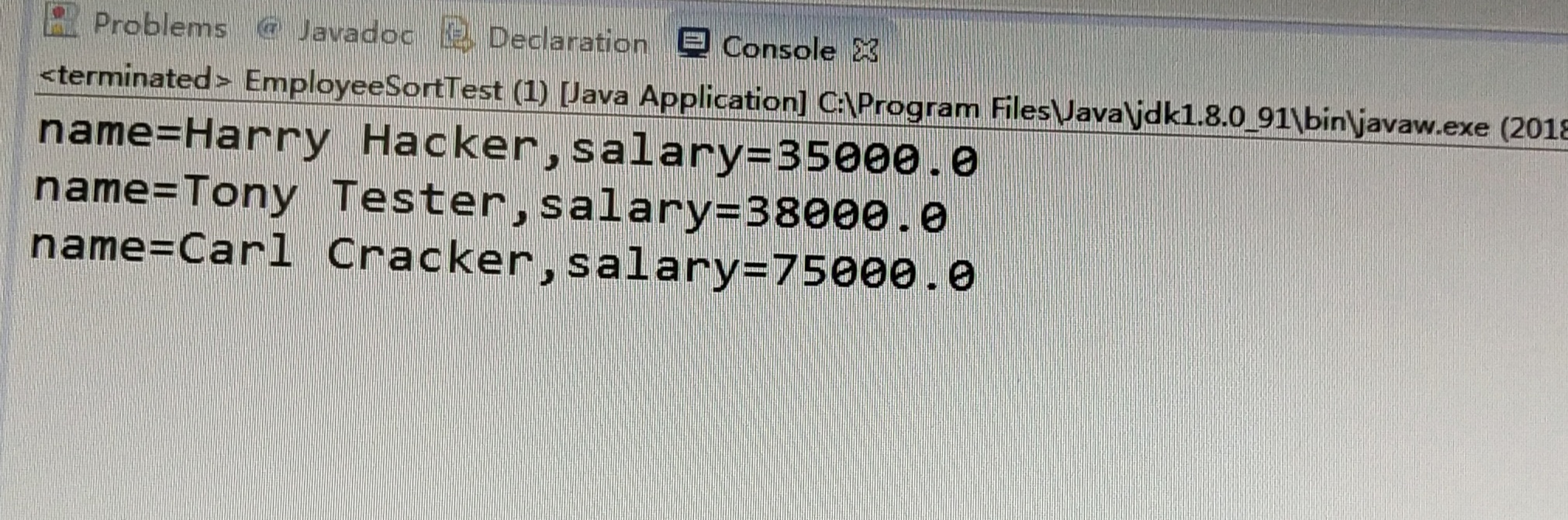
测试程序1:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行阅读教材214页-215页程序6-1、6-2,理解程序并分析程序运行结果;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握接口的实现用法;
l 掌握内置接口Compareable的用法。
package interfaces;
import java.util.*;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of the Comparable interface.
* @version 1.30 2004-02-27
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class EmployeeSortTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Employee[] staff = new Employee[3];//普通数组
staff[0] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 35000);
staff[1] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000);
staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 38000);
Arrays.sort(staff);//静态方法sort
// print out information about all Employee objects
for (Employee e : staff)
System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary());
}
}
package interfaces;
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>
{
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
/**
* Compares employees by salary
* @param other another Employee object
* @return a negative value if this employee has a lower salary than
* otherObject, 0 if the salaries are the same, a positive value otherwise
*/
public int compareTo(Employee other)
{
return Double.compare(salary, other.salary);
}
}
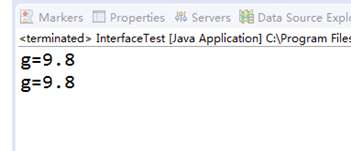
测试程序2:
l 编辑、编译、调试以下程序,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
|
interface A { double g=9.8; void show( ); } class C implements A { public void show( ) {System.out.println("g="+g);} }
class InterfaceTest { public static void main(String[ ] args) { A a=new C( ); a.show( ); System.out.println("g="+C.g); } } |
public interface A
{
double g=9.8;
void show( );
}
class C implements A
{
public void show( )
{System.out.println("g="+g);}
}
package InterfaceTest;
public class InterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
A a=new C( );
a.show( );
System.out.println("g="+C.g);
}
}
测试程序3:
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材223页6-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 26行、36行代码参阅224页,详细内容涉及教材12章。
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握回调程序设计模式;
package timer;
/**
@version 1.01 2015-05-12
@author Cay Horstmann
*/
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer;
// to resolve conflict with java.util.Timer
public class TimerTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ActionListener listener = new TimePrinter();
// construct a timer that calls the listener
// once every 10 seconds
Timer t = new Timer(10000, listener);
t.start();
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit(0);
}
}
class TimePrinter implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
System.out.println("At the tone, the time is " + new Date());
Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().beep();
}
}

测试程序4:
l 调试运行教材229页-231页程序6-4、6-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 掌握对象克隆实现技术;
l 掌握浅拷贝和深拷贝的差别。
package clone;
/**
* This program demonstrates cloning.
* @version 1.10 2002-07-01
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class CloneTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
Employee original = new Employee("John Q. Public", 50000);
original.setHireDay(2000, 1, 1);
Employee copy = original.clone();
copy.raiseSalary(10);
copy.setHireDay(2002, 12, 31);
System.out.println("original=" + original);
System.out.println("copy=" + copy);
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package clone;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
public class Employee implements Cloneable
{
private String name;
private double salary;
private Date hireDay;
public Employee(String name, double salary)
{
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
hireDay = new Date();
}
public Employee clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException
{
// call Object.clone()
Employee cloned = (Employee) super.clone();
// clone mutable fields
cloned.hireDay = (Date) hireDay.clone();
return cloned;
}
/**
* Set the hire day to a given date.
* @param year the year of the hire day
* @param month the month of the hire day
* @param day the day of the hire day
*/
public void setHireDay(int year, int month, int day)
{
Date newHireDay = new GregorianCalendar(year, month - 1, day).getTime();
// Example of instance field mutation
hireDay.setTime(newHireDay.getTime());
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
public String toString()
{
return "Employee[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]";
}
}

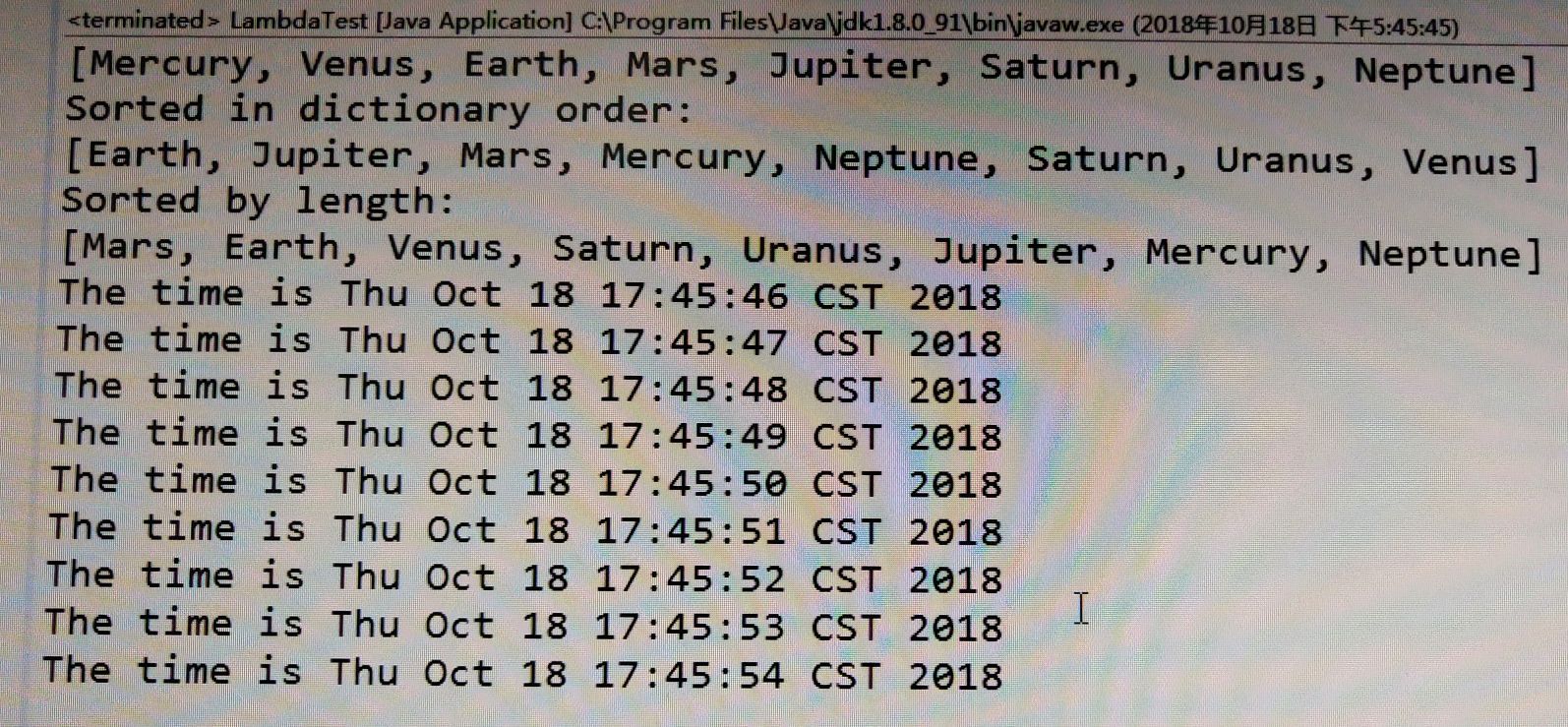
实验2: 导入第6章示例程序6-6,学习Lambda表达式用法。
l 调试运行教材233页-234页程序6-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 在程序中相关代码处添加新知识的注释。
l 将27-29行代码与教材223页程序对比,将27-29行代码与此程序对比,体会Lambda表达式的优点。
package lambda;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.Timer;
/**
* This program demonstrates the use of lambda expressions.
* @version 1.0 2015-05-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class LambdaTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String[] planets = new String[] { "Mercury", "Venus", "Earth", "Mars",
"Jupiter", "Saturn", "Uranus", "Neptune" };
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted in dictionary order:");
Arrays.sort(planets);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
System.out.println("Sorted by length:");
Arrays.sort(planets, (first, second) -> first.length() - second.length());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(planets));
Timer t = new Timer(1000, event ->
System.out.println("The time is " + new Date()));
t.start();
// keep program running until user selects "Ok"
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Quit program?");
System.exit(0);
}
}
实验总结:通过这次是实验更好地了解接口。